Abstract
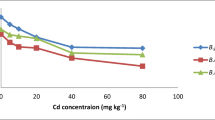
Cadmium and lead are some of several heavy metals that present a great concern for the environment because even in non-toxic concentrations for plants, their toxicity can affect animals and humans. Three different concentrations of sodium chloride solution were employed as pretreatment agents in order to increase the bioavailability of heavy metals and to analyze the interaction between heavy metals under saline soil conditions. The biomass production presented a remarkable increase for plants grown in soil pretreated with a 0.3 M NaCl solution, whereas the growth curve response of Arabidopsis thaliana in all samples showed a clear alteration compared with the control system. The conclusion was reached that saline solution pretreatment used in soil containing heavy metals produced an apparent stimulation of plant growth. In regards to the uptake of heavy metals by plants, lead and especially cadmium were the most favored metals by NaCl application.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta, J. A., Jansen, B., Kalbitz, K., Faz, K., & Martínez–Martínez, S. (2011). Salinity increases mobility of heavy metals in soils. Chemosphere, 85(8), 1318–1324.
Arthur, E. L., Rice, P. J., Rice, P. J., Anderson, T. A., Baladi, S. M., Henderson, K. L. D., & Coats, J. R. (2008). Phytoremediation—an overview. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 24(2), 109–122.
ATSDR. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2015) The 2015 Priority List of Hazardous Substances. ATSDR Publications. Available on http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/ (accessed on March 2016).
Belluck, D. A., Benjamin, S. L., & David, S. (2006). Why remediate? In J. L. Morel, G. Echevarria, & N. Gonchavora (Eds.), Phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils (pp. 1–23). Netherlands: Springer.
Boyes, D. C., Zayed, A. M., Ascenzi, R., McCaskill, A. J., Hoffman, N. E., Davis, K. R., & Görlach, J. (2001). Growth stage–based phenotypic analysis of Arabidopsis a model for high throughput functional genomics in plants. The Plant Cell, 13, 1499–1510.
Brookins, DG. (1988). Eh–pH Diagrams for Geochemistry. Springer–Verlag.
Carbonell–Barrachina, A. A., Burló–Carbonell, F., & Mataix–Beneyto, J. (1997). Arsenic uptake, distribution, and accumulation in bean plants: effect of arsenite and salinity on plant growth and yield. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 20(10), 1419–1430.
Cunningham, S. D., & Berti, W. R. (1993). Remediation of contaminated soils with green plants: an overview. Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology–Plant, 29(4), 207–212.
Cunningham, S. D., & Ow, D. W. (1996). Promises and prospects of phytoremediation. Plant Physiology, 110, 715–719.
Cunningham, S. D., Berti, W. R., & Huang, J. W. (1995). Phytoremediation of contaminated soils. Trends in Biotechnology, 13(9), 393–397.
Dar, S. R., Thomas, T., Dagar, J. C., Singh, D., Chauhan, M. K., & Kumar, A. (2011). Phytoavailability of zinc and cadmium as affected by salinity and zinc in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown on cadmium polluted soil. Libyan Agriculture Research Center Journal International, 2(4), 195–199.
Das, P., Samantaray, S., & Rout, G. R. (1997). Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environmental Pollution, 98(1), 29–36.
Davis, J.G., Waskom, R.M., Bauder, T.A. (2013). Managing sodic soils, Fact Sheet–Crop Series. Colorado State University Extension Website. http://extension.colostate.edu/docs/pubs/crops/00504.pdf. Accessed 15 January 2015.
EEA. (2014). Progress in management of contaminated sites. European Environment Agency (EEA) Website. http://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/progress-in-management-of-contaminated-sites/progress-in-management-of-contaminated-1. Accessed 10 November 2014.
Förstner, U. (1979). Metal transfer between solid and aqueous phases. In U. Förstner & G. T. Wittmann (Eds.), Metal pollution in the aquatic environment (pp. 197–270). Berlin: Spriger–Verlag.
