Abstract
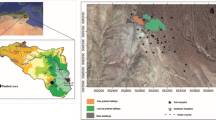
The anthropogenic effects of Antarctic refuge buildings and research stations on the surrounding soils are scarcely investigated, especially when the structures are small-sized, and sporadically used or visited. The Coppermine Peninsula (Robert Island, South Shetland Islands archipelago) possesses one of the richest flora in Antarctica, being classified as an Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA). There, a small refuge (Luis Risopatrón) has been seasonally occupied for scientific purposes since 1957, although no studies on the anthropic disturbances in the surroundings soils are reported. The aim of this study was the determination of the potentially toxic metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, V, and Zn) mass fractions in surface soils (n = 40) collected at the surroundings of the Luis Risopatrón refuge. Enrichment factors (EF) and geoaccumulation index (I geo) were also calculated, using Zr as the reference element, in order to evaluate the anthropogenic impacts of these small buildings in the studied area. The main contaminants were Pb and Zn, which presented EF and I geo values ranging from 1.0 to 18.3 and from −1.8 to 3.5. The mass fractions of these elements determined after an aqua regia extraction varied from 5.4 to 102 mg kg−1 Pb and from 43 to 210 mg kg−1 Zn. These results highlight that a small refuge can show environmental disturbance from low to moderate, with few hotspots with heavily contaminated soils. Environmental monitoring strategy for similar refuges anywhere in Antarctica is recommended.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, I. A., & Sadiq, M. (1993). Metal concentrations in Antarctic sediment samples collected during the Trans-Antarctica 1990 expedition. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 26(9), 523–527.
Amaro, E., Padeiro, A., Mão de Ferro, A., Mota, A. M., Leppe, M., Verkulich, S., Hughes, K. A., Peter, H.-U., & Canário, J. (2015). Assessing trace element contamination in Fildes Peninsula (King George Island) and Ardley Island, Antarctic. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 97(1–2), 523–527.
Bargagli, R. (2005). Antarctic ecosystems: environmental contamination, climate change, and human impact (Vol. 175, p. 395). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Braun, C., Mustafa, O., Nordt, A., Pfeiffer, S., & Peter, H.-U. (2012). Environmental monitoring and management proposals for the Fildes Region, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Research, 31, 1–18.
Cabrerizo, A., Tejedo, P., Dachs, J., & Benayas, J. (2016). Anthropogenic and biogenic hydrocarbons in soils and vegetation from the South Shetland Islands (Antarctica). Science of The Total Environment, in press. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.240.
Campbell, I. B., & Claridge, G. G. C. (1987). Antarctica: soils, weathering processes and environment (p. 16. 367 p). Elsevier: Developments in Soil Science.
Celis, J. E., Barra, R., Espejo, W., González-Acuña, D., & Jara, S. (2015). Trace element concentrations in biotic matrices of Gentoo penguins (Pygoscelis Papua) and coastal soils from different locations of the Antarctic Peninsula. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226(1), 2266.
Chandrasekaran, A., Ravisankar, R., Harikrishnan, N., Satapathy, K. K., Prasad, M. V. R., & Kanagasabapathy, K. V. (2015). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metal concentration in soils of Yelagiri Hills, Tamilnadu, India—spectroscopical approach. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 137, 589–600.
Colabuono, F. I., Taniguchi, S., Cipro, C. V. Z., Silva, J., Bícego, M. C., & Montone, R. C. (2015). Persistent organic pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in mosses after fire at the Brazilian Antarctic Station. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 93(1–2), 266–269.
CONAMA. (2009). Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. RESOLUÇÃO N° 420, DE 28 DE DEZEMBRO DE 2009, alterada pela CONAMA no 460/2013. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=620. Accesssed on December 2016.
Crockett, A. B. (1998). Background levels of metals in soils, McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 50, 289–296.
De Moreno, J. E. A., Gerpe, M. S., Moreno, V. J., & Vodopivez, C. (1997). Heavy metals in Antarctic organisms. Polar Biology, 17(2), 131–140.
Dickhut, R. M., Cincinelli, A., Cochran, M., & Kylin, H. (2012). Aerosol-mediated transport and deposition of brominated diphenyl ethers to Antarctica. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(6), 3135–3140.
Ghrefat, H. A., Abu-Rukah, Y., & Rosen, M. A. (2011). Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factor for assessing metal contamination in the sediments of Kafrain Dam, Jordan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 178(1–4), 95–109.
Giller, K. E., Witter, E., & Mcgrath, S. P. (1998). Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30(10–11), 1389–1414.
Guerra, M. B. B., Amarasiriwardena, D., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Pereira, C. D., Spielmann, A. A., Nóbrega, J. A., & Pereira-Filho, E. R. (2011a). Biomonitoring of lead in Antarctic lichens using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 26(11), 2238–2246.
Guerra, M. B. B., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Michel, R. F. M., Rosa, P. F., & Pereira-Filho, E. R. (2011b). Chemometric and analytical strategies for the study of soils from maritime Antarctica. Brazilian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 3(9), 148–157.
Guerra, M. B. B., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Rosa, P. F., Simas, F. N. B., Pereira, T. T. C., & Pereira-Filho, E. R. (2011c). Heavy metals contamination in century-old manmade Technosols of Hope Bay, Antarctic Peninsula. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 222(1–4), 91–102.
Guerra, R., Fetter, E., Ceschim, L. M. M., & Martins, C. C. (2011d). Trace metals in sediment cores from Deception and Penguin Islands (South Shetland Islands, Antarctica). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(11), 2571–2575.
Guerra, M. B. B., Rosa, P. F., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Michel, R. F. M., Almeida, I. C., & Pereira-Filho, E. R. (2012). Chemometric tools in chemical fractionation data of soil samples from five Antarctic research stations. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 23(7), 1388–1394.
