Abstract
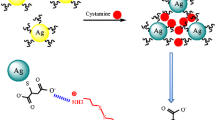
The authors have developed a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) method for the determination of pyrophosphate ion (PPi). It is based on the competitive coordination of Cu(II) between cysteine (Cys) and PPi using silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) modified with Cys and Rhodamine 6G (R6G). Cys was attached to the surface of the AgNPs via Ag−S bond, and the amino acid unit in Cys bind to Cu(II) to form a chelate complex. This results in the aggregation of AgNPs and a strong SERS signal for the probe R6G. However, in the presence of PPi, the aggregated AgNPs are solubilized because of the stronger affinity between PPi and Cu(II). This leads to a decrease of the SERS signal and forms the basis for the quantitation of PPi. The amount of AgNPs, the concentration of Cu(II), and the mixing time were optimized. The method displays a linear response in the 0.1 to 80 μM PPi concentration range, and the limit of detection is as low as 20 nM. The method was applied to the determination of PPi in spiked serum samples and urine samples, with recoveries between 95.2 to 100.5% and relative standard deviations of <4.4%.

The cysteine and R6G functionalized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were synthesized as a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) substrate to detect pyrophosphate ion (PPi). It is based on the competitive coordination of Cu(II) between cysteine (Cys) and PPi.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu W, Huang X, Guo Z, Wu X, Yu H, Tian H (2012) A novel NIR fluorescent turn-on sensor for the detection of pyrophosphate anion in complete water system. Chem Commun 48(12):1784–1786
Lee HN, Xu Z, Kim SK, Swamy K, Kim Y, Kim S-J, Yoon J (2007) Pyrophosphate-selective fluorescent chemosensor at physiological pH: formation of a unique excimer upon addition of pyrophosphate. J Am Chem Soc 129(13):3828–3829
Huang MS, Sage AP, Lu J, Demer LL, Tintut Y (2008) Phosphate and pyrophosphate mediate PKA-induced vascular cell calcification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374(3):553–558
Tsui FW (2012) Genetics and mechanisms of crystal deposition in calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep 14(2):155–160
Bhowmik S, Ghosh BN, Marjomaki V, Rissanen K (2014) Nanomolar pyrophosphate detection in water and in a self-assembled hydrogel of a simple terpyridine-Zn2+ complex. J Am Chem Soc 136(15):5543–5546
Sokkalingam P, Kim DS, Hwang H, Sessler JL, Lee C-H (2012) A dicationic calix[4] pyrrole derivative and its use for the selective recognition and displacement-based sensing of pyrophosphate. Chem Sci 3(6):1819
Yang S, Feng G, Williams NH (2012) Highly selective colorimetric sensing pyrophosphate in water by a NBD-phenoxo-bridged dinuclear Zn(II) complex. Org Biomol Chem 10(29):5606–5612
Feng X, An Y, Yao Z, Li C, Shi G (2012) A turn-on fluorescent sensor for pyrophosphate based on the disassembly of Cu2 + −mediated perylene diimide aggregates. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(2):614–618
Su X, Zhang C, Xiao X, Xu A, Xu Z, Zhao M (2013) A kinetic method for expeditious detection of pyrophosphate anions at nanomolar concentrations based on a nucleic acid fluorescent sensor. Chem Commun 49(8):798–800
Nakamura H, Yamazaki R, Shirai T, Sano H, Nakami Y, Ikebukuro K, Yano K, Nomura Y, Arikawa Y, Hasebe Y, Masuda Y, Karube I (2004) Development of an enzymatic flow-injection chemiluminescence system for determining inorganic pyrophosphate ion. Anal Chim Acta 518(1–2):45–49
Shin I-S, Bae SW, Kim H, Hong J-I (2010) Electrogenerated chemiluminescent anion sensing: selective recognition and sensing of pyrophosphate. Anal Chem 82(19):8259–8265
Deng J, Yu P, Yang L, Mao L (2013) Competitive coordination of Cu2+ between cysteine and pyrophosphate ion: toward sensitive and selective sensing of pyrophosphate ion in synovial fluid of arthritis patients. Anal Chem 85(4):2516–2522
Marques SM, Peralta F, Esteves da Silva JC (2009) Optimized chromatographic and bioluminescent methods for inorganic pyrophosphate based on its conversion to ATP by firefly luciferase. Talanta 77(4):1497–1503
Lin Y, Hu L, Li L, Wang K, Ji Y, Zou H (2015) Electrochemical determination of pyrophosphate at nanomolar levels using a gold electrode covered with a cysteine nanofilm and based on competitive coordination of Cu(II) ion to cysteine and pyrophosphate. Microchim Acta 182(11–12):2069–2075
