Abstract
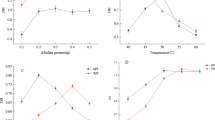
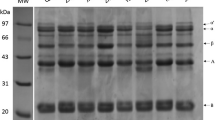
In this study, we elucidated the microbial transglutaminase-induced gelation properties and thermal gelling ability of soy protein isolate (SPI) and wheat gluten (WG) mixture following ultrahigh pressure (UHP, 100–400 MPa) pretreatment. UHP treatment induced unfolding and aggregation within SPI/WG protein molecules, which led to increases in free sulfhydryl group content and surface hydrophobicity. However, the transglutaminase cross-linking reaction facilitated the formation of hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bonds and thus resulted in higher gel strength, water holding capacity, and denser and more homogeneous gel networks of transglutaminase cross-linked SPI/WG gels. Rheological measurements revealed that the addition of UHP steps might generate a higher storage modulus (G′) value of MTGase-induced SPI/WG gelation during the heating-cooling cycle (25 °C → 95 °C → 25 °C). Our results indicated that various chemical interactions including covalent interactions (i.e., ε-(γ-glutamyl)lysine bonds and disulfide bonds) and non-covalent interactions (i.e., electrostatic forces and hydrophobic interactions) were involved in SPI/WG gel network structures. Hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bonds are significantly increased with the pressure level (100–400 MPa) compared with that of the unpressurized control. Furthermore, UHP treatment reduced the α-helix and β-turn content but increased the β-sheet and random coil structures. Thus, UHP treatment may be considered as a novel technique to expand the utilization of SPI/WG mixture in the food protein gelation industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agyare, K. K., Xiong, Y. L., & Addo, K. (2008). Influence of salt and pH on the solubility and structural characteristics of transglutaminase-treated wheat gluten hydrolysate. Food Chemistry, 107(3), 1131–1137.
Bhattacharjya, B., Dutta, H., Patwari, K., & Mahanta, C. L. (2015). Properties of annealed jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) seed starch. Acta Alimentaria, 44(4), 501–510.
Cando, D., Moreno, H. M., Tovar, C. A., Herranz, B., & Borderias, A. J. (2014). Effect of high pressure and/or temperature over gelation of isolated hake myofibrils. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(11), 3197–3207.
Cao, Y., Xia, T., Zhou, G., & Xu, X. (2012). The mechanism of high pressure-induced gels of rabbit myosin. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 16, 41–46.
Chen, X., Chen, C. G., Zhou, Y. Z., Li, P. J., Ma, F., Nishiumi, T., et al. (2014a). Effects of high pressure processing on the thermal gelling properties of chicken breast myosin containing κ-carrageenan. Food Hydrocolloids, 40, 262–272.
Chen, X., Li, P. J., Nishiumi, T., Takumi, H., Suzuki, A., & Chen, C. G. (2014b). Effects of high-pressure processing on the cooking loss and gel strength of chicken breast actomyosin containing sodium alginate. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(12), 3608–3617.
Gao, X. Q., Kang, Z. L., Zhang, W. G., Li, Y. P., & Zhou, G. H. (2015). Combination of κ-carrageenan and soy protein isolate effects on functional properties of chopped low-fat pork batters during heat-induced gelation. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(7), 1524–1531.
Gaspar, A. L., & de Góes-Favoni, S. P. (2015). Action of microbial transglutaminase (MTGase) in the modification of food proteins: a review. Food Chemistry, 171, 315–322.
He, R., He, H. Y., Chao, D., Ju, X., & Aluko, R. (2014). Effects of high pressure and heat treatments on physicochemical and gelation properties of rapeseed protein isolate. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(5), 1344–1353.
Hong, G. P., Min, S. G., & Chin, K. B. (2012). Emulsion properties of pork myofibrillar protein in combination with microbial transglutaminase and calcium alginate under various pH conditions. Meat Science, 90(1), 185–193.
Hu, H., Li-Chan, E. C., Wan, L., Tian, M., & Pan, S. (2013). The effect of high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatment on the properties of soybean protein isolate gel induced by calcium sulfate. Food Hydrocolloids, 32(2), 303–311.
Hugo, A. A., Pérez, P. F., Añón, M. C., & Speroni, F. (2014). Incorporation of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp lactis (CIDCA 133) in cold-set gels made from high pressure-treated soybean proteins. Food Hydrocolloids, 37, 34–39.
Jia, D., Huang, Q., & Xiong, S. (2016). Chemical interactions and gel properties of black carp actomyosin affected by MTGase and their relationships. Food Chemistry, 196, 1180–1187.
Jin, M. F., & Zhong, Q. X. (2013). Transglutaminase cross-linking to enhance elastic properties of soy protein hydrogels with intercalated montmorillonite nanoclay. Journal of Food Engineering, 115(1), 33–40.
