Abstract
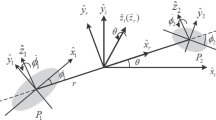
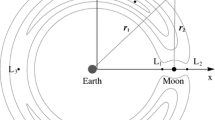
The problem of capturing a spacecraft from a heliocentric orbit into a high parking orbit around binary asteroids is investigated in the current study. To reduce the braking \(\Delta V\), a new capture strategy takes advantage of the three-body gravity of the binary asteroid to lower the inertial energy before applying the \(\Delta V\). The framework of the circular restricted three-body problem (CR3BP) is employed for the binary asteroid system. The proposed capture strategy is based on the mechanism by which inertial energy can be decreased sharply near zero-velocity curves (ZVCs). The strategy has two steps, namely, hitting the target ZVC and raising the periapsis by a small \(\Delta V\) at the apoapsis. By hitting the target ZVC, the positive inertial energy decreases and becomes negative. Using a small \(\Delta V\), the spacecraft inserts into a bounded orbit around the asteroid. In addition, a rotating mass dipole model is employed for elongated asteroids, which leads to dynamics similar to that of the CR3BP. With this approach, the proposed capture strategy can be applied to elongated asteroids. Numerical simulations validate that the proposed capture strategy is applicable for the binary asteroid 90 Antiope and the elongated asteroid 216 Kleopatra.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/90_Antiope [retrieved on 2017/3/11].
References
Bao, C., Yang, H., Barsbold, B., Baoyin, H.: Capturing near-Earth asteroids into bounded Earth orbits using gravity assist. Astrophys. Space Sci. 360(2), 61 (2015)
Battin, R.H.: An Introduction to the Mathematics and Methods of Astrodynamics. AIAA Education Series. AIAA, New York (1999)
Campagnola, S., Russell, R.P.: Endgame problem part 1: V-infinity-leveraging technique and the leveraging graph. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 33(2), 463–475 (2010a)
Campagnola, S., Russell, R.P.: Endgame problem part 2: multibody technique and the Tisserand-Poincare graph. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 33(2), 476–486 (2010b)
Campagnola, S., Skerritt, P., Russell, R.P.: Flybys in the planar, circular, restricted, three-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 113, 343–368 (2012)
Campagnola, S., Boutonnet, A., Schoenmaekers, J., Grebow, D.J., Petropoulos, A.E., Russell, R.P.: Tisserand-leveraging transfers. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 37(4), 1202–1210 (2014)
Casalino, L., Colasurdo, G., Pastrone, D.: Optimization of ? V Earth-gravity-assist trajectories. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 21(6), 991–995 (1998)
Casalino, L., Colasurdo, G., Pastrone, D.: Optimal low-thrust escape trajectories using gravity assist. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 22(5), 637–642 (1999a)
Casalino, L., Colasurdo, G., Pastrone, D.: Simple strategy for powered swingby. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 22(1), 156–159 (1999b)
Çelik, O., Sánchez, J.P.: Opportunities for ballistic soft landing in binary asteroids. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 40(6), 1390–1402 (2017)
Chen, Y., Baoyin, H., Li, J.: Accessibility of main-belt asteroids via gravity assists. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 37(2), 623–632 (2014)
Cheng, A.F., Atchison, J., Kantsiper, B., Rivkin, A.S., Stickle, A., Reed, C., Galvez, A., Carnelli, I., Michel, P., Ulamec, S.: Asteroid impact and deflection assessment mission. Acta Astronaut. 115, 262–269 (2015)
Diehl, R., Kaplan, D., Penzo, P.: Satellite tour design for the Galileo mission. In: 21st Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, Nevada (1983)
Jiang, F., Baoyin, H., Li, J.: Practical techniques for low-thrust trajectory optimization with homotopic approach. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 35(1), 245–258 (2012)
Kohlhase, C.E., Penzo, P.A.: Voyager mission description. Space Sci. Rev. 21(2), 77–101 (1977)
Lantoine, G., Russell, R.P., Campagnola, S.: Optimization of low-energy resonant hopping transfers between planetary moons. Acta Astronaut. 68(7), 1361–1378 (2011)
Lauretta, D.S., Team, O.R.: An overview of the OSIRIS-REx asteroid sample return mission. In: 43rd Lunar and Planetary Institute Science Conference, vol. 43, p. 2491 (2012)
Longuski, J.M., Williams, S.N.: Automated design of gravity-assist trajectories to Mars and the outer planets. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 52(3), 207–220 (1991)
