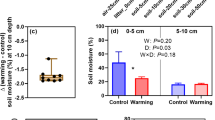
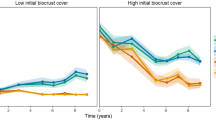
Abstract
Mountain soils stock large quantities of carbon as particulate organic matter that may be highly vulnerable to climate change. To explore potential shifts in soil organic matter (SOM) form and stability under climate change (warming and reduced precipitations), we studied the dynamics of SOM pools of a mountain grassland in the Swiss Jura as part of a climate manipulation experiment. The climate manipulation (elevational soil transplantation) was set up in October 2009 and simulated two realistic climate change scenarios. After 4 years of manipulation, we performed SOM physical fractionation to extract SOM fractions corresponding to specific turnover rates, in winter and in summer. Soil organic matter fraction chemistry was studied with ultraviolet, 3D fluorescence, and mid-infrared spectroscopies. The most labile SOM fractions showed high intra-annual dynamics (amounts and chemistry) mediated via the seasonal changes of fresh plant debris inputs and confirming their high contribution to the microbial loop. Our climate change manipulation modified the chemical differences between free and intra-aggregate organic matter, suggesting a modification of soil macro-aggregates dynamics. Interestingly, the 4-year climate manipulation affected directly the SOM dynamics, with a decrease in organic C bulk soil content, resulting from significant C-losses in the mineral-associated SOM fraction (MAOM), the most stable form of SOM. This SOC decrease was associated with a decrease in clay content, above- and belowground plants biomass, soil microbial biomass and activity. The combination of these climate changes effects on the plant–soil system could have led to increase C-losses from the MAOM fraction through clay-SOM washing out and DOC leaching in this subalpine grassland.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baisden WT, Amundson R, Cook AC, Brenner DL (2002) Turnover and storage of C and N in five density fractions from California annual grassland surface soils. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 16:64–1–64–16. doi:10.1029/2001GB001822
Baldock JA, Oades JM, Nelson PN, Skene TM, Golchin A, Clarke P (2007) Assessing the extent of decomposition of natural organic materials using solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Aust J Soil Res 35:1061–1083
Beleites C, Sergo V (2012) HyperSpec: a package to handle hyperspectral data sets in R. R package v. 0.98-20110927. http://hyperspec.r-forge.r-project.org
Bloemberg TG, Gerretzen J, Wouters HJP, Gloerich J, van Dael M, Wessels HJCT, van den Heuvel LP, Eilers PHC, Buydens LMC, Wehrens R (2010) Improved parametric time warping for proteomics. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 104(1):65–74. doi:10.1016/j.chemolab.2010.04.008
Boddy E, Hill PW, Farrar J, Jones DL (2007) Fast turnover of low molecular weight components of the dissolved organic carbon pool of temperate grassland field soils. Soil Biol Biochem 39:827–835
Budge K, Leifeld J, Hiltbrunner E, Fuhrer J (2011) Alpine grassland soils contain large proportion of labile carbon but indicate long turnover times. Biogeosciences 8:1911–1923. doi:10.5194/bg-8-1911-2011
Burns RG, DeForest JL, Marxsen J, Sinsabaugh RL, Stromberger ME, Wallenstein MD, Weintraub MN, Zoppini A (2013) Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol Biochem 58:216–234. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.11.009
C2SM (2011) Swiss Climate Change Scenarios CH2011. doi:10.3929/ethz-a-006720559
Carvalhais N, Forkel M, Khomik M, Bellarby J, Jung M, Migliavacca M, Mingquan M, Saatchi S, Santoro M, Thurner M, Weber U, Ahrens B, Beer C, Cescatti A, Randerson JT, Reichstein M (2014) Climate in terrestrial ecosystems. Nature 514:213–217. doi:10.1038/nature13731
Cécillon L, Mello NA, Danieli S, Brun JJ (2010) Soil macroaggregate dynamics in a mountain spatial climate gradient. Biogeochemistry 97:31–43. doi:10.1007/s10533-009-9341-9
Cécillon L, Certini G, Lange H, Forte C, Strand LT (2012) Spectral fingerprinting of soil organic matter composition. Org Geochem 46:127–136. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2012.02.006
