Abstract
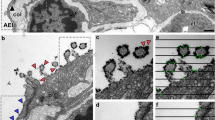
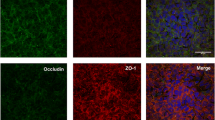
Loss of alveolar barrier function with subsequent respiratory failure is a hallmark of severe pneumonia. Although junctions between endo- and epithelial cells regulate paracellular fluid flux, little is known about their composition and regulation in the human alveolar compartment. High autofluorescence of human lung tissue in particular complicates the determination of subcellular protein localization. By comparing conventional channel mode confocal imaging with spectral imaging and linear unmixing, we demonstrate that background fluorescent spectra and fluorophore signals could be rigorously separated resulting in complete recovery of the specific signal at a high signal–to-noise ratio. Using this technique and Western blotting, we show the expression patterns of tight junction proteins occludin, ZO-1 as well as claudin-3, -4, -5 and -18 and adherence junction protein VE-cadherin in naive or Streptococcus pneumoniae-infected human lung tissue. In uninfected tissues, occludin and ZO-1 formed band-like structures in alveolar epithelial cells type I (AEC I), alveolar epithelial cells type II (AEC II) and lung capillaries, whereas claudin-3, -4 and -18 were visualised in AEC II. Claudin-5 was detected in the endothelium only. Claudin-3, -5, -18 displayed continuous band-like structures, while claudin-4 showed a dot-like expression. Pneumococcal infection reduced alveolar occludin, ZO-1, claudin-5 and VE-cadherin but did not change the presence of claudin-3, -4 and -18. Spectral confocal microscopy allows for the subcellular structural analysis of proteins in highly autofluorescent human lung tissue. The thereby observed deterioration of lung alveolar junctional organisation gives a structural explanation for alveolar barrier disruption in severe pneumococcal pneumonia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bättig P, Muhlemann K (2008) Influence of the spxB gene on competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 190:1184–1189
Bazzoni G (2006) Endothelial tight junctions: permeable barriers of the vessel wall. Thromb Haemost 95:36–42
Berkowitz DM, Danai PA, Eaton S, Moss M, Martin GS (2008) Accurate characterization of extravascular lung water in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 36:1803–1809
Chen X, Goncalves MA (2016) Engineered viruses as genome editing devices. Mol Ther J Am Soc of Gene Ther 24:447–457
Chen W, Sharma R, Rizzo AN, Siegler JH, Garcia JG, Jacobson JR (2014) Role of claudin-5 in the attenuation of murine acute lung injury by simvastatin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 50:328–336
Chu LY, Wang YF, Cheng HH, Kuo CC, Wu KK (2016) Endothelium-derived 5-methoxytryptophan protects endothelial barrier function by blocking p38 MAPK Activation. PloS One 11:e0152166
Cowan CE, Kohler EE, Dugan TA, Mirza MK, Malik AB, Wary KK (2010) Kruppel-like factor-4 transcriptionally regulates VE-cadherin expression and endothelial barrier function. Circ Res 107:959–966
De Lisle RC (2014) Disrupted tight junctions in the small intestine of cystic fibrosis mice. Cell Tissue Res 355:131–142
Dietert K, Mundhenk L, Erickson NA, Reppe K, Hocke AC, Kummer W, Witzenrath M, Gruber AD (2015) Murine CLCA5 is uniquely expressed in distinct niches of airway epithelial cells. Histochem Cell Biol 143:277–287
Drijkoningen JJ, Rohde GG (2014) Pneumococcal infection in adults: burden of disease. Clin Microbiol Infect 20:45–51
Fanning AS, Jameson BJ, Jesaitis LA, Anderson JM (1998) The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 273:29745–29753
Furuse M, Itoh M, Hirase T, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S (1994) Direct association of occludin with ZO-1 and its possible involvement in the localization of occludin at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 127:1617–1626
Gonzalez JE, DiGeronimo RJ, Arthur DE, King JM (2009) Remodeling of the tight junction during recovery from exposure to hydrogen peroxide in kidney epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 47:1561–1569
Herold S, Gabrielli NM, Vadasz I (2013) Novel concepts of acute lung injury and alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 305:L665–L681
