Abstract
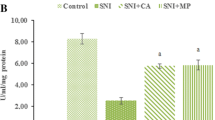
An ischemia/reperfusion injury of rat’s sciatic nerve was experimentally developed. In this model, we measured the in vivo production of superoxide radical, as a marker of oxidative stress and the occludin expression as an indicator of blood-nerve barrier function and we examined potential protective innervations against these abnormalities. Right sciatic nerves of the animals underwent 3 h of ischemia followed by 7 days of reperfusion and were divided into three groups: ischemic, pretreated with vitamin C in conjunction with vitamin E and treated with tissue plasminogen activator. Compared to measurements from left sciatic nerves used as sham, the ischemic group showed significantly increased superoxide radical and reduced expression of occludin in western blot and immunohistochemistry. No such differences were detected between sham and nerves in the vitamin or tissue plasminogen activator groups. It is suggested that the experimental ischemia/reperfusion model was suitable for studying the relationship between oxidative state and blood-nerve barrier. The reversion of abnormalities by the applied neuroprotective agents might prove to be a clinically important finding in view of the implication of vascular supply derangement in various neuropathies in humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lida H, Schmelzer JD, Schmeichel AM, Wang Y, Low PA (2003) Peripheral nerve ischemia: reperfusion injury and fiber regeneration. Exp Neurol 184:997–1002
Saray A, Can B, Akbiyik F, Askar I (1999) Ischaemia-reperfusion injury of the peripheral nerve: an experimental study. Microsurgery 19:374–380
Schmelzer JD, Zochodne DW, Low PA (1989) Ischemic and reperfusion injury of rat peripheral nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:1639–1642
He K, Nukada H, McMorran PD, Murphy MP (1999) Protein carbonyl formation and tyrosine nitration as markers of oxidative damage during ischaemia-reperfusion injury to rat sciatic nerve. Neuroscience 94:909–916
Georgiou CD, Papapostolou I, Patsoukis N, Tsegenidis T, Sideris T (2005) An ultrasensitive fluorescent assay for the in vivo quantification of superoxide radical in organisms. Anal Biochem 347:144–151
Georgiou CD, Papapostolou I, Grintzalis K (2008) Superoxide radical detection in cells, tissues, organisms (animals, plants, insects, microorganisms), and soils. Nat Protoc 3:1679–1692
Zahraoui A, Louvard D, Galli T (2000) Tight junction, a platform for trafficking and signaling protein complexes. J Cell Biol 151:31–36
Anderson GM, Nukada H, McMorran PD (1997) Carbonyl histochemistry in rat reperfusion nerve injury. Brain Res 24:156–160
Peltonen S, Alanne M, Peltonen J (2013) Barriers of the peripheral nerve. Tissue Barriers 1:24956
Hirakawa H, Okajima S, Nagaoka T, Takamatsu T, Oyamada M (2003) Loss and recovery of the blood-nerve barrier in the rat sciatic nerve after crush injury are associated with expression of intercellular junctional proteins. Exp Cell Res 284:196–210
Faropoulos K, Chroni E, Assimakopoulos SF, Mavrakis A, Stamatopoulou V, Toumpeki C, Drainas D, Grintzalis K, Papapostolou I, Georgiou CD, Konstantinou D (2010) Altered occludin expression in brain capillaries induced by obstructive jaundice in rats. Brain Res 1325:121–127
Judge AR, Selsby JT, Dodd SL (2008) Antioxidants attenuate oxidative damage in rat skeletal muscle during mild ischaemia. Exp Physiol 93:479–485
Zou T, Ling C, Xiao Y, Tao X, Ma D, Chen ZL, Strickland S, Song H (2006) Exogenous tissue plasminogen activator enhances peripheral nerve regeneration and functional recovery after injury in mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:78–86
Lochhead JJ, McCaffrey G, Quigley CE, Finch J, DeMarco KM, Nametz N, Davis TP (2011) Oxidative stress increases blood-brain barrier permeability and induces alterations in occludin during hypoxia-reoxygenation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:790–791
Dong S, Cao Y, Li H, Tian J, Yi C, Sang W (2015) Impact of ischemic preconditioning on ischemia-reperfusion injury of the rat sciatic nerve. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:16245–16251
Konstantinou D, Mavrakis A, Grintzalis K, Papapostolou I, Assimakopoulos SF, Chroni E, Georgiou C (2008) Quantification of superoxide radical in the brain of rats with experimentally induced obstructive jaundice. Neurochem Res 33:1101–1105
Assimakopoulos SF, Mavrakis AG, Grintzalis K, Papapostolou I, Zervoudakis G, Konstantinou D, Chroni E, Vagianos CE, Georgiou C (2008) Superoxide radical formation in diverse organs of rats with experimentally induced obstructive jaundice. Redox Rep 13:179–184