Conant RT, Ryan MG, Ågren GI, Birge HE, Davidson EA, Eliasson PE, Evans SE, Frey SD, Giardina CP, Hopkins FM, Hyvönen R, Kirschbaum MUF, Lavallee JM, Leifeld J, Parton WJ, Megan Steinweg J, Wallenstein MD, Martin Wetterstedt JÅ, Bradford MA (2011) Temperature and soil organic matter decomposition rates: synthesis of current knowledge and a way forward. Glob Change Biol 17:3392–3404. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02496.x
Cotrufo MF, Wallenstein MD, Boot CM, Denef K, Paul E (2013) The microbial efficiency-matrix stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob Change Biol 19:988–995. doi:10.1111/gcb.12113
Davidson EA, Janssens IA (2006) Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change. Nature 440:165–173. doi:10.1038/nature04514
Eglin T, Ciais P, Piao SL, Barre P, Bellassen V, Cadule P, Chenu C, Gasser T, Koven C, Reichstein M, Smith P (2010) Historical and future perspectives of global soil carbon response to climate and land-use changes. Tellus 62B:700–718. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0889.2010.00499.x
Embacher A, Zsolnay A, Gattinger A, Munch JC (2007) The dynamics of water extractable organic matter (WEOM) in common arable topsoils: I. Quantity, quality and function over a three year period. Geoderma 139:11–22. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.12.002
Erktan A, Cécillon L, Graf F, Roumet C, Legout C, Rey F (2016) Increase in soil aggregate stability along a Mediterranean successional gradient in severely eroded gully bed ecosystems: combined effects of soil, root traits and plant community characteristics. Plant Soil 398:121–137
Frei C, Schöll R, Fukutome S, Schmidli J, Vidale PL (2006) Future change of precipitation extremes in Europe: intercomparison of scenarios from regional climate models. J Geophys Res 111:D06105. doi:10.1029/2005JD005965
Gavazov KS (2013) Subalpine pasture-woodlands in a changing climate: the role of land use type in ecosystem resistance to simulated climate change. Thesis EPFL 5989. Lausanne, Switzerland. doi:10.5075/epfl-thesis-5989
Gavazov K, Peringer A, Buttler A, Gillet F, Spiegelberger T (2013) Dynamics of forage production in pasture-woodlands of the Swiss Jura Mountains under projected climate change scenarios. Ecol Soc 18, art38. doi:10.5751/ES-04974-180138
Gavazov K, Mills R, Spiegelberger T, Lenglet J, Buttler A (2014a) Biotic and abiotic constraints on the decomposition of Fagus sylvatica leaf litter along an altitudinal gradient in contrasting land-use types. Ecosystems 17:1326–1337. doi:10.1007/s10021-014-9798-9
Gavazov K, Spiegelberger T, Buttler A (2014b) Transplantation of subalpine wood-pasture turfs along a natural climatic gradient reveals lower resistance of unwooded pastures to climate change compared to wooded ones. Oecologia 174:1425–1435. doi:10.1007/s00442-013-2839-9
Gobiet A, Kotlarski S, Beniston M, Heinrich G, Rajczak J, Stoffel M (2014) 21st century climate change in the European Alps: a review. Sci Total Environ 493:1138–1151. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.050
Golchin A, Oades JM, Skjemstad JO, Clarke P (1994) Study of free and occluded particulate organic matter in soils by solid state 13CCP/MAS NMR spectroscopy and scanning electron mi- croscopy. Aust J Soil Res 32:285–309
Gregorich EG, Beare MH, McKim UF, Skjemstad JO (2006) Chemical and biological characteristics of physically uncomplexed organic matter. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:975–985. doi:10.2136/sssaj2005.0116
Groffman PM, Driscoll CT, Fahey TJ et al (2001) Colder soils in a warmer world: a snow manipulation study in a northern hardwood forest ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 56:135–150
Gyssels G, Poesen J, Bochet E, Li Y (2005) Impact of plant roots on the resistance of soils to erosion by water: a review. Prog Phys Geogr 29:189–217. doi:10.1191/0309133305pp443ra
Helfrich M, Ludwig B, Buurman P, Flessa H (2006) Effect of land use on the composition of soil organic matter in density and aggregate fractions as revealed by solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Geoderma 136:331–341. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.03.048
