Abstract
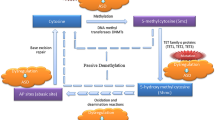
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopment disorder with abnormalities of social interaction, communication and repetitive behaviors. The higher prevalence of ASD in men implies a potential relationship between sex hormones and ASD etiology. The ESR2 gene encodes estrogen receptor beta (ESR2) and plays an important role during brain development. A relationship between ESR2 and ASD has been suggested by studies on single nucleotide polymorphisms and mRNA and protein expression levels in ASD patients. Here, we explored the possible epigenetic regulation of the ESR2 gene in autism. We collected genomic DNA from the peripheral blood of Chinese Han males with autism and age-matched normal males and measured DNA methylation of CpG islands in the ESR2 gene, which consisted of 41 CpG sites among the proximal promoter region and an untranslated exon, by bisulfite sequencing. We also investigated a relationship between DNA methylation and phenotypic features of autism, as assessed by the Children Autism Rating Scale. We found little overall difference in the DNA methylation of the ESR2 5′-flanking region in individuals with autism compared with normal individuals. However, detailed analyses revealed that eight specific CpG sites were hypermethylated in autistic individuals and that four specific CpG sites were positively associated with the severity of autistic symptoms. Our study indicates that the epigenetic dysregulation of ESR2 may govern the development of autism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
APA (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorder, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Auyeung B, Baron-Cohen S, Ashwin E, Knickmeyer R, Taylor K, Hackett G (2009) Fetal testosterone and autistic traits. Br J Psychol 100:1–22. doi:10.1348/000712608X311731
Auyeung B, Taylor K, Hackett G, Baron-Cohen S (2010) Foetal testosterone and autistic traits in 18 to 24-month-old children. Mol Autism 1:11. doi:10.1186/2040-2392-1-11
Baron-Cohen S, Lombardo MV, Auyeung B, Ashwin E, Chakrabarti B, Knickmeyer R (2011) Why are autism spectrum conditions more prevalent in males? PLoS Biol 9:e1001081. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001081
Chakrabarti B, Dudbridge F, Kent L, Wheelwright S, Hill-Cawthorne G, Allison C, Banerjee-Basu S, Baron-Cohen S (2009) Genes related to sex steroids, neural growth, and social-emotional behavior are associated with autistic traits, empathy, and Asperger syndrome. Autism Res 2:157–177. doi:10.1002/aur.80
Chlebowski C, Green JA, Barton ML, Fein D (2010) Using the childhood autism rating scale to diagnose autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 40:787–799. doi:10.1007/s10803-009-0926-x
Crider A, Thakkar R, Ahmed AO, Pillai A (2014) Dysregulation of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta), aromatase (CYP19A1), and ER co-activators in the middle frontal gyrus of autism spectrum disorder subjects. Mol Autism 5:46. doi:10.1186/2040-2392-5-46
Garfin DG, McCallon D, Cox R (1988) Validity and reliability of the childhood autism rating scale with autistic adolescents. J Autism Dev Disord 18:367–378
Gillies GE, McArthur S (2010) Estrogen actions in the brain and the basis for differential action in men and women: a case for sex-specific medicines. Pharmacol Rev 62:155–198. doi:10.1124/pr.109.002071
Gregory SG, Connelly JJ, Towers AJ, Johnson J, Biscocho D, Markunas CA, Lintas C, Abramson RK, Wright HH, Ellis P, Langford CF, Worley G, Delong GR, Murphy SK, Cuccaro ML, Persico A, Pericak-Vance MA (2009) Genomic and epigenetic evidence for oxytocin receptor deficiency in autism. BMC Med 7:62. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-7-62
Hallmayer J, Cleveland S, Torres A, Phillips J, Cohen B, Torigoe T, Miller J, Fedele A, Collins J, Smith K, Lotspeich L, Croen LA, Ozonoff S, Lajonchere C, Grether JK, Risch N (2011) Genetic heritability and shared environmental factors among twin pairs with autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:1095–1102. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.76
Imwalle DB, Gustafsson JA, Rissman EF (2005) Lack of functional estrogen receptor beta influences anxiety behavior and serotonin content in female mice. Physiol Behav 84:157–163. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.11.002
Kim YS, Leventhal BL, Koh YJ, Fombonne E, Laska E, Lim EC, Cheon KA, Kim SJ, Kim YK, Lee H, Song DH, Grinker RR (2011) Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders in a total population sample. Am J Psychiatry 168:904–912. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10101532
Krug DA, Arick J, Almond P (1980) Behavior checklist for identifying severely handicapped individuals with high levels of autistic behavior. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 21:221–229
Kudwa AE, Michopoulos V, Gatewood JD, Rissman EF (2006) Roles of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in differentiation of mouse sexual behavior. Neuroscience 138:921–928. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.10.018
Lai MC, Baron-Cohen S, Buxbaum JD (2015) Understanding autism in the light of sex/gender. Mol Autism 6:24. doi:10.1186/s13229-015-0021-4
Liang S, Wang XL, Zou MY, Wang H, Zhou X, Sun CH, Xia W, Wu LJ, Fujisawa TX, Tomoda A (2014) Family-based association study of ZNF533, DOCK4 and IMMP2L gene polymorphisms linked to autism in a northeastern Chinese Han population. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 15:264–271. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1300133
