Abstract
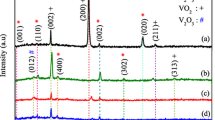
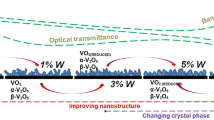
In this study, F-doped vanadium oxide thin films with doping levels up to 60 at % were prepared by spray pyrolysis method on glass substrates. To measure the electrochemical properties, some films were deposited on fluorine-tin oxide coated glass substrates. The effect of F-doping on the structural, electrical, optical and electrochemical properties of vanadium oxide samples was investigated. The X-ray diffractographs analysis has shown that all the samples grow in tetragonal β-V2O5 phase structure with the preferred orientation of [200]. The intensity of (200) peak belonging to β-V2O5 phase was strongest in the undoped vanadium oxide film. The scanning electron microscopy images show that the samples have nanorod- and nanobelt-shaped structure. The size of the nanobelts in the F-doped vanadium oxide films is smaller than that in the pure sample and the width of the nanobelts increases from 30 to 70 nm with F concentration. With increasing F-doping level from 10 to 60 at %, the resistivity, the transparency and the optical band gap decrease from 111 to 20 Ω cm, 70 to 50% and 2.4 to 2.36 eV, respectively. The cyclic voltammogram (CV) results show that the undoped sample has the most extensive CV and by increasing F-doping level from 20 to 60 at %, the area of the CV is expanded. The anodic and cathodic peaks in F-doped samples are stronger.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Luo, Z. Wu, X. Xu, M. Du, T. Wang, Y.Jian, Impact of substrate temperature on the microstructure, electrical and optical properties of sputtered nanoparticle V2O5 thin films, Vacuum 85 (2010) 145–150
D.O. Scanlon, A. Walsh, B.J. Morgan, G.W. Watson, An ab initio study of reduction of V2O5 through the formation of oxygen vacancies and Li intercalation. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 9903–9911 (2008)
P. Chatterjee, S.P. Sen Gupta, S. Suchitra, Particle fracture and plastic deformation in vanadium pentoxide powders induced by high energy vibrational ball-mill, Bull. .Mater. Sci 24, 173–180 (2001)
S. Beke, A review of the growth of V2O5 films from 1885 to 2010, Thin Solid. Films 519 (2011) 1761–1771
A. Bouzidi, N. Benramdane, A. Nakrela, C. Mathieu, B. Khelifa, R. Desfeux, A. Da Costa, First synthesis of vanadium oxide thin films by spray pyrolysis technique, Mater. Sci. Eng B 95, 141–147 (2002)
G.J. Fang, Z.L. Liu, Y.Q. Wang, H.H. Liu, K. L. Yao, Orientated growth of V2O5 electrochromic thin films on transparent conductive glass by pulsed excimer laser ablation technique. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys 33, 3018 (2000)
C.V. Ramana, O.M. Hussain, B.Srinvasalu Naidu, C. Julien, M. Balkanski, Physical investigations on electron-beam evaporated vanadium pentoxide films, Mater. Sci. Eng B 52, 32–40 (1998)
G.S. Nadkarni, V.S. Shirodkar, Experiment and theory for switching in Al/V2O5/Al devices, Thin Solid Films 105, 115–129 (1983)
C.E. Patil, N.L. Tarwal, P.S. Shinde, H.P. Deshmukh, P.S. Patil, Synthesis of electrochromic vanadium oxide by pulsed spray pyrolysis technique and its properties. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys 42, 025404–025411 (2009)
M. Benmoussa, A. Outzourhit, A. Bennouna, E.L. Ameziane, Electrochromism in sputtered V2O5 thin films: structural and optical studies, Thin. solid films 405, 11–16 (2002)
S. Zhan, Y. Wei, X. Bie, C. Wang, F. Du, G. Chen, F. Hu, Structural and electrochemical properties of Al3+ doped V2O5 nanoparticles prepared by an oxalic acid assisted soft-chemical method,J. Alloys Compd 502, 92–96 (2010)
D.M. Yu, S.T. Zhang, D.W. Liu, X.Y. Zhou, S.H. Xie, Q.F. Zhang, Y. Y. Liu ,G. Z. Cao, Effect of manganese doping on Li-ion intercalation properties of V2O5 films, J. Mater. Chem 20, 10841–10846 (2010)
F. Coustier, S. Passerini, W. H. Smyrl, Dip-coated silver-doped V2O5 xerogel hosts as cathode materials for lithium intercalation. J.Solid State Ionics 100, 247–258 (1997)
M. Giorgetti, M. Berrettoni, W.H. Smyrl, Doped V2O5-based cathode materials: where does the doping metal go? An X-ray absorption spectroscopy study. Chem. Mater 19, 5991–6000 (2007)
J. Farcy, S. Maingot, P. Soudan, J.P. Pereira-Ramos, N. Baffier, Electrochemical properties of the mixed oxide Fe0.11V2O5.16 as a Li intercalation compound, Solid State Ionic 99 (1997) 61–69
Y. Iida, Y. Kanno, Doping effect of M (M = Nb, Ce, Nd, Dy, Sm, Ag, and/or Na) on the growth of pulsed-laser deposited V2O5 thin films, J. Mater. Process.Technol 209, 2421–2427 (2009)
M. Mousavi, A. Kompany, N. Shahtahmasebi, M.-M. Bagheri-Mohagheghi, Effect of S-doping on structural, optical and electrochemical properties of vanadium oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis, Phys. Scr. 88 (2013) 065701–065706
M. Abyazisani, M.M. Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.R. Benam, Study of structural and optical properties of nanostructured V2O5 thin films doped with fluorine, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 31, 693–699 (2015)
P. Kireev, la physique des semiconducteurs. Ed. Mir, Moscou (1975) (in French)
E.G. Birgin, I. Chambouleyron, J. M. Martínez, Estimation of the optical constants and the thickness of thin films using unconstrained optimization. J. Comput. Phys. 151, 862–880 (1999)
C.V. Ramana, R. J.Smith, O.M. Hussain, C. C.Chusuei, C. M. Julien, Correlation between growth conditions, microstructure, and optical properties in pulsed-laser-deposited V2O5 thin films, Chem. Mater. 17, 1213–1219 (2005)
S. A.Mahmud, A.A. Akl, H. Kamal, Electrical and electrochromic properties of crystalline nickel oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Phys. B 311, 366–375 (2002)
H.B. Salah, H. Bouzouita, B. Rezig, Preparation and characterization of tin sulfide. Thin Solid Films 439, 480–481 (2005)
A.V. .Murugan, M.V. Reddy, G. Campet, K. Vijayamohanan, Cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance and ex situ X-ray diffraction studies of electrochemical insertion and deinsertion of lithium ion into nanostructured organic–inorganic poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) based hybrids. J. Electroanal. Chem 603, 287–296 (2007)
Y.T. Kim, S. Gopukumar, K.B. Kim, B. W. Cho, Performance of electrostatic spray-deposited vanadium pentoxide in lithium secondary cells,J. Power Sour. 117, 110–117 (2003)
K. C.Cheng, F. R.Chen, J. J.Kai, V2O5 nanowires as a functional material for electrochoromic device. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, 1156–1165 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi, M., Khorrami, G.H., Kompany, A. et al. Structural, optical and electrochemical properties of F-doped vanadium oxide transparent semiconducting thin films. Appl. Phys. A 123, 755 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1366-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1366-7