Hitz C, Egli M, Fitze P (2001) Below-ground and above-ground production of vegetational organic matter along a climosequence in alpine grasslands. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 164:389–397
IUSS Working Group WRB (2007) World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2006, first update 2007. World Soil Resources Reports No. 103. FAO, Rome., n.d
John B, Yamashita T, Ludwig B, Flessa H (2005) Storage of organic carbon in aggregate and density fractions of silty soils under different types of land use. Geoderma 128:63–79
Kaiser K, Guggenberger G, Haumaier L, Zech W (2001) Seasonal variations in the chemical composition of dissolved organic matter in organic forest floor layer leachates of old-growth Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) and European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) stands in northeastern Bavaria, Germany. Biogeochemistry 55(2):103–143
Kalbitz K, Schmerwitz J, Schwesig D, Matzner E (2003) Biodegradation of soil-derived dissolved organic matter as related to its properties. Geoderma 113:273–291. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00365-8
Kindler R, Siemens J, Kaiser K, Walmsley DC, Bernhofer C, Buchmann N, Cellier P, Eugster W, Gleixner G, Grunwald T, Heim A, Ibrom A, Jones SK, Jones M, Klumpp K, Kutsch W, Larsen KS, Lehuger S, Loubet B, Mckenzie R, Moors E, Osborne B, Pilegaard K, Rebmann C, Saunders M, Schmidt MWI, Schrumpf M, Seyfferth J, Skiba U, Soussana JF, Sutton MA, Tefs C, Vowinckel B, Zeeman MJ, Kaupenjohann M (2011) Dissolved carbon leaching from soil is a crucial component of the net ecosystem carbon balance. Glob Change Biol 17:1167–1185
Kölbl A, Kögel-Knabner I (2004) Content and composition of free and occluded particulate organic matter in a differently textured arable Cambisol as revealed by solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 167:45–53. doi:10.1002/jpln.200321185
Leifeld J, Fuhrer J (2009) Long-term management effects on soil organic matter in two cold, high-elevation grasslands: clues from fractionation and radiocarbon dating. Eur J Soil Sci 60:230–239. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2008.01111.x
Leifeld J, Kögel-Knabner I (2005) Soil organic matter fractions as early indicators for carbon stock changes under different land-use? Geoderma 124:143–155. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.04.009
Leifeld J, Zimmermann M, Fuhrer J, Conen F (2009) Storage and turnover of carbon in grassland soils along an elevation gradient in the Swiss Alps. Glob Change Biol 15:668–679. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01782.x
Malik A, Roth V-N, Hébert M, Tremblay L, Dittmar T, Gleixner G (2016) Linking molecular size, composition and carbon turnover of extractable soil microbial compounds. Soil Biol Biochem 100:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.05.019
Marschner B, Bredow A (2002) Temperature effects on release and ecologically relevant properties of dissolved organic carbon in sterilised and biologically active soil samples. Soil Biol Biochem 34:459–466
Marschner B, Kalbitz K (2003) Controls of bioavailability and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in soils. Geoderma 113:211–235. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00362-2
Martinsen V, Mulder J, Austrheim G, Mysterud A (2011) Carbon storage in low-alpine grassland soils: effects of different grazing intensities of sheep. Eur J Soil Sci 62:822–833. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2011.01393.x
Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins WD, Friedlingstein P, Gaye AT, Gregory JM, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Murphy JM, Noda A, Raper SCB, Watterson IG, Weaver AJ, Zhao ZC (2007) Global climate projections. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Meyer S, Leifeld J, Bahn M, Fuhrer J (2011) Free and protected soil organic carbon dynamics respond differently to abandonment of mountain grassland. Biogeosci Discuss 8:9943–9976. doi:10.5194/bgd-8-9943-2011
Meyer S, Leifeld J, Bahn M, Fuhrer J (2012a) Free and protected soil organic carbon dynamics respond differently to abandonment of mountain grassland. Biogeosciences 9:853–865. doi:10.5194/bg-9-853-2012
