Abstract
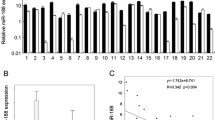
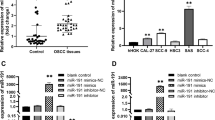
This study aimed to explore the role of miR-429 on the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). OSCC cell lines were transfected with miR-429 mimic, pcDNA3.1-RUNX1, or pcDNA3.1-ITGB1, and their cell viability, apoptosis, migration, and invasion abilities were analyzed by cell counting, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling staining, wound healing, and transwell assays, respectively. Furthermore, luciferase reporter assay, RNA pull-down, and ChIP were used to assess the regulation of miR-429, RUNX1, and ITGB1 expression in OSCC. Lastly, the biological role of the RUNX1/miR-429 feedback loop was explored in nude mice. The results revealed that miR-429 level was down-regulated, while RUNX1 and ITGB1 levels were up-regulated in OSCC tissues and that miR-429 was negatively correlated with RUNX1 and ITGB1 in OSCC tissues. Transfection of miR-429 mimic suppressed OSCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). Moreover, we found that miR-429 participated in OSCC progression by directly targeting ITGB1. Additionally, we found that RUNX1 negatively regulated miR-429 expression by binding to its promoter. Our results also revealed that the RUNX1/miR-429 feedback loop regulated ITGB1 expression and that RUNX1 overexpression rescued the inhibitory effects of miR-429 mimic on OSCC cells. In addition, miR-429 mimic significantly suppressed tumor growth, inflammatory cell infiltration, EMT, and ITGB1 expression in vivo, which were inhibited by RUNX1 overexpression. Altogether, these results indicate that the RUNX1/miR-429 feedback loop promoted growth, metastasis, and EMT in OSCC by targeting ITGB1.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Browne G, Dragon JA, Hong D, Messier TL, Gordon JA, Farina NH, Boyd JR, VanOudenhove JJ, Perez AW, Zaidi SK et al (2016) MicroRNA-378-mediated suppression of Runx1 alleviates the aggressive phenotype of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Tumour Biology: The Journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 37(7):8825–8839
Bugshan A, Farooq I (2020) Oral squamous cell carcinoma: metastasis, potentially associated malignant disorders, etiology and recent advancements in diagnosis. F1000Research 9:229
Chaw SY, Abdul Majeed A, Dalley AJ, Chan A, Stein S, Farah CS (2012) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) biomarkers–E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and vimentin–in oral squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol 48(10):997–1006
Chen L, Heikkinen L, Wang C, Yang Y, Sun H, Wong G (2019) Trends in the development of miRNA bioinformatics tools. Brief Bioinform 20(5):1836–1852
Cheng Y, Yang H, Sun Y, Zhang H, Yu S, Lu Z, Chen J (2017) RUNX1 promote invasiveness in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through regulating miR-93. Oncotarget 8(59):99567–99579
Deng Y, Luan F, Zeng L, Zhang Y, Ma K (2017) MiR-429 suppresses the progression and metastasis of osteosarcoma by targeting ZEB1. EXCLI J 16:618–627
Ding Y, Pan Y, Liu S, Jiang F, Jiao J (2017) Elevation of MiR-9-3p suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via down-regulating FN1, ITGB1 and ITGAV. Cancer Biol Ther 18(6):414–424
Feng RM, Zong YN, Cao SM, Xu RH (2019) Current cancer situation in China: good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer statistics? Cancer Commun (London England) 39(1):22
Feng H, Zhang X, Lai W, Wang J (2020) Long non-coding RNA SLC16A1-AS1: its multiple tumorigenesis features and regulatory role in cell cycle in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle (Georgetown Tex) 19(13):1641–1653
Feng X, Zheng Z, Wang Y, Song G, Wang L, Zhang Z, Zhao J, Wang Q, Lun L (2021) Elevated RUNX1 is a prognostic biomarker for human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood NJ) 246(5):538–546
Fischer J, Rossetti S, Datta A, Eng K, Beghini A, Sacchi N (2015) miR-17 deregulates a core RUNX1-miRNA mechanism of CBF acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer 14:7
Garajei A, Allameh A, Azadi M, Emami A, Atashbasteh M, Mostafavi M, Ghaderi B, Inchingolo F, Sadeghi M, Tadakamadla SK et al (2023) : Evaluation of the Expression Levels of miR-21-5p and miR-429 Genes in Biopsy Samples from Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) 13(7)
