Abstract
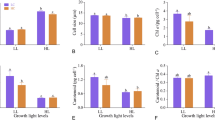
To investigate the effects of Nitrogen (N):phosphorus (P) ratio and solar ultraviolet radiation (UVR) on the growth and photophosphorylation of oceanic phytoplankton, the effects of UVR and N:P ratio on K. mikimotoi were evaluated. K. mikimotoi cells were cultured in artificial seawater (ASW) under five different N:P ratios (1:1, 16:1, 50:1, 100:1 and 200:1) for 15 days (phase 1: 1–5 day; phase 2: 6–10 day; phase 3: 11–15 days). Next, K. mikimotoi cultures were exposed to photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), PAB (PAR + UV-A + UV-B) and PA (PAR + UV-A), respectively. Finally, K. mikimotoi cells grown under the Redfield ratio (16:1) had the largest growth rate (0.257day−1), highest pigment concentrations (chlorophyll a (Chla): 0.465 × 10− 5 μg cell−1, carotenoid (Caro): 0.249 × 10−5 μg cell−1) and maximum superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (0.9 U × 10−6 cell−1) compared with those grown under other N:P ratios. The UV-absorbing compounds’ (UVabc) absorbance was largest at the N:P ratio of 50:1 during the range of 310–360 nm, with a relatively higher value at the N:P ratio of 16:1. UV intensity was positively correlated with photoinhibition. K. mikimotoi cells grown at the N:P ratio of 16:1 showed the smallest photoinhibition compared to those grown at other N:P ratios under the PAR treatment with the largest r:k ratio; similar results were found for both the PA and PAB treatments. The Redfield ratio of 16:1 is optimal for the growth and photophosphorylation of K. mikimotoi. The weakest UVR-induced photoinhibition at this ratio may be attributed to the highest photosystem II (PSII) repair rate and SOD activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Glibert PM, Burkholder JM (2002) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 25:704–726
Beardall J, Raven JA (2004) The potential effects of global climate change on microalgal photosynthesis, growth and ecology. Phycologia 43:26–40
Beardall J, Sobrino C, Stojkovic S (2009) Interactions between the impacts of ultraviolet radiation, elevated CO2, and nutrient limitation on marine primary producers. Photochem Photobiol Sci 8:1257–1265
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Berges JA, Franklin DJ, Harrison PJ (2001) Evolution of an artificial seawater medium: improvements in enriched seawater, artificial water over the last two decades. J Phycol 37:1138–1145
Brooks A (1986) Effects of phosphorus nutrition on ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase activation, photosynthetic quantum yield and amounts of some Calvin-cycle metabolites in spinach leaves. Funct Plant Biol 13:221–237
Buma A, Zemmelink H, Sjollema K, Gieskes W (1996) UVB radiation modifies protein and photosynthetic pigment content, volume and ultrastructure of marine diatoms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser Oldendorf 142:47–54
Chai C, Yu Z, Song X, Cao X (2006) The status and characteristics of eutrophication in the Yangtze River (Changjiang) Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea, China. Hydrobiologia 563:313–328
Chang J, Carpenter E (1985) Blooms of the dinoflagellate Gyrodinium aureolum in a Long Island estuary. Mar Biol 89:83–93
Fang T-H (2004) Phosphorus speciation and budget of the East China Sea. Cont Shelf Res 24:1285–1299
Gehrke C (1999) Impacts of enhanced ultraviolet-B radiation on mosses in a subarctic heath ecosystem. Ecology 80:1844–1851
Geider R, La Roche J (2002) Redfield revisited: variability of C: N: P in marine microalgae and its biochemical basis. Eur J Phycol 37:1–17
Geider RJ, Roche J, Greene RM, Olaizola M (1993) Response of the photosynthetic apparatus of phaeodactylum tricornutum (Bacillariophyceae) to nitrate, phosphate, or iron starvation1. J Phycol 29:755–766
Geider R, Macintyre, Graziano L, McKay RM (1998) Responses of the photosynthetic apparatus of Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae) to nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. Eur J Phycol 33:315–332
Genty B, Harbinson J, Baker N (1990) Relative quantum efficiencies of the two photosystems of leaves in photorespiratory and non-respiratory conditions. Plant Physiol Biochem (Paris) 28:1–10
Glibert P, Burkholder J (2006) The Complex Relationships Between Increasing Fertilization of the Earth, Coastal Eutrophication, and Hab Proliferation, Chap. 24. Ecol Harmful Algae
Guan W, Li P, Jian J, Wang J, Lu S (2011) Effects of solar ultraviolet radiation on photochemical efficiency of Chaetoceros curvisetus (Bacillariophyceae). Acta Physiol Plant 33:979–986
Guillard RR, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana hustedt, and detonula confervacea (cleve) gran. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Häder D-P, Kumar H, Smith R, Worrest R (2007) Effects of solar UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with climate change. Photochem Photobiol Sci 6:267–285
Heraud P, Beardall J (2000) Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence during exposure of Dunaliella tertiolecta to UV radiation indicate a dynamic interaction between damage and repair processes. Photosynth Res 63:123–134
