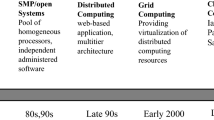
Abstract
Edge computing aims to address the challenges associated with communicating and transferring large amounts of data generated remotely to a data center in a timely and efficient manner. A central pillar of edge computing is local (i.e., at- or near-source) data processing capability so that data transfer to a data center for processing can be minimized. Data compression at the edge is therefore a natural component of edge workflows. We present a survey of data compression algorithms with a focus on edge computing. Not all compression algorithms can accommodate the data type heterogeneity, tight processing and communication time constraints, or energy efficiency requirement characteristics of edge computing. We discuss specific examples of compression algorithms that are being explored in the context of edge computing. We end our review with a brief survey of emerging quantum compression techniques that are of importance in quantum information processing, including the proposed concept of quantum edge computing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Passian A, Imam N (2019) Nanosystems, edge computing, and the next generation computing systems. Sensors 19(18):4048
Satyanarayanan M (2019) How we created edge computing. Nat Electron 2(1):42
Reinsel D, Gantz J, Rydning J (2018) The digitization of the world from edge to core. International Data Corporation, Framingham, p 16
Jayakumar H, Raha A, Kim Y, Sutar S, Lee WS, Raghunathan V (2016) Energy-efficient system design for IoT devices. In: 2016 21st Asia and South Pacific design automation conference (ASP-DAC). IEEE, pp 298–301
Väänänen O, Hämäläinen T (2018) Requirements for energy efficient edge computing: a survey. In: Internet of things, smart spaces, and next generation networks and systems. Springer, pp 3–15
Passian A, Buchs G, Seck CM, Marino AM, Peters NA (2022) Concept of a quantum edge simulator: edge computing and sensing in the quantum era. Sensors
Sonmez C, Ozgovde A, Ersoy C (2018) EdgeCloudSim: an environment for performance evaluation of edge computing systems. Trans Emerging Telecommun Technol 29(11):3493
Freymann R, et al (2021) Renovation of EdgeCloudSim: an efficient discrete-event approach. In: 2021 Sixth international conference on fog and mobile edge computing (FMEC). pp 9–16
Plesch M, Bužek V (2010) Efficient compression of unknown quantum information. Phys Rev A 81:032317
Jain AK (1981) Image data compression: a review. Proc IEEE 69(3):349–389
Deorowicz S, Grabowski S (2013) Data compression for sequencing data. Algorithms Mol Biol 8(1):1–13
Brandon MC, Wallace DC, Baldi P (2009) Data structures and compression algorithms for genomic sequence data. Bioinformatics 25(14):1731–1738
Limaye A, Adegbija T (2018) Hermit: a benchmark suite for the internet of medical things. IEEE Internet Things J 5(5):4212–4222
Athavale Y, Krishnan S (2020) A telehealth system framework for assessing knee-joint conditions using vibroarthrographic signals. Biomed Signal Process Control 55:101580
Abdellatif AA, Emam A, Chiasserini C-F, Mohamed A, Jaoua A, Ward R (2019) Edge-based compression and classification for smart healthcare systems: concept, implementation and evaluation. Expert Syst Appl 117:1–14
Shi W, Chen J, Luo M, Chen M (2019) High efficiency referential genome compression algorithm. Bioinformatics 35(12):2058–2065
Bhola V, Bopardikar AS, Narayanan R, Lee K, Ahn T (2011) No-reference compression of genomic data stored in fastq format. In: 2011 IEEE international conference on bioinformatics and biomedicine. IEEE, pp 147–150
Riffle M, Eng JK (2009) Proteomics data repositories. Proteomics 9(20):4653–4663
Tegmark M, Taylor AN, Heavens AF (1997) Karhunen–Loeve eigenvalue problems in cosmology: How should we tackle large data sets? Astrophys J 480(1):22
Maurizio T (2019) Compression of smooth one-dimensional data series using polycomp. Astron Data Anal Softw Syst XXVI 521:560
Abdellatif AA, Emam A, Chiasserini C-F, Mohamed A, Jaoua A, Ward R (2019) Edge-based compression and classification for smart healthcare systems: concept, implementation and evaluation. Expert Syst Appl 117:1–14