Sayan H, Ozacmak VH, Ozen OA, Coskun O, Arslan SO, Sezen SC, Aktas RG (2004) Beneficial effects of melatonin on reperfusion injury in rat sciatic nerve. J Pineal Res 37:143–148
Alipour M, Gadiri-Soufi F, Jafari MR (2014) Effect of aminoguanidine on sciatic functional index, oxidative stress, and rate of apoptosis in an experimental rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 92:1013–1019
Guven M, Yuksel Y, Sehitoglu MH, Tokmak M, Aras AB, Akman T, Golge UH, Goksel F, Karavelioglu E, Cosar M (2015) The effect of coumaric acid on ischemia-reperfusion injury of sciatic nerve in rats. Inflammation 38:2124–2132
Tokmak M, Sehitoglu MH, Yuksel Y, Guven M, Akman T, Aras AB, Yaka U, Gomleksiz C, Albayrak SB, Cosar M (2017) The axon protective effects of syringic acid on ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat sciatic nerve model. Turk Neurosurg 27:124–132
Manole E, Ceafalan LC, Oproiu AM, Popa-Wagner A, Popescu BO (2015) Claudin-1 and occludin expression in demyelinating peripheral neuropathies. Rom J Morphol Embryol 56:1097–1102
Ni Y, Teng T, Li R, Simonyi A, Sun YG, Lee CJ (2017) TNFα alters occludin and cerebral endothelial permeability: Role of p38MAPK. PLoS ONE 12:e0170346
Reinhold AK, Rittner HL (2017) Barrier function in the peripheral and central nervous system—a review. Pflugers Arch 469:123–134
Nagamatsu M, Schmelzer JD, Zollman PJ, Smithson IL, Nickander KK, Low PA (1996) Ischemic reperfusion causes lipid peroxidation and fiber degeneration. Muscle Nerve 19:37–47
Nukada H, Dyck PJ (1984) Microsphere embolization of nerve capillaries and fiber degeneration. Am J Pathol 115:275–287
Schreibelt G, Kooij G, Reijerkerk A, van Doorn R, Gringhuis SI, van der Pol S, Weksler BB, Romero IA, Couraud PO, Piontek J, Blasig IE, Dijkstra CD, Ronken E, de Vries HE (2007) Reactive oxygen species alter brain endothelial tight junction dynamics via RhoA, PI3 kinase, and PKB signaling. FASEB J 21(13):3666–3676
Brahma B, Forman RE, Stewart EE, Nicholson C, Rice ME (2000) Ascorbate inhibits edema in brain slices. J Neurochem 74:1263–1270
Paolini M, Pozzetti L, Pedulli GF, Marchesi E, Cantelli-Forti G (1999) The nature of prooxidant activity of vitamin C. Life Sci 64:273–278
Berger MM, Oudemans-van Straaten HM (2015) Vitamin C supplementation in the critically ill patient. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 18:193–201
Ji LL (1999) Antioxidants and oxidative stress in exercise. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 222:283–292
MacEvilly CJ, Muller DP (1996) Lipid peroxidation in neural tissues and fractions from vitamin E-deficient rats. Free Radic Biol Med 20:639–648
Ingold KU, Webb AC, Witter D, Burton GW, Metcalfe TA, Muller DP (1987) Vitamin E remains the major lipid-soluble, chain-breaking antioxidant in human plasma even in individuals suffering severe vitamin E deficiency. Arch Biochem Biophys 259:224–225
Cheeseman KH, Collins M, Maddix S, Milia A, Proudfoot K, Slater TF, Burton GW, Webb A, Ingold KU (1986) Lipid peroxidation in regenerating rat liver. FEBS Lett 209:191–196
Karageorgos N, Patsoukis N, Chroni E, Konstantinou D, Assimakopoulos SF, Georgiou C (2006) Effect of N-acetylcysteine, allopurinol and vitamin E on jaundice-induced brain oxidative stress in rats. Brain Res 1111:203–212
Riffel AP, de Souza JA, Santos MC, Horst A, Scheid T, Kolberg C, Belló-Klein A, Partata WA (2016) Systemic administration of vitamins C and E attenuates nociception induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. Brain Res Bull 121:169–177
Vassalli JD, Sappino AP, Belin D (1991) The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Investig 88:1067–1072
Lukic-Panin V, Deguchi K, Yamashita T, Shang J, Zhang X, Tian F, Liu N, Kawai H, Matsuura T, Abe K (2010) Free radical scavenger edaravone administration protects against tissue plasminogen activator induced oxidative stress and blood brain barrier damage. Curr Neurovasc Res 7:319–329
Suzuki Y (2010) Role of tissue-type plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke. J Pharmacol Sci 113:203–207
Akassoglou K, Kombrinck KW, Degen JL, Strickland S (2000) Tissue plasminogen activator-mediated fibrinolysis protects against axonal degeneration and demyelination after sciatic nerve injury. J Cell Biol 149:1157–1166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apostolopoulou, K., Konstantinou, D., Alataki, R. et al. Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury of Sciatic Nerve in Rats: Protective Role of Combination of Vitamin C with E and Tissue Plasminogen Activator. Neurochem Res 43, 650–658 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2465-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2465-8