John E, Flynn K (2000) Growth dynamics and toxicity of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae): the effect of changing N: P supply ratios on internal toxin and nutrient levels. Eur J Phycol 35:11–23
Justić D, Rabalais NN, Turner RE (1995) Stoichiometric nutrient balance and origin of coastal eutrophication. Mar Pollut Bull 30:41–46
Lagus A, Suomela J, Weithoff G, Heikkilä K, Helminen H, Sipura J (2004) Species-specific differences in phytoplankton responses to N and P enrichments and the N:P ratio in the Archipelago Sea, northern Baltic Sea. J Plankton Res 26:779–798
Larson MG (2008) Analysis of variance. Circulation 117:115–121
Lesser MP, Cullen JJ, Neale PJ (1994) Carbon uptake in a marine diatom during acute exposure to ultraviolet B radiation: Relative importance of damage and repair. J Phycol 30:183–192
Lippemeier S, Hintze R, Vanselow K, Hartig P, Colijn F (2001) In-line recording of PAM fluorescence of phytoplankton cultures as a new tool for studying effects of fluctuating nutrient supply on photosynthesis. Eur J Phycol 36:89–100
Lu S, Hodgkiss I (2004) Harmful algal bloom causative collected from Hong Kong waters Asian Pacific Phycology in the 21st Century: prospects and challenges. Springer, pp 231–238
Marwood CA, Smith RE, Furgal JA, Charlton MN, Solomon KR, Greenberg BM (2000) Photoinhibition of natural phytoplankton assemblages in Lake Erie exposed to solar ultraviolet radiation. Can J Fish Aquatic Sci 57:371–379
Murata N, Takahashi S, Nishiyama Y, Allakhverdiev SI (2007) Photoinhibition of photosystem II under environmental stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767:414–421
Porra RJ (2005) The chequered history of the development and use of simultaneous equations for the accurate determination of chlorophylls a and b Discoveries in Photosynthesis. Springer, pp 633–640
Redfield AC (1958) The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am Sci 230A-221
Rhee G-Y (1978) Effects of N:P atomic ratios and nitrate limitation on algal growth, cell composition, and nitrate uptake 1. Limnol Oceanogr 23:10–25
Shelly K, Roberts S, Heraud P, Beardall J (2005) Interactions between UV-B exposure and phosphorus nutrition.II. Effects on rates of damage and repair. J Phycol 41:1204–1211
Sinha RP, Häder D-P (2008) UV-protectants in cyanobacteria. Plant Sci 174:278–289
Srtickland J, Parson T (1968) A practical handbook of seawater analysis, Pigment analysis. Bull Fish Res Bd Canada 167
Thingstad T, Krom M, Mantoura R, Flaten GF, Groom S, Herut B, Kress N, Law C, Pasternak A, Pitta P (2005) Nature of phosphorus limitation in the ultraoligotrophic eastern Mediterranean. Science 309:1068–1071
Vanhoutte-Brunier A, Fernand L, Ménesguen A, Lyons S, Gohin F, Cugier P (2008) Modelling the Karenia mikimotoi bloom that occurred in the western English Channel during summer 2003. Ecol Model 210:351–376
Villafane VE, Sundbäck K, Figueroa FL, Helbling EW (2003) Photosynthesis in the aquatic environment as affected by UVR. UV effects in aquatic organisms and ecosystems. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 357–397
Wang Z, Liu R, Wang A, Du L, Deng X (2008) Phototoxic effect of UVR on wild type, ebony and yellow mutants of Drosophila melanogaster: Life Span, fertility, courtship and biochemical aspects. Sci Chin Ser C Life Sci 51: 885–893
Weers PM, Gulati RD (1997) Growth and reproduction of Daphnia galeata in response to changes in fatty acids, phosphorus, and nitrogen in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1584–1589
Yan W, Zhang S (2003) The composition and bioavailability of phosphorus transport through the Changjiang (Yangtze) River during the 1998 flood. Biogeochemistry 65:179–194
Yuan D, Zhu J, Li C, Hu D (2008) Cross-shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas indicated by MODIS satellite observations. J Mar Syst 70:134–149
Zhang J, Liu S, Ren J, Wu Y, Zhang G (2007) Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and re-evaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf. Prog Oceanogr 74:449–478
Zhiliang S, Qun L, Shumei Z, Hui M, Ping Z (2003) A nitrogen budget of the Changjiang River catchment. AMBIO A J Human Environ 32:65–69
Zu Y, Wei X, Yu J, Li D, Pang H, Tong L (2011) Responses in the physiology and biochemistry of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) under supplementary UV-B radiation. Photosynthetica 49:448–458
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation for Young Scholars of China (No. 41306106), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LY16D060005), Research Program of Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau (No. N20160008) and the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2014F10005). We thank H. Chen and Y. Wang who kindly prepared the cultures and helped with culture maintenance. We also thank anonymous reviewers whose comments and suggestions helped improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to state.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: K. Yin.
Reviewed by Undisclosed experts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, W., Li, P. Dependency of UVR-induced photoinhibition on atomic ratio of N to P in the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi . Mar Biol 164, 31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-3065-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-3065-x