Abstract
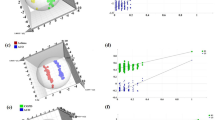
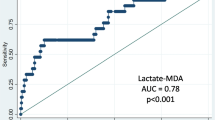
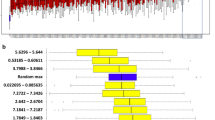
Spirometry is used to establish the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and to assess disease progression, but it seems inadequate to characterize COPD phenotypes. Metabolomics has been introduced for molecular fingerprinting of biosamples in a variety of clinical disorders. The aim of the study was to establish whether exhaled breath condensate (EBC) in COPD features a distinct metabolic fingerprint, and to identify the metabolites that characterize the EBC profile in COPD. EBC was collected using a home-made glass condenser in 37 stable COPD patients, and 25 non-obstructed controls. Samples were analyzed using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR). Random forest was applied for both supervised and unsupervised learning, using spectral buckets as input variables. Metabolomics of EBC discriminated COPD patients from controls with an overall accuracy of 86 %. As compared to controls, EBC from COPD featured significantly lower (p < 0.05) levels of acetone, valine and lysine, and significantly higher (p < 0.05) levels of lactate, acetate, propionate, serine, proline, and tyrosine. Based on unsupervised analysis of NMR spectra, the COPD sample was split in three clusters, one of which had the highest prevalence of radiologic emphysema. NMR spectroscopy of EBC holds promise in COPD fingerprinting. It may prove valuable in outcome studies, and in assessing the efficacy of therapeutic interventions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agusti, A. G., Sauleda, J., Miralles, C., Gomez, C., Togores, B., Sala, E., et al. (2002). Skeletal muscle apoptosis and weight loss in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 166, 485–489.
Aranjbar, N., Ott, K. H., Roongta, V., & Mueller, L. (2006). Metabolomic analysis using optimized NMR and statistical methods. Analytical Biochemistry, 355, 62–70.
Assfalg, M., Bertini, I., Colangiuli, D., Luchinat, C., Schafer, H., Schutz, B., et al. (2008). Evidence of different metabolic phenotypes in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 1420–1424.
Barnes, P. J., Chowdhury, B., Kharitonov, S. A., Magnussen, H., Page, C. P., Postma, D., et al. (2006). Pulmonary biomarkers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 174, 6–14.
Baumann, K. (2010). Cross-validation is dead. Long live cross-validation! Model validation based on resampling. Journal of Cheminformatics,. doi:10.1186/1758-2946-2-S1-O5.
Bensel, T., Stotz, M., Borneff-Lipp, M., Wollschlager, B., Wienke, A., Taccetti, G., et al. (2011). Lactate in cystic fibrosis sputum. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis, 10, 37–44.
Bertini, I., Cacciatore, S., Jensen, B. V., Schou, J. V., Johansen, J. S., Kruhoffer, M., et al. (2012). Metabolomic NMR fingerprinting to identify and predict survival of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Research, 72, 356–364.
Bertini, I., Calabro, A., De Carli, V., Luchinat, C., Nepi, S., Porfirio, B., et al. (2009). The metabonomic signature of celiac disease. Journal of Proteome Research, 8, 170–177.
Bertram, H. C., Eggers, N., & Eller, N. (2009). Potential of human saliva for nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics and for health-related biomarker identification. Analytical Chemistry, 81, 9188–9193.
Bofan, M., Mores, N., Baron, M., Dabrowska, M., Valente, S., Schmid, M., et al. (2013). Within-day and between-day repeatability of measurements with an electronic nose in patients with COPD. Journal of Breath Research, 7(1), 017103.
Borrill, Z. L., Roy, K., & Singh, D. (2008). Exhaled breath condensate biomarkers in COPD. European Respiratory Journal, 32, 472–486.
Borrill, Z. L., Starkey, R. C., & Singh, S. D. (2007). Variability of exhaled breath condensate leukotriene B4 and 8-isoprostane in COPD patients. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, 2, 71–76.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45, 5–32.
Carraro, S., Rezzi, S., Reniero, F., Heberger, K., Giordano, G., Zanconato, S., et al. (2007). Metabolomics applied to exhaled breath condensate in childhood asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 175, 986–990.
Cerveri, I., Corsico, A. G., Grosso, A., Albicini, F., Ronzoni, V., Tripon, B., et al. (2013). The rapid FEV(1) decline in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is associated with predominant emphysema: A longitudinal study. Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, 10, 55–61.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Mahwah: L. Erlbaum Associates.