Guo L, Sun C, Xu S, Xu Y, Dong Q, Zhang L, Li W, Wang X, Ying G, Guo F (2019) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA linc-ITGB1 inhibits cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by reducing the expression of snail in non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac cancer 10(2):128–136
Guo CM, Liu SQ, Sun MZ (2020) miR-429 as biomarker for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of cancers and its potential action mechanisms: a systematic literature review. Neoplasma 67(2):215–228
Jang TH, Huang WC, Tung SL, Lin SC, Chen PM, Cho CY, Yang YY, Yen TC, Lo GH, Chuang SE et al (2022) MicroRNA-485-5p targets keratin 17 to regulate oral cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the integrin/FAK/Src/ERK/β-catenin pathway. J Biomed Sci 29(1):42
Jiang W, Mitra R, Lin CC, Wang Q, Cheng F, Zhao Z (2016) Systematic dissection of dysregulated transcription factor-miRNA feed-forward loops across tumor types. Brief Bioinform 17(6):996–1008
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui VWY, Bauman JE, Grandis JR (2020) Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Reviews Disease Primers 6(1):92
Joseph JP, Harishankar MK, Pillai AA, Devi A (2018) Hypoxia induced EMT: a review on the mechanism of tumor progression and metastasis in OSCC. Oral Oncol 80:23–32
Ju JA, Godet I, Ye IC, Byun J, Jayatilaka H, Lee SJ, Xiang L, Samanta D, Lee MH, Wu PH et al (2017) Hypoxia selectively enhances integrin α(5)β(1) receptor expression in breast Cancer to promote metastasis. Mol cancer Research: MCR 15(6):723–734
Lei W, Liu YE, Zheng Y, Qu L (2015) MiR-429 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma growth by targeting ZEB1. Med Sci Monitor: Int Med J Experimental Clin Res 21:383–389
Li Q, Lai Q, He C, Fang Y, Yan Q, Zhang Y, Wang X, Gu C, Wang Y, Ye L et al (2019) RUNX1 promotes tumour metastasis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and EMT in colorectal cancer. J Experimental Clin cancer Research: CR 38(1):334
Lin TC (2022) RUNX1 and cancer. Biochim et Biophys acta Reviews cancer 1877(3):188715
Ling Z, Cheng B, Tao X (2021) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma: challenges and opportunities. Int J Cancer 148(7):1548–1561
Liu X, Ma X, Li H, Wang Y, Mao M, Liang C, Hu Y (2022a) LINC00472 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma growth by targeting miR-455-3p/ELF3 axis. Bioengineered 13(1):1162–1173
Liu J, Yang T, Huang Z, Chen H, Bai Y (2022b) : Transcriptional regulation of nuclear miRNAs in tumorigenesis (review). Int J Mol Med 50(1)
Panarese I, Aquino G, Ronchi A, Longo F, Montella M, Cozzolino I, Roccuzzo G, Colella G, Caraglia M, Franco R (2019) Oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: prognostic and predictive parameters in the etiopathogenetic route. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 19(2):105–119
Qin SY, Li B, Chen M, Qin MQ, Liu JM, Lv QL (2022) MiR-32-5p promoted epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via regulating the KLF2/CXCR4 pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 38(2):120–128
Ren L, Mo W, Wang L, Wang X (2020) Matrine suppresses breast cancer metastasis by targeting ITGB1 and inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 19(1):367–374
Sarode GS, Sarode SC, Maniyar N, Anand R, Patil S (2018) Oral cancer databases: a comprehensive review. J oral Pathol Medicine: Official Publication Int Association Oral Pathologists Am Acad Oral Pathol 47(6):547–556
Shen J, Hong L, Yu D, Cao T, Zhou Z, He S (2019) LncRNA XIST promotes pancreatic cancer migration, invasion and EMT by sponging miR-429 to modulate ZEB1 expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 113:17–26
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34
Sun Y, Shen S, Liu X, Tang H, Wang Z, Yu Z, Li X, Wu M (2014) MiR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting Onecut2 in colorectal carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 390(1–2):19–30
Sun B, Zheng X, Ye W, Zhao P, Ma G (2021a) : LncRNA LINC01303 Promotes the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas via the miR-429/ZEB1/EMT Axis. Journal of oncology 2021:7974012
Sun Y, Shen S, Liu X, Tang H, Wang Z, Yu Z, Li X, Wu M (2021b) Correction to: miR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting Onecut2 in colorectal carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 476(8):3215–3216
Takahara T, Kasamatsu A, Yamatoji M, Iyoda M, Kasama H, Saito T, Takeuchi S, Endo-Sakamoto Y, Shiiba M, Tanzawa H et al (2017) SIPA1 promotes invasion and migration in human oral squamous cell carcinoma by ITGB1 and MMP7. Exp Cell Res 352(2):357–363
