Abstract
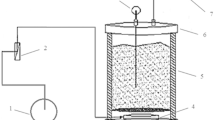
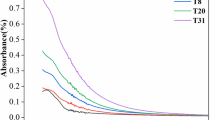
Composting is an effective method in treating solid organic wastes, in which dissolved organic matter (DOM) plays an important role in transformation of organic matter and microbial activity. Therefore, an understanding of the properties and evolution of DOM during composting is crucial. In this study, DOM was studied using elemental analysis, spectroscopic analysis (UV-vis, FTIR, and pyrolysis-GC/MS), and colloidal analysis during a 120-day composting. Results showed that the content of N and O in DOM increased while C and H content declined progressively over the composting time. Aliphatic C–H stretching, aromatic C=C or C=O stretching of amide groups, and C–O stretch (carbohydrates) showed an obvious decrease, while COO– and C–N groups had a significant increase. The evolution of DOM indicated a gradual decrease of the lipid and polysaccharide fractions, whereas an increase of aromatic and nitrogenous compounds was observed. The DOM also showed a more stable status, and an accumulation of small molecular compounds occurred with composting proceeded. Taken together, these results shed a good insight into the properties and evolution of DOM during a composting process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avetta P, Berto S, Prevot AB, Minella M, Montoneri E, Persico D, Vione D, Gonzalez MC, Mártire CL, Arques A (2015) Photoinduced transformation of waste-derived soluble bio-based substances. Chem Eng J 274:247–255
Busato JG, Lima LS, Aguiar NO, Canellas LP, Olivares FL (2012) Changes in labile phosphorus forms during maturation of vermicompost enriched with phosphorus-solubilizing and diazotrophic bacteria. Bioresour Technol 110:390–395
Camarero L, Rogora M, Mosello R, Anderson NJ, Barbieri A, Botev I, Muri G (2009) Regionalisation of chemical variability in European mountain lakes. Freshw Biol 54(12):2452–2469
Caricasole P, Provenzano MR, Hatcher PG, Senesi N (2011) Evolution of organic matter during composting of different organic wastes assessed by CPMAS 13 C NMR spectroscopy. Waste Manag 31(3):411–415
Chefetz B, Hadar Y, Chen Y (1998) Dissolved organic carbon fractions formed during composting of municipal solid waste: properties and significance. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 26(3):172–179
Chen Y, Senesi N, Schnitzer M (1977) Information provided on humic substances by E4/E6 ratios. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41(2):352–358
Cheng KY, Wong JWC (2006) Combined effect of nonionic surfactant Tween 80 and DOM on the behaviors of PAHs in soil–water system. Chemosphere 62(11):1907–1916
Dong Q, Zhang S, Zhang L, Ding K, Xiong Y (2015) Effects of four types of dilute acid washing on moso bamboo pyrolysis using Py-GC/MS. Bioresour Technol 185:62–69
Gajalakshmi S, Abbasi SA (2008) Solid waste management by composting: state of the art. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 38(5):311–400
Gigliotti G, Kaiser K, Guggenberger G, Haumaier L (2002) Differences in the chemical composition of dissolved organic matter from waste material of different sources. Biol Fertil Soils 36(5):321–329
Guo X, Huang J, Lu Y, Shan G, Li Q (2016a) The influence of flue gas desulphurization gypsum additive on characteristics and evolution of humic substance during co-composting of dairy manure and sugarcane pressmud. Bioresour Technol 219:169–174
Guo X, Lu Y, Li Q (2016b) Effect of adding flue gas desulphurization gypsum on the transformation and fate of nitrogen during composting. Compost Sci Util 24(4):230–237
He X, Xi B, Wei Z, Guo X, Li M, An D, Liu H (2011a) Spectroscopic characterization of water extractable organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. Chemosphere 82(4):541–548
He XS, Xi BD, Wei ZM, Jiang YH, Geng CM, Yang Y, Liu HL (2011b) Physicochemical and spectroscopic characteristics of dissolved organic matter extracted from municipal solid waste (MSW) and their influence on the landfill biological stability. Bioresour Technol 102(3):2322–2327