Hocke AC, Becher A, Knepper J, Peter A, Holland G, Tonnies M, Bauer TT, Schneider P, Neudecker J, Muth D, Wendtner CM, Ruckert JC, Drosten C, Gruber AD, Laue M, Suttorp N, Hippenstiel S, Wolff T (2013) Emerging human middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus causes widespread infection and alveolar damage in human lungs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188:882–886
Horie S, Masterson C, Devaney J, Laffey JG (2016) Stem cell therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome: a promising future? Curr Opin Crit Care 22:14–20
Kage H, Flodby P, Gao D, Kim YH, Marconett CN, DeMaio L, Kim KJ, Crandall ED, Borok Z (2014) Claudin 4 knockout mice: normal physiological phenotype with increased susceptibility to lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L524–L536
Kirk A, Campbell S, Bass P, Mason J, Collins J (2010) Differential expression of claudin tight junction proteins in the human cortical nephron. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:2107–2119
Knepper J, Schierhorn KL, Becher A, Budt M, Tonnies M, Bauer TT, Schneider P, Neudecker J, Ruckert JC, Gruber AD, Suttorp N, Schweiger B, Hippenstiel S, Hocke AC, Wolff T (2013) The novel human influenza A(H7N9) virus is naturally adapted to efficient growth in human lung tissue. MBio 4:e00601–00613
Koda R, Zhao L, Yaoita E, Yoshida Y, Tsukita S, Tamura A, Nameta M, Zhang Y, Fujinaka H, Magdeldin S, Xu B, Narita I, Yamamoto T (2011) Novel expression of claudin-5 in glomerular podocytes. Cell Tissue Res 343:637–648
Komarova Y, Malik AB (2010) Regulation of endothelial permeability via paracellular and transcellular transport pathways. Annu Rev Physiol 72:463–493
Koppe U, Suttorp N, Opitz B (2012) Recognition of Streptococcus pneumoniae by the innate immune system. Cell Microbiol 14:460–466
Koval M (2013) Claudin heterogeneity and control of lung tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 75:551–567
Laakkonen JP, Lappalainen JP, Theelen TL, Toivanen PI, Nieminen T, Jauhiainen S, Kaikkonen MU, Sluimer JC, Yla-Herttuala S (2016) Differential regulation of angiogenic cellular processes and claudin-5 by histamine and VEGF via PI3K-signaling, transcription factor SNAI2 and interleukin-8. Angiogenesis 20:109–124
LaFemina MJ, Rokkam D, Chandrasena A, Pan J, Bajaj A, Johnson M, Frank JA (2010) Keratinocyte growth factor enhances barrier function without altering claudin expression in primary alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 299:L724–L734
LaFemina MJ, Sutherland KM, Bentley T, Gonzales LW, Allen L, Chapin CJ, Rokkam D, Sweerus KA, Dobbs LG, Ballard PL, Frank JA (2014) Claudin-18 deficiency results in alveolar barrier dysfunction and impaired alveologenesis in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 51:550–558
Li G, Flodby P, Luo J, Kage H, Sipos A, Gao D, Ji Y, Beard LL, Marconett CN, DeMaio L, Kim YH, Kim KJ, Laird-Offringa IA, Minoo P, Liebler JM, Zhou B, Crandall ED, Borok Z (2014a) Knockout mice reveal key roles for claudin 18 in alveolar barrier properties and fluid homeostasis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 51:210–222
Li H, Singh S, Potula R, Persidsky Y, Kanmogne GD (2014b) Dysregulation of claudin-5 in HIV-induced interstitial pneumonitis and lung vascular injury. Protective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190:85–97
Linares GR, Brommage R, Powell DR, Xing W, Chen ST, Alshbool FZ, Lau KH, Wergedal JE, Mohan S (2012) Claudin 18 is a novel negative regulator of bone resorption and osteoclast differentiation. J Bone mineral Res 27:1553–1565
Liu KM, Chuang SM, Long CY, Lee YL, Wang CC, Lu MC, Lin RJ, Lu JH, Jang MY, Wu WJ, Ho WT, Juan YS (2015a) Ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis and bladder apoptosis involve oxidative stress mediated by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 309:F318-F331
Liu WJ, Zhong ZJ, Cao LH, Li HT, Zhang TH, Lin WQ (2015b) Paclitaxel-induced lung injury and its amelioration by parecoxib sodium. Sci Rep 5:12977
Lopez R, Garcia E (2004) Recent trends on the molecular biology of pneumococcal capsules, lytic enzymes, and bacteriophage. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:553–580
Lu Z, Ding L, Lu Q, Chen YH (2013) Claudins in intestines: Distribution and functional significance in health and diseases. Tissue Barriers 1:e24978
