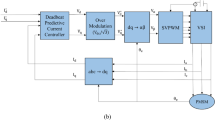
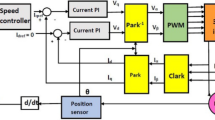
Abstract
Direct torque control (DTC) of permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) drives is receiving increasing attention due to important advantages, such as fast dynamic and low dependence on motor parameters. However, conventional DTC scheme, based on comparators and the switching table, suffers from large torque and flux ripples. In this paper, two intelligent approaches are proposed in order to improve DTC performance. The first approach is based on two adaptive fuzzy logic controllers (AFLC). The first AFLC replaces the conventional comparators and switching table and the second AFLC adjusts in real time the outer loop PI parameters. In the second approach, particle swarm optimization (PSO) is used as another alternative to adjust the PI parameters. Simulation and experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed intelligent techniques. Besides, the system associated with these techniques can effectively reduce flux and torque ripples with better dynamic and steady state performance. Quantitatively, PSO-based DTC approach reduces greatly flux and torque ripples. Further, PSO-based approach maintains a constant switching frequency which improves the PMSM drive system control performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tulasi Ram Das G (2008) J. NTUCE Hyderabad, Introduction and control of permanent magnet synchronous machines. Workshop on ‘Modern AC Drives’ at RGMCET, Nandyala, Febrauary-2008
Finch JW, Giaouris D (2008) Controlled AC electrical drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(2):481–491
Rodriguez J, Kennel RM, Espinoza JR, Trincado M, Silva CA, Rojas CA (2012) High-performance control strategies for electrical drives: an experimental assessment. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59:812–820
Zhang Y, Akujuobi CM, Ali WH, Tolliver CL, Shieh L-S (2006) Load disturbance resistance speed controller design for PMSM. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 53(4):1198–1208
Dongemei X, Daokui Q, Fang X (2005) Design of H8 feedback controller and IP position controller of PMSM servo system. IEEE Int Conf Mechatron Autom 2(29):578–1108
Nash JH (1986) Direct torque control, induction motor vector control without an encoder. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 33(2):333–341
Idris NRN, Yatim AHM (2004) Direct torque control of induction machines with constant switching frequency and reduced torque ripple. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 51(4):758–767
Bossoufi B, Karim M, Ionita S, Lagrioui A (2010) Performance analysis of direct torque control (DTC) for synchronous machine permanent magnet (PMSM). In: Proc. IEEE-SIITME’2010, pp. 275–280, 23–26 Sep 2010, Pitesti, Romania
Kumar V, Gaur P, Mittal AP (2014) ANN based self tuned PID like adaptive controller design for high performance PMSM position control. Expert Syst Appl 41:7995–8002
Nyanteh YD, Srivastava SK, Edrington CS, Cartes DA (2013) Application of artificial intelligence to stator winding fault diagnosis in permanent magnet synchronous machines. Electr Power Syst Res 103:201–213
Labiod S, Guerra TM (2012) Fuzzy adaptive control for a class of nonlinear systems with unknown control gain. Evol Syst 3:57–64
Gao Y, Wang J, Qiu X (2011) The improvement of DTC system performance on fuzzy control. Procedia Environ Sci 10:589–594
HAZZAB A, BOUSSERHANE IK, ZERBO M, SICARD P (2006) Real time implementation of fuzzy gain scheduling of PI controller for induction motor machine control. Neural Process Lett 24:203–215
Hajebi P, Taghi AlModarresi SM (2012) Online adaptive fuzzy logic controller using genetic algorithm and neural network for networked control systems. ICACT Transactions on Advanced Communications Technology (TACT) 1(3)
Boudana D, Nezli L, Tlemcani A, Mahmoudi MO, Djemai M (2008) DTC based on fuzzy logic control of a double star synchronous machine drive. Nonlinear Dyn Syst Theory 8(3):269–286
Al Gizia A, Mustafaa MW, Jebur HH (2014) A novel design of high-sensitive fuzzy PID controller. Appl Soft Comput 24:794–805
Maldonado Y, Castillo O, Melin P (2013) Particle swarm optimization of interval type-2 fuzzy system for FPGA applications. Appl Soft Comput 13:496–508
Shahnazi R, Shanechi HM, Pariz N (2008) Position control of induction and DC servomotors: a novel adaptive fuzzy PI sliding mode control. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 23(1)
Sangram K, Routray NN, Pravat Kumar RA (2012) Robust fuzzy sliding mode control design for current source inverter based STATCOM. Appl Procedia Technol 4:342–349
Singh M, Chandra A (2011) Application of adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system for sensor less control of PMSG-based wind turbine with nonlinear-load-compensation capabilities. IEEE Trans Power Electron 26(1):165–175
Bhattacharya A, Chakraborty C (2011) A shunt active power filter with enhanced performance using ANN based predictive and adaptive controllers. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(2):421–428