Jones DL, Simfukwe P, Hill PW, Mills RT, Emmett BA (2014) Evaluation of dissolved organic carbon as a soil quality indicator in national monitoring schemes. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090882
Jones MN, Bryan ND (1998) Colloidal properties of humic substances. J Colloid Interface Sci 78(1):1–48
Jouraiphy A, Amir S, El Gharous M, Revel JC, Hafidi M (2005) Chemical and spectroscopic analysis of organic matter transformation during composting of sewage sludge and green plant waste. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 56(2):101–108
Jouraiphy A, Amir S, Winterton P, El Gharous M, Revel JC, Hafidi M (2008) Structural study of the fulvic fraction during composting of activated sludge–plant matter: elemental analysis, FTIR and 13 C NMR. Bioresour Technol 99(5):1066–1072
Jurado MM, Suárez-Estrella F, López MJ, Vargas-García MC, López-González JA, Moreno J (2015) Enhanced turnover of organic matter fractions by microbial stimulation during lignocellulosic waste composting. Bioresour Technol 186:15–24
Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park JH, Michalzik B, Matzner E (2000) Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: a review. Soil Sci 165(4):277–304
Liang Y, Lu Y, Li Q (2016) Comparative study on the performances and bacterial diversity from anaerobic digestion and aerobic composting in treating solid organic wastes. Waste Biomass Valor. doi:10.1007/s12649-016-9572-7
Liu Z, Huang S, Sun G, Xu Z, Xu M (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in the Dongjiang River, China. Microbiol Res 166(5):337–345
López-González JA, López MJ, Vargas-García MC, Suárez-Estrella F, Jurado M, Moreno J (2013) Tracking organic matter and microbiota dynamics during the stages of lignocellulosic waste composting. Bioresour Technol 146:574–584
López-González JA, del Carmen V-GM, López MJ, Suárez-Estrella F, Jurado M, Moreno J (2014) Enzymatic characterization of microbial isolates from lignocellulose waste composting: chronological evolution. J Environ Manag 145:137–146
Lv B, Xing M, Yang J, Qi W, Lu Y (2013) Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of water extractable organic matter during vermicomposting of cattle dung. Bioresour Technol 132:320–326
Malik A, Gleixner G (2013) Importance of microbial soil organic matter processing in dissolved organic carbon production. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 86(1):139–148
Ni JZ, Xu JM, Xie ZM (2001) The size and characterization of biologically active organic carbon pool in soils. Plant Nutr Fert Sci 7(1):56–63
Parsi Z, Hartog N, Gorecki T, Poerschmann J (2007) Analytical pyrolysis as a tool for the characterization of natural organic matter—a comparison of different approaches. J Anal Appl Pyrol 79(1):9–15
Pognani M, Barrena R, Font X, Adani F, Scaglia B, Sánchez A (2011) Evolution of organic matter in a full-scale composting plant for the treatment of sewage sludge and biowaste by respiration techniques and pyrolysis-GC/MS. Bioresour Technol 102(6):4536–4543
Pollastri S, Gualtieri AF, Gualtieri ML, Hanuskova M, Cavallo A, Gaudino G (2014) The zeta potential of mineral fibres. J Hazard Mater 276:469–479
Ramírez-Godínez J, Beltrán-Hernández I, Álvarez-Hernández A, Coronel-Olivares C, Contreras-López E, Quezada-Cruz M, Vázquez-Rodríguez G (2015) Evaluation of natural materials as exogenous carbon sources for biological treatment of low carbon-to-nitrogen wastewater. Biomed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2015/754785
Romero E, Plaza C, Senesi N, Nogales R, Polo A (2007) Humic acid-like fractions in raw and vermicomposted winery and distillery wastes. Geoderma 139(3):397–406
Ros M, Garcia C, Hernández T (2006) A full-scale study of treatment of pig slurry by composting: kinetic changes in chemical and microbial properties. Waste Manag 26(10):1108–1118
