Abstract
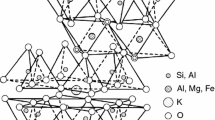
In ceramic materials, depolarization effects take place when an external electrical field is removed. Therefore, an understanding of mechanisms of polarization and depolarization is important for a more accurate control of furnace temperature and DC or pulse electrical field in flash sintering. In this paper, depolarization currents were measured in illitic clay samples in the temperature range 450–1100 °C for 150–300 min. The ionic component was dominant in these depolarization currents. Time dependences of depolarization currents suggested several depolarization mechanisms took place. They were caused by localized hopping or migration of K+, Na+, H+, and OH− ions, which were the dominant charge carriers in various temperature ranges, in the internal electric field induced by space charges at electrodes. Depolarization is a long-lasting process at high temperatures and influences the internal electrical field in ceramics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gualtieri AF, Ferrari S. Kinetics of illite dehydroxylation. Phys Chem Miner. 2006;33:490–501.
Hanykýř V, Kutzendorfer J. Technology of ceramics. Praha: Silikátový svaz; 2008.
Ptáček P, Šoukal F, Opravil T, Nosková M, Havlica J, Brandštetr J. The kinetics of Al–Si spinel phase crystallization from calcined kaolin. J Solid State Chem. 2010;183:2565–9.
Escalera E, Antti ML, Odén M. Thermal treatment and phase formation in kaolinite and illite based clays from tropical regions of Bolivia. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. 2012;31:12017.
Traoré K, Kabré TS, Blanchart P. Gehlenite and anorthite crystallisation from kaolinite and calcite mix. Ceram Int. 2003;29:377–83.
Ruotsala AP. Solid state formation of anorthite from some clay mineral-calcium mineral mixtures. Am Miner. 1963;48:792–803.
Kurama S, Ozel E. The influence of different CaO source in the production of anorthite ceramics. Ceram Int. 2009;35:827–30.
Wattanasiriwech D, Srijan K, Wattanasiriwech S. Vitrification of illitic clay from Malaysia. Appl Clay Sci. 2009;43:57–62.
Podoba R, Štubňa I, Trnovcová V, Trník A. Temperature dependence of DC electrical conductivity of kaolin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;118:597–601.
Podoba R, Trník A, Štubňa I. DC conductivity of waste calcite-clay ceramics in the temperature range 20–1050 °C. In: Thermophys 2012–Conference Proceedings. Podkylavá: Slovak Academy of Sciences. 2012. pp. 186–91.
Ondruška J, Trnovcová V, Štubňa I, Podoba R. DC conductivity of ceramics with calcite waste in the temperature range 20–1050 °C. Ceram–Silik. 2015;59:176–80.
Kubliha M, Trnovcová V, Ondruška J, Štubňa I, Bošák O, Kaljuvee T, et al. DC conductivity of illitic clay after various firing. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:81–6.
Ondruška J, Štubňa I, Trnovcová V, Húlan T, Vozár L. DC Conductivity of Illite with Fly-Ash between 20–1050 °C. Adv Mater Res. 2015;1126:123–8.
Kubliha M, Trnovcová V, Ondruška J, Štubňa I, Bošák O, Kaljuvee T. Comparison of dehydration in kaolin and illite using DC conductivity measurements. Appl Clay Sci. 2017;149:8–12.
Oreshkin PT. Electrical conductivity of refractories. Moscow: Izd. Metalurgija; 1965.
Ondruška J, Štubňa I, Trnovcová V, Medveď I, Kaljuvee T. Polarization and depolarization currents in kaolin. Appl Clay Sci. 2015;114:157–60.
Ondruška J, Štubňa I, Trnovcová V, Vozár L, Bačík P. Polarization currents in illite at various temperatures. Appl Clay Sci. 2017;135:414–7.
Lerdprom W, Li C, Jayaseelan DD, Skinner SJ, Lee WE. Temperature dependence of electrical conductivity of a green porcelain mixture. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2017;37:343–9.
Lerdprom W, Grasso S, Jayaseelan DD, Reece MJ, Lee WE. Densification behaviour and physico-mechanical properties of porcelains prepared using spark plasma sintering. Adv Appl Ceram. 2017;116:307–15.
Trombin F, Raj R. Developing processing maps for implementing flash sintering into manufacture of whiteware ceramics. Am Ceram Soc Bull. 2014;93:32–5.
Caliman LB, Bichaud E, Soudant P, Gouvea D, Steil MC. A simple flash sintering setup under applied mechanical stress and controlled atmosphere. MethodsX. 2015;2:392–8.
Štubňa I, Trnovcová V, Vozár L, Csáki Š. Uncertainty of the measurement of dc conductivity of ceramics at elevated temperatures. J Electr Eng. 2015;66:33–8.
Blumenthal RN, Seitz MA. Experimental techniques. In: Tallan NM, editor. Electr. Conducting Ceramics and Glass. part A. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. 1974. P. 35–168.
Ursianu E, Ursianu R, Ursianu V, Pop C. An iterative nonlinear regression for polarization/depolarization current. UPB Sci Bull Ser A Appl Math Phys. 2006;68:35–42.
Benchenane-Mehor H, Soufi MM, Saiter JM, Benzohra M. Simplex-TSDC spectroscopy: an efficient tool to measure the relaxation time of the isothermal transient depolarization current in organic dielectrics. Phys B: Condensed Matter. 2013;412:94–9.
Abhishek J, Aaradhi P. Dielectric diagnosis of EHV current transformer using frequency domain spectroscopy (FDS) & polarization and depolarization current (PDC) techniques. Int J Sci Eng Res. 2012;3:1–11.
Jamail NAM, Piah MAM, Muhamad NA, Zainir RA, Kasri NF, Kamarudin QE. Polarization and depolarization current measurement of polymer added with nano-particles of silicon oxide for HV insulation. J Teknol. 2013;64:141–4.
Štubňa I, Trník A, Podoba R, Ondruška J, Vozár L. The influence of thermal expansion and mass loss on the Young’s modulus of ceramics during firing. Int J Thermophys. 2014;35:1879–87.
D’ujanga FM, Kaahwa Y, Atteraas L. The polarization effects in sintered kaolin. Tanzania J Sci. 2002;28:63–70.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Ministry of Education, Science, Research, and Sport of the Slovak Republic [grant number VEGA 1/0162/15] and by the Grant Agency of Constantine the Philosopher University [grant number UGA VII/13/2016]. The authors are indebted to K. Mitterpach for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ondruška, J., Trnovcová, V., Štubňa, I. et al. Depolarization currents in illite. J Therm Anal Calorim 131, 2285–2289 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6862-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6862-7