Abstract
Purpose
This paper aims to examine the effectiveness of structural imaging as an aid in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Methods
High-resolution T 1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging was performed in 72 patients with idiopathic PD (mean age, 61.08 years) and 73 healthy subjects (mean age, 58.96 years). The whole brain was parcellated into 95 regions of interest using composite anatomical atlases, and region volumes were calculated. Three diagnostic classifiers were constructed using binary multiple logistic regression modeling: the (i) basal ganglion prior classifier, (ii) data-driven classifier, and (iii) basal ganglion prior/data-driven hybrid classifier. Leave-one-out cross validation was used to unbiasedly evaluate the predictive accuracy of imaging features. Pearson’s correlation analysis was further performed to correlate outcome measurement using the best PD classifier with disease severity.
Results
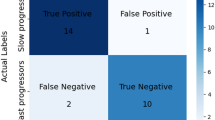
Smaller volume in susceptible regions is diagnostic for Parkinson’s disease. Compared with the other two classifiers, the basal ganglion prior/data-driven hybrid classifier had the highest diagnostic reliability with a sensitivity of 74%, specificity of 75%, and accuracy of 74%. Furthermore, outcome measurement using this classifier was associated with disease severity.
Conclusions
Brain structural volumetric analysis with multiple logistic regression modeling can be a complementary tool for diagnosing PD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks DJ (2010) Imaging approaches to Parkinson disease. J Nucl Med 51(4):596–609. doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.059998
Price S, Paviour D, Scahill R, Stevens J, Rossor M, Lees A, Fox N (2004) Voxel-based morphometry detects patterns of atrophy that help differentiate progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage 23(2):663–669. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.013
Paviour DC, Price SL, Stevens JM, Lees AJ, Fox NC (2005) Quantitative MRI measurement of superior cerebellar peduncle in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 64(4):675–679. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000151854.85743.C7
Brenneis C, Seppi K, Schocke MF, Muller J, Luginger E, Bosch S, Loscher WN, Buchel C, Poewe W, Wenning GK (2003) Voxel-based morphometry detects cortical atrophy in the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 18(10):1132–1138. doi:10.1002/mds.10502
Minnerop M, Specht K, Ruhlmann J, Schimke N, Abele M, Weyer A, Wullner U, Klockgether T (2007) Voxel-based morphometry and voxel-based relaxometry in multiple system atrophy-a comparison between clinical subtypes and correlations with clinical parameters. NeuroImage 36(4):1086–1095. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.028
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2009) The elements of statistical learning—data mining inference, and prediction, second edn. Springer, New York
Teipel SJ, Kurth J, Krause B, Grothe MJ, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I (2015) The relative importance of imaging markers for the prediction of Alzheimer’s disease dementia in mild cognitive impairment—beyond classical regression. NeuroImage Clinical 8:583–593. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2015.05.006
Politis M (2014) Neuroimaging in Parkinson disease: from research setting to clinical practice. Nat Rev Neurol 10(12):708–722. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2014.205
Zarow C, Lyness SA, Mortimer JA, Chui HC (2003) Neuronal loss is greater in the locus coeruleus than nucleus basalis and substantia nigra in Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Arch Neurol 60(3):337–341
Frisina PG, Haroutunian V, Libow LS (2009) The neuropathological basis for depression in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(2):144–148. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.04.038
Lin WC, Chou KH, Lee PL, Huang YC, Tsai NW, Chen HL, Cheng KY, Wang HC, Lin TK, Li SH, Chen MH, Lu CH, Lin CP (2015) Brain mediators of systemic oxidative stress on perceptual impairments in Parkinson’s disease. J Transl Med 13(1):386. doi:10.1186/s12967-015-0749-9
Pan PL, Song W, Shang HF (2012) Voxel-wise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. European Journal of Neurology: the Official Journal of the European Federation of Neurological Societies 19(2):199–206. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03474.x
Yu CC, Chen MH, Lu CH, Huang YC, Chen HL, Tsai NW, Wang HC, Yang IH, Li SH, Lin WC (2016) Altered striatocerebellar metabolism and systemic inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:1810289. doi:10.1155/2016/1810289
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55(3):181–184
Gasser T, Bressman S, Durr A, Higgins J, Klockgether T, Myers RH (2003) State of the art review: molecular diagnosis of inherited movement disorders. Movement disorders society task force on molecular diagnosis. Mov Disord 18(1):3–18. doi:10.1002/mds.10338
Goetz CG, Poewe W, Rascol O, Sampaio C, Stebbins GT, Counsell C, Giladi N, Holloway RG, Moore CG, Wenning GK, Yahr MD, Seidl L (2004) Movement Disorder Society task force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: status and recommendations. Mov Disord 19(9):1020–1028. doi:10.1002/mds.20213
Schwab RS, Engeland A (1969) Projection technique for evaluating surgery in Parkinson’s disease. Third symposium on Parkinson’s disease. E and S Livingstone, Edinburgh
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–198
Chang CC, Liu JS, Chang YY, Chang WN, Chen SS, Lee CH (2008) (99m)Tc-ethyl cysteinate dimer brain SPECT findings in early stage of dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease patients: a correlation with neuropsychological tests. Eur J Neurol 15(1):61–65. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.02001.x
