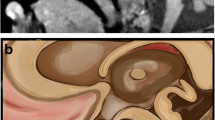
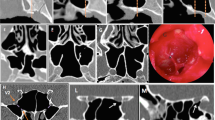
Abstract
Purpose
Inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus (IPSS) is a rare tumor with debated surgical management due to its proximity to vital structures. The aim of this manuscript is to highlight the role of a transpterygoid approach (TPA) and pedicle-orientated strategy in case of involvement of critical structures in IPSS and compare it with data from the literature.
Methods
Patients with primary IPSS between January 2000 and June 2021 were included. Pre-operative CT/MRI were analyzed to classify the pneumatization of the SS and predict the insertion point of the inverted papilloma. All patients were treated with a trans-sphenoidal approach which was combined with a TPA in case of lateral insertion point. A systematic search was also performed to summarize the available literature.
Results
Twenty-two patients were treated for IPSS. By CT, the SS was categorized with type III pneumatization in 72.8% of cases. Eleven patients (50%) were treated with a TPA with a statistical association with the insertion point on the SS lateral wall (p = 0.01), rather than a SS pneumatization (p = 0.63). The overall success was 95.5% after a mean follow-up of 35.9 months. For the literature, 26 publications were included on 97 patients and described a trans-sphenoidal approach with a success rate of 84.6% after a mean follow-up of 24.5 months.
Conclusion
IPSS is generally treated with a sphenoidotomy approach, although in selected cases, a TPA should be preferred to expose the whole SS lateral wall though allowing a complete pedicled oriented resection of the tumor.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Upon reasonable request.
References
Trent MS, Goshtasbi K, Hui L et al (2021) A systematic review of definitive treatment for inverted papilloma attachment site and associations with recurrence. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12:1945998211051975. https://doi.org/10.1177/01945998211051975
Krouse JH (2000) Development of a staging system for inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 110:965–968. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200006000-00015
Guillemaud JP, Witterick IJ (2009) Inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus: clinical presentation, management, and systematic review of the literature. Laryngoscope 119:2466–2471. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20718
Pagella F, Pusateri A, Giourgos G, Tinelli C, Matti E (2014) Evolution in the treatment of sinonasal inverted papilloma: pedicle-oriented endoscopic surgery. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28:75–81. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2014.28.3985
Suh JD, Ramakrishnan VR, Thompson CF et al (2015) Inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus: risk factors for disease recurrence. Laryngoscope 125:544–548. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24929
Akkari M, Lassave J, Mura T et al (2016) Atypical presentations of sinonasal inverted papilloma: surgical management and influence on the recurrence rate. Am J Rhinol Allergy 30:149–154. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4288
Kasemsiri P, Solares CA, Carrau RL et al (2013) Endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid approaches: anatomical landmarks for planning the surgical corridor. Laryngoscope 123:811–815. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.23697
Vaezi A, Cardenas E, Pinheiro-Neto C et al (2015) Classification of sphenoid sinus pneumatization: relevance for endoscopic skull base surgery. Laryngoscope 125:577–581. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24989
Hammer G, Radberg C (1961) The sphenoidal sinus. An anatomical and roentgenologic study with reference to transsphenoid hypophysectomy. Acta radiol 56:401–422
Fang G, Lou H, Yu W et al (2016) Prediction of the originating site of sinonasal inverted papilloma by preoperative magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 6:1221–1228. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21836
Lee DK, Chung SK, Dhong HJ et al (2007) Focal hyperostosis on CT of sinonasal inverted papilloma as a predictor of tumor origin. Am J Neuroradiol 28:618–621
Liu TW, Hung SH, Chen PY (2016) Sinonasal spindle cell carcinoma presenting with bilateral visual loss: a case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett 12:401–404. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4620
Rabelo GFN, Freitas VA, Santos BH, Ferreira DCDS, Magalhães AEMS, De CMCM (2014) Sphenoid sinus inverted papilloma: a case report and literature review. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 18:332–335. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1370761
Strojan P, Jereb S, Borsos I, But-Hadzic J, Zidar N (2013) Radiotherapy for inverted papilloma: a case report and review of the literature. Radiol Oncol 47:71–76. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10019-012-0045-8
Cheng K, Chen H, Zhou S, Wang S, Zhong B (2012) Isolated inverting papilloma of the sphenoid sinus: clinical presentations, imaging manifestations, and therapeutic strategies. J Craniofac Surg 23:1109–1114. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e31825434fc