Lucas R, Verin AD, Black SM, Catravas JD (2009) Regulators of endothelial and epithelial barrier integrity and function in acute lung injury. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1763–1772
Matthay MA, Zemans RL (2011) The acute respiratory distress syndrome: pathogenesis and treatment. Annu Rev Pathol 6:147–163
Matthay MA, Ware LB, Zimmerman GA (2012) The acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest 122:2731–2740
Meyer TN, Schwesinger C, Ye J, Denker BM, Nigam SK (2001) Reassembly of the tight junction after oxidative stress depends on tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem 276:22048–22055
Milatz S, Krug SM, Rosenthal R, Gunzel D, Muller D, Schulzke JD, Amasheh S, Fromm M (2010) Claudin-3 acts as a sealing component of the tight junction for ions of either charge and uncharged solutes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1798:2048–2057
Morita K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 147:185–194
Moroi S, Saitou M, Fujimoto K, Sakakibara A, Furuse M, Yoshida O, Tsukita S (1998) Occludin is concentrated at tight junctions of mouse/rat but not human/guinea pig Sertoli cells in testes. Am J Physiol 274:C1708–C1717
Morrow CM, Mruk D, Cheng CY, Hess RA (2010) Claudin and occludin expression and function in the seminiferous epithelium. Philos Transa R Soci Lond Ser B Biol Sci 365:1679–1696
Mortality GBD, Causes of Death C (2016) Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388:1459–1544
Müller-Redetzky HC, Will D, Hellwig K, Kummer W, Tschernig T, Pfeil U, Paddenberg R, Menger MD, Kershaw O, Gruber AD, Weissmann N, Hippenstiel S, Suttorp N, Witzenrath M (2014) Mechanical ventilation drives pneumococcal pneumonia into lung injury and sepsis in mice: protection by adrenomedullin. Crit Care 18:R73
Navone SE, Marfia G, Invernici G, Cristini S, Nava S, Balbi S, Sangiorgi S, Ciusani E, Bosutti A, Alessandri G, Slevin M, Parati EA (2013) Isolation and expansion of human and mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells. Nat Protoc 8:1680–1693
Pienaar IS, Lee CH, Elson JL, McGuinness L, Gentleman SM, Kalaria RN, Dexter DT (2015) Deep-brain stimulation associates with improved microvascular integrity in the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 74:392–405
Pletz MW, von Baum H, van der Linden M, Rohde G, Schutte H, Suttorp N, Welte T (2012) The burden of pneumococcal pneumonia—experience of the German competence network CAPNETZ. Pneumologie (Stuttgart, Germany) 66:470–475
Rao RK, Basuroy S, Rao VU, Karnaky KJ Jr, Gupta A (2002) Tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation of occludin-ZO-1 and E-cadherin-beta-catenin complexes from the cytoskeleton by oxidative stress. Biochem J 368:471–481
Ren H, Birch NP, Suresh V (2016) An optimised human cell culture model for alveolar epithelial transport. PloS One 11:e0165225
Rode K, Sieme H, Richterich P, Brehm R (2015) Characterization of the equine blood-testis barrier during tubular development in normal and cryptorchid stallions. Theriogenology 84:763–772
Rokkam D, Lafemina MJ, Lee JW, Matthay MA, Frank JA (2011) Claudin-4 levels are associated with intact alveolar fluid clearance in human lungs. Am J Pathol 179:1081–1087
Soini Y, Takasawa A, Eskelinen M, Juvonen P, Karja V, Hasegawa T, Murata M, Tanaka S, Kojima T, Sawada N (2012) Expression of claudins 7 and 18 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: association with features of differentiation. J Clin Pathol 65:431–436
Spellerberg B, Cundell DR, Sandros J, Pearce BJ, Idanpaan-Heikkila I, Rosenow C, Masure HR (1996) Pyruvate oxidase, as a determinant of virulence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol 19:803–813
Spieth PM, Bluth T, Gama De Abreu M, Bacelis A, Goetz AE, Kiefmann R (2014) Mechanotransduction in the lungs. Minerva Anestesiol 80:933–941
Stammler A, Luftner BU, Kliesch S, Weidner W, Bergmann M, Middendorff R, Konrad L (2016) Highly conserved testicular localization of claudin-11 in normal and impaired spermatogenesis. PloS One 11:e0160349
Szymanski KV, Toennies M, Becher A, Fatykhova D, N’Guessan PD, Gutbier B, Klauschen F, Neuschaefer-Rube F, Schneider P, Rueckert J, Neudecker J, Bauer TT, Dalhoff K, Dromann D, Gruber AD, Kershaw O, Temmesfeld-Wollbrueck B, Suttorp N, Hippenstiel S, Hocke AC (2012) Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in human lung tissue. Eur Respir J 40:1458–1467