De Jong, S. (1993). SIMPLS: An alternative approach to partial least-squares regression. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 18, 251–263.
de Laurentiis, G., Paris, D., Melck, D., Maniscalco, M., Marsico, S., Corso, G., et al. (2008). Metabonomic analysis of exhaled breath condensate in adults by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. European Respiratory Journal, 32, 1175–1183.
DeMeo, D. L., Hersh, C. P., Hoffman, E. A., Litonjua, A. A., Lazarus, R., Sparrow, D., et al. (2007). Genetic determinants of emphysema distribution in the national emphysema treatment trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 176, 42–48.
Dieterle, F., Ross, A., Schlotterbeck, G., & Senn, H. (2006). Probabilistic quotient normalization as Robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4281–4290.
Dumas, M. E., Maibaum, E. C., Teague, C., Ueshima, H., Zhou, B., Lindon, J. C., et al. (2006). Assessment of analytical reproducibility of 1H NMR spectroscopy based metabonomics for large-scale epidemiological research: The INTERMAP study. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 2199–2208.
Fisher, R. A. (1936). The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Annals of Eugenics, 7, 179–188.
Franklin, P., Moeller, A., Hall, G. L., Horak, F, Jr, Patterson, H., & Stick, S. M. (2006). Variability of nitric oxide metabolites in exhaled breath condensate. Respiratory Medicine, 100, 123–129.
Horvíth, I., Hunt, J., Barnes, P. J., & On behalf of the ATS/ERS Task Force on Exhaled Breath Condensate. (2005). Exhaled breath condensate: methodological recommendations and unresolved questions. European Respiratory Journal, 26, 523–548.
Hurst, J. R., Vestbo, J., Anzueto, A., Locantore, N., Mullerova, H., Tal-Singer, R., et al. (2010). Susceptibility to exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 363, 1128–1138.
Izquierdo-Garcia, J. L., Peces-Barba, G., Heili, S., Diaz, R., Want, E., & Ruiz-Cabello, J. (2011). Is NMR-based metabolomic analysis of exhaled breath condensate accurate? European Respiratory Journal, 37, 468–470.
Lanza, I. R., Zhang, S., Ward, L. E., Karakelides, H., Raftery, D., & Nair, K. S. (2010). Quantitative metabolomics by H-NMR and LC-MS/MS confirms altered metabolic pathways in diabetes. PLoS One, 5, e10538.
Lucidi, V., Ciabattoni, G., Bella, S., Barnes, P. J., & Montuschi, P. (2008). Exhaled 8-isoprostane and prostaglandin E2 in patients with stable and unstable cystic fibrosis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 45, 913–919.
MacIntyre, D. A., Jimenez, B., Lewintre, E. J., Martin, C. R., Schafer, H., Ballesteros, C. G., et al. (2010). Serum metabolome analysis by 1H-NMR reveals differences between chronic lymphocytic leukaemia molecular subgroups. Leukemia, 24, 788–797.
Malerba, M., & Montuschi, P. (2012). Non-invasive biomarkers of lung inflammation in smoking subjects. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 19, 187–196.
Mannino, D. M., Homa, D. M., Akinbami, L. J., Ford, E. S., & Redd, S. C. (2002). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease surveillance—United States, 1971–2000. Respiratory Care, 47, 1184–1199.
Miller, M. R., Hankinson, J., Brusasco, V., Burgos, F., Casaburi, R., Coates, A., et al. (2005). Standardisation of spirometry. European Respiratory Journal, 26, 319–338.
Miniati, M., Catapano, G. A., Monti, S., Mannucci, F., & Bottai, M. (2013). Effects of emphysema on oxygen uptake during maximal exercise in COPD. Internal and Emergency Medicine, 8, 41–47.
Miniati, M., Monti, S., Stolk, J., Mirarchi, G., Falaschi, F., Rabinovich, R., et al. (2008). Value of chest radiography in phenotyping chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. European Respiratory Journal, 31, 509–515.
Montuschi, P. (2009). LC/MS/MS analysis of leukotriene B4 and other eicosanoids in exhaled breath condensate for assessing lung inflammation. Journal of Chromatography B, 877, 1272–1280.
Montuschi, P. (2010). Toward a personalized pharmacotherapy of respiratory diseases. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 1, 131.
Montuschi, P., Currò, D., Ragazzoni, E., Preziosi, P., & Ciabattoni, G. (1999). Anaphylaxis increases 8-iso-prostaglandin Fα release from guinea-pig lung in vitro. European Journal of Pharmacology, 365, 59–64.