Chou KH, Lin WC, Lee PL, Tsai NW, Huang YC, Chen HL, Cheng KY, Chen PC, Wang HC, Lin TK, Li SH, Lin WM, Lu CH, Lin CP (2015) Structural covariance networks of striatum subdivision in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 36(4):1567–1584. doi:10.1002/hbm.22724
Yang FC, Chou KH, Fuh JL, Huang CC, Lirng JF, Lin YY, Lin CP, Wang SJ (2013) Altered gray matter volume in the frontal pain modulation network in patients with cluster headache. Pain 154(6):801–807. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.02.005
Ashburner J (2007) A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage 38(1):95–113. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007
Diedrichsen J, Balsters JH, Flavell J, Cussans E, Ramnani N (2009) A probabilistic MR atlas of the human cerebellum. NeuroImage 46(1):39–46. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.01.045
Diedrichsen J (2006) A spatially unbiased atlas template of the human cerebellum. NeuroImage 33(1):127–138. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.056
Hammers A, Allom R, Koepp MJ, Free SL, Myers R, Lemieux L, Mitchell TN, Brooks DJ, Duncan JS (2003) Three-dimensional maximum probability atlas of the human brain, with particular reference to the temporal lobe. Hum Brain Mapp 19(4):224–247. doi:10.1002/hbm.10123
Gousias IS, Rueckert D, Heckemann RA, Dyet LE, Boardman JP, Edwards AD, Hammers A (2008) Automatic segmentation of brain MRIs of 2-year-olds into 83 regions of interest. NeuroImage 40(2):672–684. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.11.034
Tritsch NX, Sabatini BL (2012) Dopaminergic modulation of synaptic transmission in cortex and striatum. Neuron 76(1):33–50. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.023
Helmich RC, Derikx LC, Bakker M, Scheeringa R, Bloem BR, Toni I (2010) Spatial remapping of cortico-striatal connectivity in Parkinson’s disease. Cereb Cortex 20(5):1175–1186. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp178
Pickrell AM, Pinto M, Hida A, Moraes CT (2011) Striatal dysfunctions associated with mitochondrial DNA damage in dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 31(48):17649–17658. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4871-11.2011
Tibshirani R (2011) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso: a retrospective. J R Stat Soc B Stat Methodol 73(3):273–282
Sawada M, Imamura K, Nagatsu T (2006) Role of cytokines in inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:373–381
Tam CW, Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, O’Brien JT (2005) Temporal lobe atrophy on MRI in Parkinson disease with dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 64(5):861–865. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000153070.82309.D4
Lin WC, Chen PC, Huang YC, Tsai NW, Chen HL, Wang HC, Lin TK, Chou KH, Chen MH, Chen YW, Lu CH (2016) Dopaminergic therapy modulates cortical perfusion in Parkinson disease with and without dementia according to arterial spin labeled perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Medicine 95(5):e2206. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002206
Focke NK, Helms G, Scheewe S, Pantel PM, Bachmann CG, Dechent P, Ebentheuer J, Mohr A, Paulus W, Trenkwalder C (2011) Individual voxel-based subtype prediction can differentiate progressive supranuclear palsy from idiopathic Parkinson syndrome and healthy controls. Hum Brain Mapp 32(11):1905–1915. doi:10.1002/hbm.21161
Duchesne S, Rolland Y, Verin M (2009) Automated computer differential classification in parkinsonian syndromes via pattern analysis on MRI. Acad Radiol 16(1):61–70. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2008.05.024
Marquand AF, Filippone M, Ashburner J, Girolami M, Mourao-Miranda J, Barker GJ, Williams SC, Leigh PN, Blain CR (2013) Automated, high accuracy classification of parkinsonian disorders: a pattern recognition approach. PLoS One 8(7):e69237. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069237
Haller S, Badoud S, Nguyen D, Garibotto V, Lovblad KO, Burkhard PR (2012) Individual detection of patients with Parkinson disease using support vector machine analysis of diffusion tensor imaging data: initial results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(11):2123–2128. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3126
Szewczyk-Krolikowski K, Menke RA, Rolinski M, Duff E, Salimi-Khorshidi G, Filippini N, Zamboni G, Hu MT, Mackay CE (2014) Functional connectivity in the basal ganglia network differentiates PD patients from controls. Neurology 83(3):208–214. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000592
Martin WR, Wieler M, Stoessl AJ, Schulzer M (2008) Dihydrotetrabenazine positron emission tomography imaging in early, untreated Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 63(3):388–394. doi:10.1002/ana.21320
Wang JJ, Lin WY, Lu CS, Weng YH, Ng SH, Wang CH, Liu HL, Hsieh RH, Wan YL, Wai YY (2011) Parkinson disease: diagnostic utility of diffusion kurtosis imaging. Radiology 261(1):210–217. doi:10.1148/radiol.11102277
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patients affected by PD and their families for their involvement and altruism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the National Science Council (103-2314-B-182A-010-MY3 to W-C Lin) and the Chang Gang Memorial Hospital (CMRPG891511 and CMRPG8B0831 to W-CL and CMRPG8E0621 to M-HC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, WC., Chou, KH., Lee, PL. et al. Parkinson’s disease: diagnostic utility of volumetric imaging. Neuroradiology 59, 367–377 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1808-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1808-0