Zhang W, Wang J, Han G, Huang S, Feng Y, Shu L (2020) A data set accuracy weighted random forest algorithm for IoT fault detection based on edge computing and blockchain. IEEE Internet Things J 8(4):2354–2363
Hosseini M-P, Tran TX, Pompili D, Elisevich K, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2020) Multimodal data analysis of epileptic EEG and rs-fMRI via deep learning and edge computing. Artif Intell Med 104:101813
Yu Z, Hu J, Min G, Lu H, Zhao Z, Wang H, Georgalas N (2018) Federated learning based proactive content caching in edge computing. In: 2018 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM). IEEE, pp 1–6
Du M, Wang K, Chen Y, Wang X, Sun Y (2018) Big data privacy preserving in multi-access edge computing for heterogeneous internet of things. IEEE Commun Mag 56(8):62–67
Kamath C (2009) Scientific data mining: a practical perspective. SIAM, Philadelphia
Sufian A, Ghosh A, Sadiq AS, Smarandache F (2020) A survey on deep transfer learning to edge computing for mitigating the COVID-19 pandemic. J Syst Architect 108:101830
Liu Y, Sun Y, Li B (2019) A modified IP-based NILM approach using appliance characteristics extracted by 2-sax. IEEE Access 7:48119–48128
Sinaeepourfard A, Garcia J, Masip-Bruin X, Marin-Tordera E (2017) A novel architecture for efficient fog to cloud data management in smart cities. In: 2017 IEEE 37th international conference on distributed computing systems (ICDCS). IEEE, pp 2622–2623
Pieterse C, du Plessis WP, Focke RW (2018) Metrics to evaluate compression algorithms for raw SAR data. IET Radar Sonar Navig 13(3):333–346
Liu S, Wang D, Maljovec D, Anirudh R, Thiagarajan JJ, Jacobs SA, Van Essen BC, Hysom D, Yeom J-S, Gaffney J et al (2019) Scalable topological data analysis and visualization for evaluating data-driven models in scientific applications. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graphics 26(1):291–300
Chevyrev I, Nanda V, Oberhauser H (2018) Persistence paths and signature features in topological data analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(1):192–202
Wasserman L (2018) Topological data analysis. Annu Rev Stat Appl 5:501–532
Lloyd S, Garnerone S, Zanardi P (2016) Quantum algorithms for topological and geometric analysis of data. Nat Commun 7(1):1–7
Dłotko P, Qiu W, Rudkin S (2019) Cyclicality, periodicity and the topology of time series. arXiv:1905.12118
Soler M, Plainchault M, Conche B, Tierny J (2018) Topologically controlled lossy compression. In: 2018 IEEE Pacific visualization symposium (PacificVis). IEEE, pp 46–55
Snášel V, Nowaková J, Xhafa F, Barolli L (2017) Geometrical and topological approaches to big data. Future Gener Comput Syst 67:286–296
Raja S (2019) Joint medical image compression-encryption in the cloud using multiscale transform-based image compression encoding techniques. Sādhanā 44(2):28
Putra TA, Leu J-S (2019) Multilevel neural network for reducing expected inference time. IEEE Access 7:174129–174138
Yan Y, Pei Q (2019) A robust deep-neural-network-based compressed model for mobile device assisted by edge server. IEEE Access 7:179104–179117
Gurney K (2018) An introduction to neural networks. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Yang J, Shen X, Xing J, Tian X, Li H, Deng B, Huang J, Hua X-s (2019) Quantization networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 7308–7316
Han S, Mao H, Dally WJ (2015) Deep compression: Compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and huffman coding. arXiv:1510.00149
Li H, Guo Y, Wang Z, Xia S, Zhu W (2019) Adacompress: adaptive compression for online computer vision services. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on multimedia. pp 2440–2448
Guo D, Wang W, Chen Q, Zhao N, Zhang Z (2019) Queue-stable dynamic compression and transmission with mobile edge computing. In: ICC 2019–2019 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC). IEEE, pp 1–6
Ren J, Ruan Y, Yu G (2019) Data transmission in mobile edge networks: Whether and where to compress? IEEE Commun Lett 23(3):490–493
