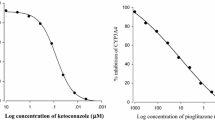
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of cilostazol on the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of nifedipine and its main metabolite, dehydronifedipine, in rats. The pharmacokinetic parameters of nifedipine and dehydronifedipine were determined following oral and intravenous administration of nifedipine (1.5 and 6.0 mg ・ kg-1) in rats. Cilostazol inhibited CYP3A4 enzyme activity at a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 4.1 μM. The areas under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC 0-∞) and the peak concentration (C max) of nifedipine were significantly increased, respectively, in the presence of cilostazol compared to that in the control. The total body clearance (CL/F) was significantly decreased by cilostazol. Consequently, the absolute bioavailability (AB) of nifedipine with cilostazol was significantly higher than that in the control. The metabolite to parent AUC ratio (MR) in the presence of cilostazol was significantly decreased compared to that in the control. The AUC 0-∞ of intravenous nifedipine was significantly increased with cilostazol compared to that in the control. The increased bioavailability of nifedipine in rats can be mainly due to the inhibition of CYP3A4-mediated metabolism in the small intestine and/or liver by cilostazol. In addition, the reduction of CL/F of nifedipine by cilostazol may also be a factor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. M. Sorkin, S. P. Clissold, and R. N. Brogden, Drugs, 30, 182 – 274 (1985).
J. L. Blackshear, C. Orlandi, N. K. Hollenberg, et al., J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 8, 37 – 43 (1986).
S. R. Hamann, M. T. Piascik, and R. G. McAllister, Biopharm. Drug Dispos., 7, 1 – 10 (1986).
T. Funaki, P. A. Soons, F. P. Guengerich, et al., Biochem. Pharmacol., 38, 4213 – 4216 (1989).
P. B. Watkins, Pharmacogenetics, 4, 171 – 184 (1994).
F. He, H. C. Bi, Z. Y. Xie, et al., Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 21, 635 – 643 (2007).
T. Shimada, H. Yamazaki, M. Mimura, et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 270, 414 – 423 (1994).
S. Rendic and F. J. Di Carlo, Drug Metab. Rev., 29, 413 – 580 (1997).
J. H. Lin, M. Chiba, and T. A. Baillie, Pharmacol. Rev., 51, 135 – 158 (1999).
G. K. Dresser, J. D. Spence, and D. G. Bailey, Clin. Pharmacokinet., 38, 41 – 57 (2000).
M. M. Doherty and W. N. Charman, Clin. Pharmacokinet., 41, 235 – 253 (2002).
K. Schror, Diabetes Obes. Metab., 4, S14 – S19 (2002).
M. P. Reilly and E. R. Mohler, Ann. Pharmacother., 35, 48 – 56 (2001).
K. P. Kim, B. H. Kim, K. S. Lim, et al., Clin. Ther., 31, 2098 – 2106 (2009).
R. Abbas, C. P. Chow, N. J. Browder, et al., Hum. Exp. Toxicol., 19, 178 – 184 (2000).
S. L. Bramer, W. P. Forbes, and S. Mallikaarjun, Clin. Pharmacokinet., 37 (Suppl 2), 1 – 11 (1999).
V. J. Wacher, C. Y. Wu, and L. Z. Benet, Mol. Carcinog., 13, 129 – 134 (1995).
D. Leveque and F. Jehl, Anticancer Res., 15, 231 – 336 (1995).
M. V. Relling, Ther. Drug Monit., 18, 350 – 356 (1996).
M. Dorababu, A. Nishimura, and T. Prabha, Biomed. Pharmacother., 63, 697 – 702 (2009).
J. S. Grundy, R. Kherani, and R. T. Foste, J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Appl ., 654, 146 – 151 (1994).
C. L. Crespi, V. P. Miller, and B. W. Penman, Anal. Biochem., 248, 188 – 190 (1997).
C. Y. Han, K. B. Cho, H. S. Choi, et al., Carcinogenesis, 29, 1837 – 1844 (2008).
W. L. Chiou, J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 6, 539 – 546 (1978).
P. B. Watkins, Gastroenterol Clin. North Am., 21, 511 – 526 (1992).
Q. Zhang, D. Dunbar, A. Ostrowska, et al., Drug Metab. Dispos., 27, 804 – 809 (1999).
R. McKinnon and and M. McManus, Pathology, 28, 148 – 155 (1996).
M. Tubic-Grozdanis, J. M. Hilfinger, G. L. Amidon, et al., Pharm. Res., 25, 1591 – 1600 (2008).
C. K. Lee, J. S. Choi, and J. S. Bang, Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 17, 245 – 251 (2013).
S. H. Yang, J. S. Choi, and D. H. Choi, Pharmacology, 88, 1 – 9 (2011).
D. H. Choi, J. S. Choi, J. S. Choi, et al., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 63, 129 – 135 (2011).
P. A. Kelly, H. Wang, K. L. Napoli, et al., Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet., 24, 321 – 328 (1999).
J. J. Bogaards, M. Bertrand, P. Jackson, et al., Xenobiotica, 30, 1131 – 1152 (2000).
F. P. Guengerich, M. V. Martin, P. H. Beaune, et al., J. Biol. Chem., 261, 5051 – 5060 (1986).
D. F. V. Lewis, Cytochrome P450 Structure, Function, and Mechanisms, Taylor & Francis, Bristol (1996), pp._122 – 123.
M. Kuroha, H. Kayaba, S. Kishimoto, et al., J. Pharm. Sci., 91, 868 – 873 (2002).
A. Nishimura, M. Fujimura, F. Hasegawa, et al., J. Health Sci., 56, 310 – 320 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CK., Choi, JS. & Choi, DH. Effects of Cilostazol on the Pharmacokinetics of Nifedipine After Oral and Intravenous Administration in Rats. Pharm Chem J 51, 748–755 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-017-1686-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-017-1686-0