Magyar CI, Pandolfi V (2007) Factor structure evaluation of the childhood autism rating scale. J Autism Dev Disord 37:1787–1794. doi:10.1007/s10803-006-0313-9
McCarthy M (2008) Estradiol and the developing brain. Physiol Rev 88:91–124. doi:10.1152/physrev.00010.2007
McCarthy MM, Wright CL (2016) Convergence of sex differences and the Neuroimmune system in autism Spectrum disorder. Biol Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.10.004
Nakao M (2001) Epigenetics: interaction of DNA methylation and chromatin. Gene 278:25–31
Nardone S, Sams DS, Reuveni E, Getselter D, Oron O, Karpuj M, Elliott E (2014) DNA methylation analysis of the autistic brain reveals multiple dysregulated biological pathways. Transl Psychiatry 4:e433. doi:10.1038/tp.2014.70
Nguyen A, Rauch TA, Pfeifer GP, Hu VW (2010) Global methylation profiling of lymphoblastoid cell lines reveals epigenetic contributions to autism spectrum disorders and a novel autism candidate gene, RORA, whose protein product is reduced in autistic brain. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 24:3036–3051. doi:10.1096/fj.10-154484
Nordahl CW, Iosif AM, Young GS, Perry LM, Dougherty R, Lee A, Li D, Buonocore MH, Simon T, Rogers S, Wandell B, Amaral DG (2015) Sex differences in the corpus callosum in preschool-aged children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol Autism 6:26. doi:10.1186/s13229-015-0005-4
Ogawa S, Chan J, Chester AE, Gustafsson JA, Korach KS, Pfaff DW (1999) Survival of reproductive behaviors in estrogen receptor beta gene-deficient (betaERKO) male and female mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:12887–12892
Osterlund MK, Grandien K, Keller E, Hurd YL (2000a) The human brain has distinct regional expression patterns of estrogen receptor α mRNA isoforms derived from alternative promoters. J Neurochem 75:1390–1397. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0751390.x
Osterlund MK, Gustafsson JA, Keller E, Hurd YL (2000b) Estrogen receptor β (ERβ) messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression within the human forebrain: distinct distribution pattern to ERα mRNA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3840–3846
Ostlund H, Keller E, Hurd YL (2003) Estrogen receptor gene expression in relation to neuropsychiatric disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1007:54–63
Rissman EF, Heck AL, Leonard JE, Shupnik MA, Gustafsson JA (2002) Disruption of estrogen receptor beta gene impairs spatial learning in female mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:3996–4001. doi:10.1073/pnas.012032699
Rocha BA, Fleischer R, Schaeffer JM, Rohrer SP, Hickey GJ (2005) 17 Beta-estradiol-induced antidepressant-like effect in the forced swim test is absent in estrogen receptor-beta knockout (BERKO) mice. Psychopharmacology 179:637–643. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-2078-1
Roselli CE, Liu M, Hurn PD (2009) Brain aromatization: classic roles and new perspectives. Semin Reprod Med 27:207–217. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1216274
Ter Horst GJ (2010) Estrogen in the limbic system. Vitam Horm 82:319–338. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(10)82017-5
Wang Y, Fang Y, Zhang F, Xu M, Zhang J, Yan J, Ju W, Brown WT, Zhong N (2014) Hypermethylation of the enolase gene (ENO2) in autism. Eur J Pediatr 173:1233–1244. doi:10.1007/s00431-014-2311-9
Werling DM (2016) The role of sex-differential biology in risk for autism spectrum disorder. Biol Sex Differ 7:58. doi:10.1186/s13293-016-0112-8
Werling DM, Geschwind DH (2015) Recurrence rates provide evidence for sex-differential, familial genetic liability for autism spectrum disorders in multiplex families and twins. Mol Autism 6:27. doi:10.1186/s13229-015-0004-5
Zhao C, Lam EW, Sunters A, Enmark E, De Bella MT, Coombes RC, Gustafsson JA, Dahlman-Wright K (2003) Expression of estrogen receptor beta isoforms in normal breast epithelial cells and breast cancer: regulation by methylation. Oncogene 22:7600–7606. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207100
Zhu X, Leav I, Leung YK, Wu M, Liu Q, Gao Y, McNeal JE, Ho SM (2004) Dynamic regulation of estrogen receptor-beta expression by DNA methylation during prostate cancer development and metastasis. Am J Pathol 164:2003–2012
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Mayumi Oda (Keio University) for the advice on BSP. We thank all members of the laboratory for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (M.N. and N.S.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81202221 to S.L.), and the Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (12521232 to S.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (M.N. and N.S.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81202221 to S.L.), and the Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (12521232 to S.L.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
“All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.”
Informed consent
“Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Liang, S., Sun, Y. et al. Analysis of estrogen receptor β gene methylation in autistic males in a Chinese Han population. Metab Brain Dis 32, 1033–1042 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-9990-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-9990-7