Meyer S, Leifeld J, Bahn M, Fuhrer J (2012b) Land-use change in subalpine grassland soils: effect on particulate organic carbon fractions and aggregation. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 175:401–409. doi:10.1002/jpln.201100220
Mills RTE, Gavazov KS, Spiegelberger T, Johnson D, Buttler A (2014) Diminished soil functions occur under simulated climate change in a sup-alpine pasture, but heterotrophic temperature sensitivity indicates microbial resilience. Sci Total Environ 473–474:465–472. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.071
Moore JC, Berlow EL, Coleman DC, Ruiter PC, Dong Q, Hastings A, Johnson NC, McCann KS, Melville K, Morin PJ, Nadelhoffer K, Rosemond AD, Post DM, Sabo JL, Scow KM, Vanni MJ, Wall DH (2004) Detritus, trophic dynamics and biodiversity. Ecol Lett 7:584–600. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00606.x
NF ISO 10390 (2005) Soil quality. Determination of pH. AFNOR
NF ISO 10693 (1995) Soil quality. Determination of carbonate content. Volumetric method. AFNOR
NF ISO 10694 (1995) Soil quality. Determination of organic and total carbon after dry combustion (elementary analysis). AFNOR
NF ISO 11464 (2006) Soil quality. Pretreatment of samples for physico-chemical analysis. AFNOR
NF ISO 13878 (1995) Soil quality. Determination of total nitrogen content by dry combustion (“elemental analysis”). AFNOR
NF ISO 16586 (2003) Soil quality. Determination of soil water content as a volume fraction on the basis of known dry bulk density: gravimetric method. AFNOR
NF X31-130 (1999) Soil quality. Determination of cation exchange capacity (CEC) and the extractable cations. AFNOR
NF X31-107 (2003) Soil quality. Determination of particle size distribution of the soil particles: method pipetted. AFNOR
Pengerud A, Cécillon L, Johnsen LK, Rasse DP, Strand LT (2013) Permafrost distribution drives soil organic matter stability in a Subarctic Palsa Peatland. Ecosystems 16:934–947. doi:10.1007/s10021-013-9652-5
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, Core TR (2014). nlme: Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-117. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme
Poirier N, Sohi S, Gaunt J, Mahieu N, Randall E, Powlson D, Evershed R (2005) The chemical composition of measurable soil organic matter pools. Org Geochem 36:1174–1189. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2005.03.005
Puissant J, Cécillon L, Mills RTE, Robroek BJM, Gavazov K, De Danieli S, Spiegelberger T, Buttler A, Brun J-J (2015) Seasonal influence of climate manipulation on microbial community structure and function in mountain soils. Soil Biol Biochem 80:296–305. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.10.013
Qualls RG, Haines BL (1992) Biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in forest throughfall, soil solution, and stream water. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:578
Rees RM, Parker J (2005) Filtration increases the correlation between water extractable organic carbon and soil microbial activity. Soil Biol Biochem 37:2240–2248. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.03.024
Robroek BJM, Jassey VEJ, Kox MAR, Berendsen RL, Mills RTE, Cécillon L, Puissant J, Meima-Franke M, Bakker PAHM, Bodelier PLE (2015) Peatland vascular plant functional types affect methane dynamics by altering microbial community structure. J Ecol 103:925–934. doi:10.1111/1365-2745.12413
Saenger A, Cécillon L, Poulenard J, Bureau F, De Daniéli S, Gonzalez J-M, Brun J-J (2014) Surveying the carbon pools of mountain soils: a comparison of physical fractionation and Rock-Eval pyrolysis. Geoderma 241–242:279–288. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.12.001
Schmidt MWI, Rumpel C, Kögel-Knabner I (1999) Evaluation of an ultrasonic dispersion procedure to isolate primary organomineral complexes from soils. Eur J Soil Sci 50:87–94. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2389.1999.00211.x
Siano DB, Metzler DE (1969) Band shapes of the electronic spectra of complex molecules. J Chem Phys 51:1856–1861