Montuschi, P., Mores, N., Trove, A., Mondino, C., & Barnes, P. J. (2013). The electronic nose in respiratory medicine. Respiration, 85, 72–84.
Montuschi, P., Paris, D., Melck, D., Lucidi, V., Ciabattoni, G., Raia, V., et al. (2012). NMR spectroscopy metabolomic profiling of exhaled breath condensate in patients with stable and unstable cystic fibrosis. Thorax, 67, 222–228.
Motta, A., Paris, D., Melck, D., de Laurentiis, G., Maniscalco, M., Sofia, M., et al. (2012). Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics of exhaled breath condensate: methodological aspects. European Respiratory Journal, 39, 498–500.
Nicholson, J. K., & Lindon, J. C. (2008). Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature, 455, 1054–1056.
Nicholson, J. K., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (1999). ‘Metabonomics’: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica, 29, 1181–1189.
Oakman, C., Tenori, L., Biganzoli, L., Santarpia, L., Cappadona, S., Luchinat, C., et al. (2010). Uncovering the metabolomic fingerprint of breast cancer. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 43(7), 1010–1020.
Pers, T. H., Albrechtsen, A., Holst, C., Sorensen, T. I., & Gerds, T. A. (2009). The validation and assessment of machine learning: A game of prediction from high-dimensional data. PLoS One, 4, e6287.
Rabe, K. F., Hurd, S., Anzueto, A., Barnes, P. J., Buist, S. A., Calverley, P., et al. (2007). Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 176, 532–555.
Saetta, M., Kim, W. D., Izquierdo, J. L., Ghezzo, H., & Cosio, M. G. (1994). Extent of centrilobular and panacinar emphysema in smokers’ lungs: pathological and mechanical implications. European Respiratory Journal, 7, 664–671.
Saude, E., Adamko, D., Rowe, B., Marrie, T., & Sykes, B. (2007). Variation of metabolites in normal human urine. Metabolomics, 3, 439–451.
Serkova, N. J., & Niemann, C. U. (2006). Pattern recognition and biomarker validation using quantitative 1H-NMR-based metabolomics. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 6, 717–731.
Shockcor, J. P., & Holmes, E. (2002). Metabonomic applications in toxicity screening and disease diagnosis. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 2, 35–51.
Slupsky, C. M., Rankin, K. N., Wagner, J., Fu, H., Chang, D., Weljie, A. M., et al. (2007). Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 6995–7004.
Sreekumar, A., Poisson, L. M., Rajendiran, T. M., Khan, A. P., Cao, Q., Yu, J., et al. (2009). Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature, 457, 910–914.
Sutinen, S., Christofordis, A. J., Klough, G. A., & Pratt, P. C. (1965). Roentgenologic criteria for the recognition of nonsymptomatic pulmonary emphysema. Correlation between roentgenologic findings and pulmonary pathology. American Review of Respiratory Disease, 91, 69–76.
Szymanska, E., Saccenti, E., Smilde, A., & Westerhuis, J. (2011). Double-check: Validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics, 8(Suppl 1), 3–16.
Ubhi, B. K., Riley, J. H., Shaw, P. A., Lomas, D. A., Tal-Singer, R., MacNee, W., et al. (2012). Metabolic profiling detects biomarkers of protein degradation in COPD patients. European Respiratory Journal, 40, 345–355.
Vapnik, V. N. (1995). The nature of statistical learning theory. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Vestbo, J., Edwards, L. D., Scanlon, P. D., Yates, J. C., Agusti, A., Bakke, P., et al. (2011). Changes in forced expiratory volume in 1 s over time in COPD. New England Journal of Medicine, 365, 1184–1192.
Westerhuis, J. A., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Smit, S., Vis, D. J., Smilde, A. K., van Velzen, E. J. J., et al. (2008). Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics, 4, 81–89.
Wishart, D. S., Tzur, D., Knox, C., Eisner, R., Guo, A. C., Young, N., et al. (2007). HMDB: The human metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, D521–D526.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Edo Fornai for his technical skills, and Mirko Passera for preparing the artwork. Permission was obtained from those who are acknowledged. This study was supported in part by a Grant from Boehringer Ingelheim Italia S.p.A. The funding source had no role in the study design, the analysis of data, or the writing of the report.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ivano Bertini passed away on July 7, 2012.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertini, I., Luchinat, C., Miniati, M. et al. Phenotyping COPD by 1H NMR metabolomics of exhaled breath condensate. Metabolomics 10, 302–311 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0572-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0572-3