McAdams, J.V., Dunham, D.W., Farquhar, R.W., Taylor, A.H., Williams, B.G.: Trajectory design and maneuver strategy for the MESSENGER mission to Mercury. J. Spacecr. Rockets 43(5), 1054–1064 (2006)
McConaghy, T.T., Debban, T.J., Petropoulos, A.E., Longuski, J.M.: Design and optimization of low-thrust trajectories with gravity assists. J. Spacecr. Rockets 40(3), 380–387 (2003)
Michałowski, T., Bartczak, P., Velichko, F.P., Kryszczyńska, A., Kwiatkowski, T., Breiter, S., Colas, F., Fauvaud, S., Marciniak, A., Michalowshi, J., Hirsch, R., Behrend, R., Bernasconi, L., Rinner, C., Charbonnel, S.: Eclipsing binary asteroid 90 Antiope. Astron. Astrophys. 423(3), 1159–1168 (2004)
Penzo, P.A., Mayer, H.L.: Tethers and asteroids for artificial gravity assist in the solar system. J. Spacecr. Rockets 23(1), 79–82 (1986)
Petropoulos, A.E., Longuski, J.M.: Shape-based algorithm for the automated design of low-thrust, gravity assist trajectories. J. Spacecr. Rockets 41(5), 787–796 (2004)
Qiao, D., Cui, H., Cui, P.: Evaluating accessibility of near-Earth asteroids via Earth gravity assists. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 29(2), 502–505 (2006)
Ross, S.D., Scheeres, D.J.: Multiple gravity assists, capture, and escape in the restricted three-body problem. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 6(3), 576–596 (2007)
Scheeres, D.J., Ostro, S.J., Hudson, R.S., Werner, R.A.: Orbits close to asteroid 4769 Castalia. Icarus 121(1), 67–87 (1996)
Shen, H.X., Casalino, L.: Indirect optimization of three-dimensional multiple-impulse Moon-to-Earth transfers. J. Astronaut. Sci. 61(3), 255–274 (2014)
Sims, J.A., Longuski, J.M., Staugler, A.J.: V8 leveraging for interplanetary missions: multiple-revolution orbit techniques. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 20(3), 409–415 (1997)
Strange, N.J., Longuski, J.M.: Graphical method for gravity-assist trajectory design. J. Spacecr. Rockets 39(1), 9–16 (2002)
Strange, N., Landau, D., McElrath, T., Lantoine, G., Lam, T., McGuire, M., Burke, L., Martini, M., Dankanich, J.: Overview of mission design for NASA asteroid redirect robotic mission concept. In: 33rd International Electric Propulsin Conference. The George Washington University, Washington (2013)
Tsuda, Y., Yoshikawa, M., Abe, M., Minamino, H., Nakazawa, S.: System design of the Hayabusa 2—asteroid sample return mission to 1999 JU3. Acta Astronaut. 91, 356–362 (2013)
Wang, X.Y., Gong, S.P., Li, J.F.: A method for classifying orbits near asteroids. Acta Mech. Sin. 30(3), 316–325 (2014)
Yang, H., Li, J., Baoyin, H.: Low-cost transfer between asteroids with distant orbits using multiple gravity assists. Adv. Space Res. 56(5), 837–847 (2015a)
Yang, H.W., Zeng, X.Y., Baoyin, H.: Feasible region and stability analysis for hovering around elongated asteroids with low thrust. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 15(9), 1571–1586 (2015b)
Yang, H., Jiang, Y., Baoyin, H.: Fuel efficient control strategy for constellation orbital deployment. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 88(1), 159–167 (2016)
Yang, H., Baoyin, H., Bai, X., Li, J.: Bounded trajectories near collinear-like equilibrium points of elongated asteroids using linear control. Astrophys. Space Sci. 362(2), 27 (2017)
Yu, Y., Baoyin, H.: Resonant orbits in the vicinity of asteroid 216 Kleopatra. Astrophys. Space Sci. 343(1), 75–82 (2013)
Zeng, X., Alfriend, K.T.: Periodic orbits in the Chermnykh problem. Astrodynamics 1(1), 41–55 (2017)
Zeng, X., Jiang, F., Li, J., Baoyin, H.: Study on the connection between the rotating mass dipole and natural elongated bodies. Astrophys. Space Sci. 356(1), 29–42 (2015)
Zeng, X., Fang, B., Li, J., Yu, Y.: Generalized flyby trajectories around elongated minor celestial bodies as a rotating mass dipole. Acta Mech. Sin. 32(3), 535–545 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Shanghai Key Laboratory of Deep Space Exploration Technology (Grant No. 13dz2260100), National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2014CB744200), Innovation Funded Project of Shanghai Aerospace Science and Technology (Grant No. SAST2017-032) and Scientific Research Foundation for New Staffs of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (Grant No. 1011-YAH17071). The authors would like to thank Xianyu Wang, from Tsinghua University, for the many discussions on the inertial energy of three-body systems.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Yang, H., Zhang, W. et al. Capture orbits around asteroids by hitting zero-velocity curves. Astrophys Space Sci 362, 229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-017-3206-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-017-3206-9