Signal Developers (2013) Signal: signal processing. http://r-forge.r-project.org/projects/signal/
Six J, Bossuyt H, Degryze S, Denef K (2004) A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res 79:7–31. doi:10.1016/j.still.2004.03.008
Sjögersten S, Alewell C, Cécillon L, Hagedorn F, Jandl R, Leifeld J, Martinsen V, Schindlbacher A, Sebastian MT, Van Miegroet H (2011) Mountain soils in a changing climate: vulnerability of carbon stocks and ecosystem feedbacks. In: Soil carbon in sensitive European ecosystems: from science to land management. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 118–148. doi:10.1002/9781119970255.ch6
Sohi SP, Mahieu N, Arah JRM, Powlson DS, Madari B, Gaunt JL (2001) A procedure for isolating soil organic matter fractions suitable for modeling. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:1121–1128
Sollins P, Homann P, Caldwell BA (1996) Stabilization and destabilization of soil organic matter: mechanisms and controls. Geoderma 74:65–105
Sollins P, Swanston C, Kramer M (2007) Stabilization and destabilization of soil organic matter: a new focus. Biogeochemistry 85:1–7. doi:10.1007/s10533-007-9099-x
Toberman H, Evans CD, Freeman C, Fenner N, White M, Emmett BA, Artz RRE (2008) Summer drought effects upon soil and litter extracellular phenol oxidase activity and soluble carbon release in an upland Calluna heathland. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1519–1532. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.01.004
Torn MS, Swanston CW, Castanha C, Trumbore SE (2009) Storage and turnover of organic matter in soil. In: Biophysico-chemical processes involving natural nonliving organic matter in environmental systems. doi:10.1002/9780470494950.ch6
Von Lützow M, Kögel-Knabner I, Ekschmitt K, Matzner E, Guggenberger G, Marschner B, Flessa H (2006) Stabilization of organic matter in temperate soils: mechanisms and their relevance under different soil conditions—a review. Eur J Soil Sci 57:426–445. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2006.00809.x
Von Lützow M, Kögel-Knabner I, Ekschmitt K, Flessa H, Guggenberger G, Matzner E, Marschner B (2007) SOM fractionation methods: relevance to functional pools and to stabilization mechanisms. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2183–2207. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.03.007
Yano Y, McDowell WH, Aber JD (2000) Biodegradable dissolved organic carbon in forest soil solution and effects of chronic nitrogen deposition. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1743–1751. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00092-4
Zsolnay Á (2003) Dissolved organic matter: artefacts, definitions, and functions. Geoderma 113:187–209. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00361-0
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded by IRSTEA, by the CCES (Competence Center Environment and Sustainability of the ETH Domain, Switzerland) as part of the Mountland project, and supported by a grant from Labex OSUG@2020 (Investissements d’avenir – ANR10 LABX56) and by a grant from the French Ministry of Higher Education and Research (Ph.D. thesis of J. Puissant, EDISCE Doctoral School). BJMR was supported through the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO; Research Innovation Scheme 863.10.014). P. Barré (CNRS/Ens Paris, France) provided useful advices regarding the SOM fractionation scheme used in this work. Robert Griffiths (Centre of Ecology and Hydrology, UK) is thanked for his precious helps. T. Goïtré and T. Rolland are thanked for the help with soil fractionation work and Giles Strachan is thanked for his precious help with SSB. Two anonymous reviewers and the editor are thanked for their constructive comments which strongly improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Edward Brzostek.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puissant, J., Mills, R.T.E., Robroek, B.J.M. et al. Climate change effects on the stability and chemistry of soil organic carbon pools in a subalpine grassland. Biogeochemistry 132, 123–139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-016-0291-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-016-0291-8