Tang EI, Mok KW, Lee WM, Cheng CY (2015) EB1 regulates tubulin and actin cytoskeletal networks at the sertoli cell blood-testis barrier in male rats: an in vitro study. Endocrinology 156:680–693
Todd MC, Petty HM, King JM, Piana Marshall BN, Sheller RA, Cuevas ME (2015) Overexpression and delocalization of claudin-3 protein in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-415 breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Lett 10:156–162
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2014) Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin Cell Dev Biol 36:157–165
Walsh TG, Murphy RP, Fitzpatrick P, Rochfort KD, Guinan AF, Murphy A, Cummins PM (2011) Stabilization of brain microvascular endothelial barrier function by shear stress involves VE-cadherin signaling leading to modulation of pTyr-occludin levels. J Cell Physiol 226:3053–3063
Weinheimer VK, Becher A, Tonnies M, Holland G, Knepper J, Bauer TT, Schneider P, Neudecker J, Ruckert JC, Szymanski K, Temmesfeld-Wollbrueck B, Gruber AD, Bannert N, Suttorp N, Hippenstiel S, Wolff T, Hocke AC (2012) Influenza A viruses target type II pneumocytes in the human lung. J Infect Dis 206:1685–1694
Williams AE, Chambers RC (2014) The mercurial nature of neutrophils: still an enigma in ARDS? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 306:L217–L230
Witzenrath M, Gutbier B, Hocke AC, Schmeck B, Hippenstiel S, Berger K, Mitchell TJ, de los Toyos JR, Rosseau S, Suttorp N, Schutte H (2006) Role of pneumolysin for the development of acute lung injury in pneumococcal pneumonia. Crit Care Med 34:1947–1954
Wray C, Mao Y, Pan J, Chandrasena A, Piasta F, Frank JA (2009) Claudin-4 augments alveolar epithelial barrier function and is induced in acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 297:L219–L227
Xu R, Feng X, Xie X, Zhang J, Wu D, Xu L (2012) HIV-1 Tat protein increases the permeability of brain endothelial cells by both inhibiting occludin expression and cleaving occludin via matrix metalloproteinase-9. Brain Res 1436:13–19
You K, Xu X, Fu J, Xu S, Yue X, Yu Z, Xue X (2012) Hyperoxia disrupts pulmonary epithelial barrier in newborn rats via the deterioration of occludin and ZO-1. Respir Res 13:36
Yuksel H, Yilmaz O, Karaman M, Firinci F, Turkeli A, Kanik ET, Inan S (2015) Vascular endothelial growth factor antagonism restores epithelial barrier dysfunction via affecting zonula occludens proteins. Exp Ther Med 10:362–368
Zahlten J, Steinicke R, Bertrams W, Hocke AC, Scharf S, Schmeck B, Witzenrath M, Hammerschmidt S, Suttorp N, Hippenstiel S (2013) TLR9- and Src-dependent expression of Krueppel-like factor 4 controls interleukin-10 expression in pneumonia. Eur Respir J 41:384–391
Zahlten J, Kim YJ, Doehn JM, Pribyl T, Hocke AC, Garcia P, Hammerschmidt S, Suttorp N, Hippenstiel S, Hubner RH (2014) Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced oxidative stress in lung epithelial cells depends on pneumococcal autolysis and is reversible by resveratrol. J Infect Dis 211:1822–1830
Zhou X, Dai Q, Huang X (2012) Neutrophils in acute lung injury. Front Biosci (Landmark ed) 17:2278–2283
Acknowledgements
Parts of this work are included in the doctoral thesis of Andrea Peter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Support statement
This study was supported by the Transregional Collaborative Research Center SFB-TR84 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grants B6 to A.C. Hocke and S. Hippenstiel, Z1a to A.C. Hocke as well as Z1b to A.D. Gruber and B1 to N. Suttorp) and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Grant C1 to S. Hippenstiel and C8 to A.C. Hocke; PROGRESS—Pneumonia Research Network on Genetic Resistance and Susceptibility for the Evolution of Severe Sepsis).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Additional information
A. C. Hocke and S. Hippenstiel contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peter, A., Fatykhova, D., Kershaw, O. et al. Localization and pneumococcal alteration of junction proteins in the human alveolar–capillary compartment. Histochem Cell Biol 147, 707–719 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-017-1551-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-017-1551-y