Li, H., Zhu, K., Zhou, H., & Peng, W. (2011). Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on some functional and nutritional properties of soy protein isolate for infant formula. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(22), 12028–12036.
Li, X., & Xia, W. (2010). Effects of chitosan on the gel properties of salt-soluble meat proteins from silver carp. Carbohydrate Polymers, 82(3), 958–964.
Ma, X. S., Yi, S. M., Yu, Y. M., Li, J. R., & Chen, J. R. (2015). Changes in gel properties and water properties of Nemipterus virgatus surimi gel induced by high-pressure processing. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 61(2), 377–384.
Moreno, H. M., Bargiela, V., Tovar, C. A., Cando, D., Borderias, A. J., & Herranz, B. (2015). High pressure applied to frozen flying fish (Parexocoetus brachyterus) surimi: effect on physicochemical and rheological properties of gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 48, 127–134.
Motoki, M., & Seguro, K. (1998). Transglutaminase and its use for food processing. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 9(5), 204–210.
Nishinari, K., Fang, Y., Guo, S., & Phillips, G. O. (2014). Soy proteins: a review on composition, aggregation and emulsification. Food Hydrocolloids, 39, 301–318.
Qin, X. S., Luo, S. Z., Cai, J., Zhong, X. Y., Jiang, S. T., Zheng, Z., et al. (2016b). Effects of microwave pretreatment and transglutaminase crosslinking on the gelation properties of soybean protein isolate and wheat gluten mixtures. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 96(10), 3559–3566.
Qin, X. S., Luo, S. Z., Cai, J., Zhong, X. Y., Jiang, S. T., Zhao, Y. Y., et al. (2016a). Transglutaminase-induced gelation properties of soy protein isolate and wheat gluten mixtures with high intensity ultrasonic pretreatment. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 31, 590–597.
Shimada, K., & Cheftel, J. C. (1988). Determination of sulfhydryl groups and disulfide bonds in heat-induced gels of soy protein isolate. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 36(1), 147–153.
Speroni, F., & Añón, M. C. (2013). Cold-set gelation of high pressure-treated soybean proteins. Food Hydrocolloids, 33(1), 85–91.
Sun, X. D., & Arntfield, S. D. (2010). Gelation properties of salt-extracted pea protein induced by heat treatment. Food Research International, 43(2), 509–515.
Sun, X. D., & Arntfield, S. D. (2011). Gelation properties of chicken myofibrillar protein induced by transglutaminase crosslinking. Journal of Food Engineering, 107(2), 226–233.
Tang, C. H., & Ma, C. Y. (2009). Effect of high pressure treatment on aggregation and structural properties of soy protein isolate. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 42(2), 606–611.
Valipour, M. (2015). Future of agricultural water management in Africa. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 61(7), 907–927.
Wang, K., Luo, S., Cai, J., Sun, Q., Zhao, Y., Zhong, X., et al. (2016). Effects of partial hydrolysis and subsequent cross-linking on wheat gluten physicochemical properties and structure. Food Chemistry, 197, 168–174.
Wang, P., Jin, Z., & Xu, X. (2015). Physicochemical alterations of wheat gluten proteins upon dough formation and frozen storage—a review from gluten, glutenin and gliadin perspectives. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 46, 189–198.
Xiong, Y. L., Agyare, K. K., & Addo, K. (2008). Hydrolyzed wheat gluten suppresses transglutaminase-mediated gelation but improves emulsification of pork myofibrillar protein. Meat Science, 80(2), 535–544.
Zhang, P., Hu, T., Feng, S., Xu, Q., Zheng, T., Zhou, M., et al. (2016). Effect of high intensity ultrasound on transglutaminase-catalyzed soy protein isolate cold set gel. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 29, 380–387.
Zhang, Z., Yang, Y., Tang, X., Chen, Y., & You, Y. (2015). Chemical forces and water holding capacity study of heat-induced myofibrillar protein gel as affected by high pressure. Food Chemistry, 188, 111–118.
Zhu, Z., Lanier, T. C., & Farkas, B. E. (2015). High pressure effects on heat-induced gelation of threadfin bream (Nemipterus spp.) surimi. Journal of Food Engineering, 146, 23–27.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) of China (No. 2013AA102201), the Key program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31271931), and the Key Scientific and Technological Project of Anhui Province of China (No. 1301031031 and 15czz03096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, XS., Chen, SS., Li, XJ. et al. Gelation Properties of Transglutaminase-Induced Soy Protein Isolate and Wheat Gluten Mixture with Ultrahigh Pressure Pretreatment. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 866–874 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1864-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1864-9