Hatje, V., Payne, T. E., Hill, D. M., McOrist, G., Birch, G. F., & Szymczak, R. (2003). Kinetics of trace elements uptake and release by particles in estuarine waters: effects of pH, salinity, and particle loading. Environmental International, 29, 619–629.
Hattori, H., Kuniyasu, K., Chiba, K., & Chino, M. (2006). Effect of chloride application and low soil pH on cadmium uptake from soil by plants. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 52(1), 89–94.
Hermann, R., & Neumann–Mahlkau, P. (1985). The mobility of zinc, cadmium, copper, lead, iron and arsenic in ground water as a function of redox potential and pH. The Science of the Total Environment, 43, 1–12.
Huang, J. W., Chen, J., Berti, W. R., & Cunningham, S. D. (1997). Phytoremediation of lead–contaminated soils: role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction. Environmental Science and Technology, 31(3), 800–805.
Husson, O. (2013). Redox potential (Eh) and pH as drivers of soil/plant/microorganism systems: a trans disciplinary overview pointing to integrative opportunities for agronomy. Plant and Soil, 362(1), 389–417.
Jørgensen, S. E. (1993). Removal of heavy metals from compost and soil by ecotechnological methods. Ecological Engineering, 2, 89–100.
Kabata–Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press–Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, Florida.
Kayser, A., Wenger, K., Keller, A., Attinger, W., Felix, H. R., Gupta, S. K., & Schulin, R. (2000). Enhancement of phytoextraction of Zn, Cd, and Cu from calcareous soil: the use of NTA and sulfur amendments. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(9), 1778–1783.
Keunen, E., Truyens, S., Bruckers, L., Remans, T., Vangronsveld, J., & Cuypers, A. (2011). Survival of Cd-exposed Arabidopsis thaliana are these plants reproductively challenged. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 49, 1084–1091.
Khoshgoftar, A. H., Shariatmadari, H., Karimian, N., Kalbasi, M., van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M., & Parker, D. R. (2004). Salinity and zinc application effects in phytoavailability of cadmium and zinc. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 68, 1885–1889.
Khoshgoftarmanesh, A. H., Shariatmadari, H., Karimian, N., Kalbasi, M., & van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M. (2006). Cadmium and zinc in saline solutions and their concentrations in wheat. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 70, 582–589.
Koopmans, G. F., Römkens, P. F. A. M., Fokkema, M. J., Song, J., Luo, Y. M., Japenga, J., & Zhao, F. J. (2008). Feasibility of phytoextraction to remediate cadmium and zinc contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 156, 905–914.
Mane, A. V., Saratale, G. D., Karadge, B. A., & Samant, J. S. (2011). Studies on the effects of salinity on growth, polyphenol content and photosynthetic response in Vetiveria zizanioides (L) Nash. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture, 23(1), 59–70.
Manousaki, E., & Kalogerakis, N. (2009). Phytoextraction of Pb and Cd by the Mediterranean saltbush (Atriplex halimus L) metal uptake in relation to salinity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 16(7), 844–855.
Manousaki, E., Kadukova, J., Papadantonakis, N., & Kalogerakis, N. (2008). Phytoextraction and phytoexcretion of Cd by the leaves of Tamarix smyrnensis growing on contaminated non-saline and saline soils. Environmental Research, 106, 326–332.
McGrath, S. P., Lombi, E., Gray, C. W., Caille, N., Dunham, S. J., & Zhao, F. J. (2006). Field evaluation of Cd and Zn phytoextraction potential by the hyperaccumulators Thlaspi caerulescens and Arabidopsis halleri. Environmental Pollution, 141, 115–125.
McLaughlin, M. J., Palmer, L. T., Tiller, K. G., Beech, T. A., & Smart, M. K. (1994). Increased soil salinity causes elevated cadmium concentrations in field-grown potato tubers. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23(5), 1013–1018.
Moradi, S., Yosefi, R., & Ghaderi, O. (2013). Bioconcentration factor and relative growth rate on Azolla (Azolla caroliniana) in arsenic and salinity stress conditions. International Journal of Agronomy and Plant Production, 4(10), 2617–2623.