Sakasegawa S, Hayashi J, Ikura Y, Ueda S, Imamura S, Kumazawa T, Nishimura A, Ohshima T, Sakuraba H (2011) Colorimetric inorganic pyrophosphate assay using a double cycling enzymatic method. Anal Biochem 416(1):61–66
Jana NR, Pal T (2007) Anisotropic metal nanoparticles for use as surface-enhanced Raman substrates. Adv Mater 19(13):1761–1765
Le Ru EC, Etchegoin PG, Meyer M (2006) Enhancement factor distribution around a single surface-enhanced Raman scattering hot spot and its relation to single molecule detection. J Chem Phys 125(20):204701
Doering WE, Nie S (2002) Single-molecule and single-nanoparticle SERS: examining the roles of surface active sites and chemical enhancement. J Phys Chem B 106(2):311–317
Stiles PL, Dieringer JA, Shah NC, Van Duyne RP (2008) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu Rev Anal Chem 1:601–626
Ma P, Liang F, Wang D, Yang Q, Cao B, Song D, Gao D, Wang X (2014) Selective determination of o-phenylenediamine by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using silver nanoparticles decorated with α-cyclodextrin. Microchim Acta 182(1–2):167–174
Cui M, Zhao Y, Wang C, Song Q (2016) Synthesis of 2.5 nm colloidal iridium nanoparticles with strong surface enhanced Raman scattering activity. Microchim Acta 183(6):2047–2053
Wang Y, Irudayaraj J (2013) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy at single-molecule scale and its implications in biology. Phil Trans R Soc B 368(1611):20120026
Henry AI, Sharma B, Cardinal MF, Kurouski D, Van Duyne RP (2016) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy Biosensing: in vivo diagnostics and multimodal imaging. Anal Chem 88(13):6638–6647
Dasary SS, Zones YK, Barnes SL, Ray PC, Singh AK (2016) Alizarin dye based ultrasensitive plasmonic SERS probe for trace level cadmium detection in drinking water. Sensors Actuators B Chem 224:65–72
Mungroo NA, Oliveira G, Neethirajan S (2015) SERS based point-of-care detection of food-borne pathogens. Microchim Acta 183(2):697–707
Munro CH, Smith WE, Garner M, Clarkson J, White PC (1995) Characterization of the surface of a citrate-reduced colloid optimized for use as a substrate for surface-enhanced resonance Raman-scattering. Langmuir 11(10):3712–3720
Marino N, Ikotun OF, Julve M, Lloret F, Cano J, Doyle RP (2011) Pyrophosphate-mediated magnetic interactions in Cu(II) coordination complexes. Inorg Chem 50(1):378–389
Lenz G, Martell A (1964) Metal chelates of some sulfur-containing amino acids*. Biochemistry 3(6):745–750
English JB, Martell AE, Motekaitis RJ, Murase I (1997) Molecular interaction of pyrophosphate with 1, 13-dioxa-4, 7, 10, 16, 20, 24-hexaazacyclohexacosane (OBISDIPEN) and its mononuclear and dinuclear copper (II) complexes. Inorg Chim Acta 258(2):183–192
Li F, Wang J, Lai Y, Wu C, Sun S, He Y, Ma H (2013) Ultrasensitive and selective detection of copper (II) and mercury (II) ions by dye-coded silver nanoparticle-based SERS probes. Biosens Bioelectron 39(1):82–87
Graham D, Thompson DG, Smith WE, Faulds K (2008) Control of enhanced Raman scattering using a DNA-based assembly process of dye-coded nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 3(9):548–551
Zhao X, Zhang B, Ai K, Zhang G, Cao L, Liu X, Sun H, Wang H, Lu L (2009) Monitoring catalytic degradation of dye molecules on silver-coated ZnO nanowire arrays by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J Mater Chem 19(31):5547
Zhang C, Jiang SZ, Huo YY, Liu AH, Xu SC, Liu XY, Sun ZC, Xu YY, Li Z, Man BY (2015) SERS detection of R6G based on a novel graphene oxide/silver nanoparticles/silicon pyramid arrays structure. Opt Express 23(19):24811–24821
Sutor DJ, Wilkie LI (1978) The estimation of pyrophosphate in urine with uridine-5′-diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase. Clin Chim Acta 86(3):329–332
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 15.2 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, L., Chen, Y., Zhang, L. et al. SERS assay for pyrophosphate based on its competitive binding to Cu(II) ion on silver nanoparticles modified with cysteine and rhodamine 6G. Microchim Acta 184, 595–601 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2044-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2044-8