Wang N, Chang LL (2020) Maspin suppresses cell invasion and migration in gastric cancer through inhibiting EMT and angiogenesis via ITGB1/FAK pathway. Hum Cell 33(3):663–675
Wang X, Zhao Y, Qian H, Huang J, Cui F, Mao Z (2015) The miR-101/RUNX1 feedback regulatory loop modulates chemo-sensitivity and invasion in human lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(9):15030–15042
Wu CL, Ho JY, Hung SH, Yu DS (2018) miR-429 expression in bladder cancer and its correlation with tumor behavior and clinical outcome. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 34(6):335–340
Xue J, Zhu S, Qi F, Zhu K, Cao P, Yang J, Wang Z (2021) RUNX1/miR-582-5p pathway regulates the Tumor Progression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Targeting COL5A1. Front Oncol 11:610992
Yao Y, Xu Q, Yan L, Jiao Y, Su Q, Li X, Liu C, Zhao F (2020) MiRNA-128 and MiRNA-142 regulate tumorigenesis and EMT in oral squamous cell carcinoma through HOXA10. Cancer Manage Res 12:9987–9997
Zhang M, Dong BB, Lu M, Zheng MJ, Chen H, Ding JZ, Xu AM, Xu YH (2016) miR-429 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FSCN1 in gastric cancer cells. OncoTargets and Therapy 9:1123–1133
Zhang X, Feng H, Li Z, Li D, Liu S, Huang H, Li M (2018a) Application of weighted gene co-expression network analysis to identify key modules and hub genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. OncoTargets and Therapy 11:6001–6021
Zhang X, Feng H, Li D, Liu S, Amizuka N, Li M (2018b) Identification of differentially expressed genes Induced by aberrant methylation in oral squamous cell carcinomas using Integrated Bioinformatic Analysis. Int J Mol Sci 19(6)
Zhang X, Feng H, Li Z, Guo J, Li M (2018c) Aspirin is involved in the cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, Cell Migration, and Invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 19(7)
Zhang L, Zhang T, Deng Z, Sun L (2019) MicroRNA–3653 inhibits the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting ITGB1. Oncol Rep 41(3):1669–1677
Zhang X, Ren L, Yan X, Shan Y, Liu L, Zhou J, Kuang Q, Li M, Long H, Lai W (2020a) Identification of immune-related lncRNAs in periodontitis reveals regulation network of gene-lncRNA-pathway-immunocyte. Int Immunopharmacol 84:106600
Zhang L, Liu Q, Mu Q, Zhou D, Li H, Zhang B, Yin C (2020b) MiR-429 suppresses proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Thorac cancer 11(11):3126–3138
Zhang X, Zhang S, Yan X, Shan Y, Liu L, Zhou J, Kuang Q, Li M, Long H, Lai W (2021) m6A regulator-mediated RNA methylation modification patterns are involved in immune microenvironment regulation of periodontitis. J Cell Mol Med 25(7):3634–3645
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
Ningxia Natural Science Foundation Project Plan (Project number: 2022AAC03565).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation, XZ, and XL; formal analysis, YY, JC, and TZ; data curation, XZ, YY, JC, and TZ; writing, original draft preparation, XL; writing, review and editing, XZ, and XL; supervision, XZ; project administration, XZ, and XL; and funding acquisition, XZ. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The consent agreement was signed by all patients and the project was approved by the Ethics Committee of General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University (Ethics approval number: KYLL-2021-772).
Consent to participate
All individuals have individual rights that are not to be infringed. Identifying details (names, dates of birth, identity numbers, biometrical characteristics (such as facial features, fingerprint, writing style, voice pattern, DNA or other distinguishing characteristic) and other information) of the participants in the study will not be published. When biological material is donated or data generated as part of a research project, as part of the informed consent process, we ensure that participants understand what kind of (personal) data will be processed, how it will be used and for what purpose. Informed written consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Consent for publication
All authors declare that they have seen and approved the submitted version of this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Yang, Y., Chen, J. et al. RUNX1/miR-429 feedback loop promotes growth, metastasis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting ITGB1. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-02960-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-02960-9