Jiang X, Huang Q, Tang J, Hoffman MR (2012) Monophasic epithelial synovial sarcoma accompanied by an inverted papilloma in the sphenoid sinus. Case Rep Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/379720
Liu SC, Lee JC, Chen JJ, Lin YS (2010) Isolated inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus. J Chin Med Assoc 73:503–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1726-4901(10)70108-8
Balasubramani Y, Ellul S, Kam A, McLean C, Malham G (2009) Sinonasal inverted papilloma mimicking a pituitary macroadenoma. J Clin Neurosci 16:328–330
Joseph JA, Moorthy R, Saleh H (2009) Endoscopic management of inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2007.12.010
Cho HJ, Kim JK, Kim K, Kim YS, Lee JG, Yoon JH (2008) Endoscopic surgery for inverted papilloma originating from the sphenoid sinus and related clinical characteristics. Acta Otolaryngol 128:1120–1125. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480701874469
Yiotakis I, Gkoritsa E, Manolopoulos L, Kandiloros D, Korres S, Ferekidis E (2006) Inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus: presentation of three cases. Rhinology 44:164–168
Fakhri S, Citardi MJ, Wolfe S, Batra PS, Prayson RA, Lanza DC (2005) Challenges in the management of sphenoid inverted papilloma. Am J Rhinol 19:207–213
Lee JT, Bhuta S, Lufkin R, Castro DJ (2003) Isolated inverting papilloma of the sphenoid sinus. Laryngoscope 113:41–44. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200301000-00008
Yiotakis J, Hantzakos A, Kandiloros D, Ferekidis E (2002) A rare location of bilateral inverted papilloma of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Rhinology 40:220–222
Eisen MD, Buchmann L, Litman RS, Kennedy DW (2002) Inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus presenting with auditory symptoms: a report of two cases. Laryngoscope 112:1197–1200. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200207000-00010
Nishio S, Samoto K, Takeshita I, Matsumoto K, Matsushima T, Fukui M (2001) Inverting papilloma of the sphenoid sinus: report of two cases. J Clin Neurosci 8:168–170. https://doi.org/10.1054/jocn.2000.0727
Peters BW, O’Reilly RC, Willcox TO, Rao VM, Lowry LD, Keane WM (1995) Inverted papilloma isolated to the sphenoid sinus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113:771–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0194-59989570019-6
Tam YY, Chen CK, Chang KP (2013) Sphenoethmoidal inverted papilloma causing ipsilateral abducens nerve palsy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148:703–704. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599812473236
Srinivasan R, Portillo E, Takashima M (2012) Inverted papilloma ooriginating from the opticocarotid recess. Otolaryngol Neck Surg 147:P250–P250
Ho AKH, Brinkman D, Khan MH (2020) Inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus— a case report. Otolaryngol Case Reports 15:100173
Kim JS, Lee EJ (2021) Endoscopic Findings of Inverted Papilloma in the Sphenoid Sinus. Ear Nose Throat J 100:NP212–NP213. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561319871238
McElveen JT, Fee WE (1981) Inverting papilloma of the sphenoid sinus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 89:710–712. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459988108900502
Alba JR, Armengot M, Díaz A, Pérez A, Rausell N (2002) BJI papilloma of the sphenoid sinus. AOB 56:399–402
Richard WKY, Asha’AriAhmadRahman ZAMZAA (2017) Bilateral sinonasal inverted papilloma: case report and literature review. Int Med J 24:422–424
Yiotakis I, Psarommatis I, Manolopoulos L, Ferekidis E (2001) AGI inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus. Isolated inverted papilloma of the sphenoid sinus. Laryngol Otol 15:227. https://doi.org/10.1258/0022215011907046
Kim JS, Kwon SH (2017) Recurrence of sinonasal inverted papilloma following surgical approach: a meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 127:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.26222
Hiremath SB, Gautam AA, Sheeja K, Benjamin G (2018) Assessment of variations in sphenoid sinus pneumatization in Indian population: a multidetector computed tomography study. Indian J Radiol Imaging 28:273–279. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijri.IJRI_70_18
Lee JJ, Roland LT, Licata JJ et al (2020) Morphologic, intraoperative, and histologic risk factors for sinonasal inverted papilloma recurrence. Laryngoscope 130(3):590–596. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28078
Tong CCL, Patel NN, Maina IW et al (2019) Inverted papilloma with multifocal attachment is associated with increased recurrence. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 9:865–869. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22342
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vinciguerra, A., Guichard, J.P., Verillaud, B. et al. Extended sphenoidotomy combined with transpterygoid approach for sphenoidal sinus inverted papilloma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 5369–5378 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08106-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08106-6