Guerra, M. B. B., Lima Neto, E., Prianti, M. T. A., Pereira-Filho, E. R., & Schaefer, C. E. G. R. (2013). Post-fire study of the Brazilian Scientific Antarctic Station: toxic element contamination and potential mobility on the surrounding environment. Microchemical Journal, 110, 21–27.
Hasan, A. B., Kabir, S., Reza, A. H. M. S., Zaman, M. N., Ahsan, A., & Rashid, M. (2013). Enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index of trace metals in sediments of the ship breaking area of Sitakund Upazilla (Bhatiary-Kumira), Chittagong, Bangladesh. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 125, 130–137.
Jerez, S., Motas, M., Benzal, J., Diaz, J., & Barbosa, A. (2013). Monitoring trace elements in Antarctic penguin chicks from South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 69(1–2), 67–75.
Kizilkaya, R., Aşkin, T., Bayrakli, B., & Sağlam, M. (2004). Microbiological characteristics of soils contaminated with heavy metals. European Journal of Soil Biology, 40(2), 95–102.
Lee, P. K., Touray, J. C., Baillif, P., & Ildefonse, J. P. (1997). Heavy metal contamination of settling particles in a retention pond along the A-71 motorway in Sologne, France. The Science of the Total Environment, 201, 1–15.
Machado, A., Lima, E. F., Chemale, F., Jr., Morata, D., Oteiza, O., Almeida, D. P. M., Figueiredo, A. M. G., Alexandre, F. M., & Urrutia, J. L. (2005). Geochemistry constraints of Mesozoic-Cenozoic calc-alkaline magmatism in the South Shetland arc, Antarctica. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 18(3–4), 407–425.
Malandrino, M., Abollino, O., Buoso, S., Casalino, C. E., Gasparon, M., Giacomino, A., Gioia, C. L., & Mentasti, E. (2009). Geochemical characterisation of Antarctic soils and lacustrine sediments from Terra Nova Bay. Microchemical Journal, 92(1), 21–31.
Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan. (2003). Antarctic Specially Protected Areas. Environmetal Protection of Antarctica. http://www.env.go.jp/nature/nankyoku/kankyohogo_en/kankyo_en/hogo/kokunai/fuzokusho/map/. Accessed on December 2016.
Müller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins - Veränderungen seit 1971. Umschau, 79(24), 778–783.
Poblet, A., Andrade, S., Scagliola, M., Vodopivez, C., Curtosi, A., Pucci, A., & Marcovecchio, J. (1997). The use of epilithic Antarctic lichens (Usnea aurantiacoatra and U. antarctica) to determine deposition patterns of heavy metals in the Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Science of the Total Environment, 207(2–3), 187–194.
Préndez, M., & Carrasco, M. A. (2003). Elemental composition of surface waters in the Antarctic Peninsula and interactions with the environment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 25(3), 347–363.
Sandrin, T. R., & Maier, R. M. (2003). Impact of metals on the biodegradation of organic pollutants. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111(8), 1093–1101.
Santos, I. R., Silva-Filho, E. V., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Albuquerque-Filho, M. R., & Campos, L. S. (2005). Heavy metal contamination in coastal sediments and soils near the Brazilian Antarctic Station, King George Island. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(2), 185–194.
Sheppard, D. S., Claridge, G. G. C., & Campbell, I. B. (2000). Metal contamination of soils at Scott Base, Antarctica. Applied Geochemistry, 15(4), 513–530.
Simas, F. N. B., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Melo, V. F., Guerra, M. B. B., Saunders, M., & Gilkes, R. J. (2006). Clay-sized minerals in permafrost-affected soils (Cryosols) from King George Island, Antarctica. Clays and Clay Minerals, 54(6), 723–738.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Szopińska, M., Namieśnik, J., & Polkowska, Ż. (2016). How important is research on pollution levels in Antarctica? Historical approach, difficulties and current trends. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 239, 79–156.
Tin, T., Fleming, Z. L., Hughes, K. A., Ainley, D. G., Convey, P., Moreno, C. A., Pfeiffer, S., Scott, J., & Snape, I. (2009). Impacts of local human activities on the Antarctic environment. Antarctic Science, 21(1), 3–33.
Torres-Mellado, G. A., Jaña, R., & Casanova-Katny, M. A. (2011). Antarctic hairgrass expansion in the South Shetland archipelago and Antarctic Peninsula revisited. Polar Biology, 34(11), 1679–1688.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192.
Ward, P. (2001). Antarctica Fire History. http://www.coolantarctica.com/Antarctica_fact_file/antarctica_fire_history.php. Accessed on December 2016.
Webster, J., Webster, K., Nelson, P., & Waterhouse, E. (2003). The behaviour of residual contaminants at a former station site, Antarctica. Environmental Pollution, 123(2), 163–179.
Wuana, R. A., & Okieimen, F. E. (2011). Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecology, 2011, 1–20.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq) for financing this research, the Brazilian Navy for the logistic support during the Antarctic expeditions, and the Universidade Federal de Viçosa for technical support. This is a contribution of the Terrantar Laboratory, part of the Brazilian National Institute of Cryospheric Science and Technology (INCT da Criosfera). We also thank the Chilean Antarctic Institute (INACH) for the logistical support to the field activities and National Science Foundation (NSF MRI Award 1429544) for financial support. We also express our gratitude to Dr. Brianna Mount for language improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Lima Neto, E., Guerra, M.B.B., Thomazini, A. et al. Soil Contamination by Toxic Metals Near an Antarctic Refuge in Robert Island, Maritime Antarctica: A Monitoring Strategy. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 66 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3245-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3245-4