Mudgal, V., Madaan, N., & Mudgal, A. (2010). Heavy metals in plants: phytoremediation: plants used to remediate heavy metal pollution. Agriculture and Biology Journal of North America, 1(1), 40–46.
Novo, L. A. B., Covelo, E. F., & González, L. (2014a). Effect of salinity on zinc uptake by Brassica juncea. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 16(7–8), 704–718.
Novo, L. A. B., Manousaki, E., Kalogerakis, N., & González, L. (2014b). The effect of cadmium and salinity on germination and early growth of Brassica juncea (L) var. juncea. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 22(12a), 3709–3717.
Pedron, F., Petruzzelli, G., Barbafieri, M., & Tassi, E. (2009). Strategies to use phytoextraction in very acidic soil contaminated by heavy metals. Chemosphere, 75, 808–814.
Raskin, I., Nanda, P. B. A. K., Dushenkov, S., & Salt, D. E. (1994). Bioconcentration of heavy metals by plants. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 5, 285–290.
Salt, D. E., Blaylock, M., Kumar, N. P. B. A., Dushenkov, V., Ensley, B. E., Chet, I., & Raskin, I. (1995). Phytoremediation: A novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology, 13, 468–474.
Sari, I., & Din, Z. B. (2012). Effects of salinity on the uptake of lead and cadmium by two mangrove species Rhizophora apiculata Bl. and Avicennia alba Bl. Chemistry and Ecology, 28(4), 365–374.
Smolders, E., & McLaughlin, M. J. (1996). Effect of Cl on Cd uptake by Swiss chard in nutrient solutions. Plant and Soils, 179, 57–64.
Sommers, L., Lambrechts, R. M., McLaughlin, M. J., & Tiller, K. G. (1987). Effects of soil properties on accumulation of trace elements by crops. In A. L. Page, T. G. Logan, & J. A. Ryan (Eds.), Land application of sludge (pp. 5–23). Chelsea: Lewis Publisher.
Sposito, G. (2008). The chemistry of soils. New York: Oxford University Press.
Alberta Agriculture and Food (AF) Staff (2008) Nutrient Management: Planning Guide, Module 3: Field and Soil Evaluation. Alberta Agriculture and Food Department, Canada. http://www1.agric.gov.ab.ca/$department/deptdocs.nsf/all/epw11920/$FILE/nutrient-management-planning-guide.pdf. Accessed 27 July 2015.
Takeda, A., Kimura, K., & Yamasaki, S. (2004). Analysis of 57 elements in Japanese soils, with special reference to soil group and agricultural use. Geoderma, 119, 291–307.
Thomas, G. W. (1996). Soil pH and soil acidity. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis part 3: chemical methods. USA: Soil Science of America.
US EPA. (2014). Superfund: National Priorities List (NPL). United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) Webpage. http://www2.epa.gov/superfund/superfund-national-priorities-list-npl. Accessed November 2015.
Vazquez, M. D., Lopez, J., & Carballeira, A. (1999). Uptake of heavy metals to the extracellular and intracellular compartments in three species of aquatic bryophyte. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 44, 12–24.
Wasay, S. A., Barrington, S. F., & Tokunaga, S. (1998). Remediation of soils polluted by heavy metals using salts of organic acids and chelating agents. Environmental Technology, 19(4), 369–379.
Weggler, K., McLaughlin, M. J., & Graham, R. D. (2004). Effect of chloride in soil solution on the plant availability of biosolid–borne cadmium. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33(2), 496–504.
Zhao, F. J., Lombi, E., & McGrath, S. P. (2003). Assessing the potential for zinc and cadmium phytoremediation with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant and Soil, 249, 37–43.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the Technical Team (C. Maruo and N. Chiba) from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering of Tohoku University for its invaluable collaboration during the development of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
León-Romero, M.A., Soto-Ríos, P.C., Fujibayashi, M. et al. Impact of NaCl Solution Pretreatment on Plant Growth and the Uptake of Multi-heavy Metal by the Model Plant Arabidopsis thaliana . Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3241-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3241-8