Sahlström L (2003) A review of survival of pathogenic bacteria in organic waste used in biogas plants. Bioresour Technol 87(2):161–166
Said-Pullicino D, Erriquens FG, Gigliotti G (2007) Changes in the chemical characteristics of water-extractable organic matter during composting and their influence on compost stability and maturity. Bioresour Technol 98(9):1822–1831
Schulten HR, Gleixner G (1999) Analytical pyrolysis of humic substances and dissolved organic matter in aquatic systems: structure and origin. Water Res 33(11):2489–2498
Senesi N, Miano TM, Brunetti G (1996) Humic-like substances in organic amendments and effects on native soil humic substances. In: Piccolo A (ed) Humic substances in terrestrial ecosystems. Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam, pp 531–593
Tandy S, Healey JR, Nason MA, Williamson JC, Jones DL, Thain SC (2010) FT-IR as an alternative method for measuring chemical properties during composting. Bioresour Technol 101(14):5431–5436
Traversa A, Loffredo E, Gattullo CE, Senesi N (2010) Water-extractable organic matter of different composts: a comparative study of properties and allelochemical effects on horticultural plants. Geoderma 156(3):287–292
Vaca-Paulin R, Esteller-Alberich MV, Lugo-De La Fuente J, Zavaleta-Mancera HA (2006) Effect of sewage sludge or compost on the sorption and distribution of copper and cadmium in soil. Waste Manag 26(1):71–81
Veeken A, Nierop K, de Wilde V, Hamelers B (2000) Characterisation of NaOH-extracted humic acids during composting of a biowaste. Bioresour Technol 72(1):33–41
Wang K, Li W, Gong X, Li Y, Wu C, Ren N (2013) Spectral study of dissolved organic matter in biosolid during the composting process using inorganic bulking agent: UV–vis, GPC, FTIR and EEM. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:617–623
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37(20):4702–4708
Yu H, Huang GH, An CJ, Wei J (2011) Combined effects of DOM extracted from site soil/compost and biosurfactant on the sorption and desorption of PAHs in a soil–water system. J Hazard Mater 190(1):883–890
Yuan Y, Tao Y, Zhou S, Yuan T, Lu Q, He J (2012) Electron transfer capacity as a rapid and simple maturity index for compost. Bioresour Technol 116:428–434
Zbytniewski R, Buszewski B (2005) Characterization of natural organic matter (NOM) derived from sewage sludge compost. Part 1: chemical and spectroscopic properties. Bioresour Technol 96(4):471–478
Zbytniewski R, Kosobucki P, Kowalkowski T, Buszewski B (2002) The comparison study of compost and natural organic matter samples. Environ Sci Pollut Res 9(1):68–74
Zhou LX, Wong JWC (2001) Effect of dissolved organic matter from sludge and sludge compost on soil copper sorption. J Environ Qual 30(3):878–883
Zhou Y, Selvam A, Wong JWC (2014) Evaluation of humic substances during co-composting of food waste, sawdust and Chinese medicinal herbal residues. Bioresour Technol 168:229–234
Zhou Y, Selvam A, Wong JWC (2016) Effect of Chinese medicinal herbal residues on microbial community succession and anti-pathogenic properties during co-composting with food waste. Bioresour Technol 217:190–199
Zmora-Nahum S, Markovitch O, Tarchitzky J, Chen Y (2005) Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) as a parameter of compost maturity. Soil Biol Biochem 37(11):2109–2116
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the Fangchenggang Science and Technology Program (14043001). The authors wish to acknowledge the scientific input of other members in our laboratory. The anonymous reviewers were also acknowledged for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 174 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Lu, Y., Guo, X. et al. Properties and evolution of dissolved organic matter during co-composting of dairy manure and Chinese herbal residues. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 8629–8636 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8540-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8540-5