Kashif SA, Saqib MA (2014) Sensorless control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor using artificial neural network based estimator—an application of the four-switch three-phase inverter. Electr Power Compon Syst 42(1)
Zhan Z-H, Zhang J, Li Y, Chung HS-H (2009) Adaptive particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 39:1362–1381
Kiranyaz S, Ince T, Yildirim A, Gabbouj M (2009) Fractional particle swarm optimization in multidimensional search space. IEEE Transactions on: Accepted for future publication Vol. pp 1–1, Forthcoming
Vasumathi B, Moorthi S (2012) Implementation of hybrid ANN–PSO algorithm on FPGA for harmonic estimation. Eng Appl Artif Intell 25:476–483
Pourjafari E, Mojallali H (2011) Predictive control for voltage collapse avoidance using a modified discrete multi-valued PSO algorithm. ISA Trans 50:195–200
Mohkami H, Hooshmand R, Khodabakhshian A (2011) Fuzzy optimal placement of capacitors in the presence of nonlinear loads in unbalanced distribution networks using BF-PSO algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 11:3634–3642
Oh S-K, Jang H-J, Pedrycz W (2011) A comparative experimental study of type-1/type-2 fuzzy cascade controller based on genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 38:11217–11229
Chiou J-S, Tsai S-H, Liu M-T (2012) A PSO-based adaptive fuzzy PID-controllers. Simul Model Pract Theory 26:49–59
Bouallegue S, Haggege J, Ayadi M, Benrejeb M (2012) PID-type fuzzy logic controller tuning based on particle swarm optimization. Eng Appl Artif Intell 25:484–493
Takahashi I, Noguchi T (1986) A new quick response and high-efficiency control strategy of an induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl IA-22(5):820–827
Boldea I (2000) Direct torque and flux control (DTFC) of A.C. drives: a review. In: Proceedings of EPEPEMC’2000, vol. 1, Kosice, Slovakia, pp 88–97
Pacas M, Weber J (2005) Predictive direct torque control for the PM synchronous machine. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 52(5):1350–1356
Gatto G, Marongiu I, Serpi A, Perfetto A (2008) A predictive direct torque control of induction machines. In: Proceedings of SPEEDAM 2008, June 2008, Ischia, Italy, pp 1103–1108
Sharmeela C, Mohan MR, Uma G, Baskaran J (2007) Fuzzy logic based controlled three phase shunt active filter for line harmonics reduction. J Comput Sci 3(2):76–80
Mikkili S, Panda AK (2012) Real-time implementation of power theory using FLC based shunt active filter with different fuzzy M.F.s, 38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2012) pp 702–707
Benchouia MT, Ghadbane I, Golea A, Srairi K, Benbouzid MH (2014) Implementation of adaptive fuzzy logic and pi controllers to regulate the DC bus voltage of shunt active power filter. Appl Soft Comput 56:1826–1838
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, vol 4, Perth, Australia, pp 1942–1948
Marinakis Y, Marinaki M, Dounias G (2010) A hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for the vehicle routing problem. Eng Appl Artif Intell 23:463–472
Samanta B, Nataraj C (2009) Use of particle swarm optimization for machinery fault detection. Eng Appl Artif Intell 22:308–316
Liu L, Liu W, Cartes DA (2008) Particle swarm optimization-based parameter identification applied to permanent magnet synchronous motors. Eng Appl Artif Intell 21:1092–1100
Venayagamoorthy GK, Smith SC, Singhal G (2007) Particle swarm-based optimal partitioning algorithm for combinational CMOS circuits. Eng Appl Artif Intell 20:177–184
Bouallegue S, Haggege J, Benrejeb M (2010a) Structured loop-shaping HN controller design using particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2010 I.E. International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics SMC’10, Istanbul
Bouallegue S, Haggege J, Benrejeb M (2010b) Structured mixed-sensitivity HN design using particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices SSD’10, Amman
Bouallegue S, Haggege J, Benrejeb M (2011) Particle swarm optimization-based fixed-structure H∞ control design. Int J Control Autom Syst 9(2):258–266
Ray RN, Chatterjee D, Goswami SK (2009) An application of PSO technique for harmonic elimination in a PWM inverter. Appl Soft Comput 9:1315–1320
Kao C-C, Chuang C-W, Fung R-F (2006) The self-tuning PID control in a slider–crank mechanism system by applying particle swarm optimization approach. Mechatronics 16:513–522
Wain R-J, Lin Y-F, Chuang K-L (2014) Total sliding-mode-based particle swarm optimization control for linear induction motor. J Frankl Inst 351:2755–2780
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mesloub, H., Benchouia, M.T., Goléa, A. et al. A comparative experimental study of direct torque control based on adaptive fuzzy logic controller and particle swarm optimization algorithms of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90, 59–72 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9092-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9092-4