Duvignau R, Gulisano V, Papatriantafilou M, Savic V (2019) Streaming piecewise linear approximation for efficient data management in edge computing. In: Proceedings of the 34th ACM/SIGAPP symposium on applied computing. pp 593–596
Liu L, Chen X, Lu Z, Wang L, Wen X (2019) Mobile-edge computing framework with data compression for wireless network in energy internet. Tsinghua Sci Technol 24(3):271–280
Borova M, Prauzek M, Konecny J, Gaiova K (2019) Environmental WSN edge computing concept by wavelet transform data compression in a sensor node. IFAC-PapersOnLine 52(27):246–251
Azar J, Makhoul A, Barhamgi M, Couturier R (2019) An energy efficient IoT data compression approach for edge machine learning. Future Gen Comput Syst 96:168–175
Yoshida S, Izumi S, Kajihara K, Yano Y, Kawaguchi H, Yoshimoto M (2019) Energy-efficient spectral analysis method using autoregressive model-based approach for internet of things. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 66(10):3896–3905
Xu D, Li Q, Zhu H (2019) Energy-saving computation offloading by joint data compression and resource allocation for mobile-edge computing. IEEE Commun Lett 23(4):704–707
Hossain K, Rahman M, Roy S (2019) IoT data compression and optimization techniques in cloud storage: current prospects and future directions. Int J Cloud Appl Comput (IJCAC) 9(2):43–59
Xu Q, Zhang P, Liu W, Liu Q, Liu C, Wang L, Toprac A, Qin SJ (2018) A platform for fault diagnosis of high-speed train based on big data. IFAC-PapersOnLine 51(18):309–314
Li H, Hu C, Jiang J, Wang Z, Wen Y, Zhu W (2018) Jalad: Joint accuracy-and latency-aware deep structure decoupling for edge-cloud execution. In: 2018 IEEE 24th international conference on parallel and distributed systems (ICPADS). IEEE, pp 671–678
Athavale Y, Krishnan S (2018) A device-independent efficient actigraphy signal-encoding system for applications in monitoring daily human activities and health. Sensors 18(9):2966
Rahman M, Islam M, Calhoun J, Chowdhury M (2019) Real-time pedestrian detection approach with an efficient data communication bandwidth strategy. Transp Res Rec 2673(6):129–139
Bhargava K, Ivanov S, Donnelly W, Kulatunga C (2016) Using edge analytics to improve data collection in precision dairy farming. In: 2016 IEEE 41st conference on local computer networks workshops (LCN workshops). IEEE, pp 137–144
Zaydman O, Zhirin R (2019) Teleportation of VM disk images over WAN. In: International conference on cloud computing. Springer, pp 83–98
Queralta JP, Gia T, Tenhunen H, Westerlund T (2019) Edge-ai in LoRa-based health monitoring: fall detection system with fog computing and LSTM recurrent neural networks. In: 2019 42nd International conference on telecommunications and signal processing (TSP). IEEE, pp 601–604
Barik RK, Dubey H, Mankodiya K, Sasane SA, Misra C (2019) GeoFog4health: a fog-based SDI framework for geospatial health big data analysis. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 10(2):551–567
Guo Y, Zou B, Ren J, Liu Q, Zhang D, Zhang Y (2019) Distributed and efficient object detection via interactions among devices, edge, and cloud. IEEE Trans Multimed 21(11):2903–2915
Jiang T, Lu T, Gu N (2019) Themis: An AST-based lock-free routes synchronizing and sharing system for self-driving in edge computing environments. IEEE Access 7:151692–151704
Havers B, Duvignau R, Najdataei H, Gulisano V, Koppisetty AC, Papatriantafilou M (2019) Driven: a framework for efficient data retrieval and clustering in vehicular networks. In: 2019 IEEE 35th International conference on data engineering (ICDE). IEEE, pp 1850–1861
Farayez A, Reaz MBI, Arsad N (2018) Spade: activity prediction in smart homes using prefix tree based context generation. IEEE Access 7:5492–5501
Prentice C, Karakonstantis G (2018) Smart office system with face detection at the edge. In: 2018 IEEE SmartWorld, ubiquitous intelligence and computing, advanced and trusted computing, scalable computing and communications, cloud and big data computing, internet of people and smart city innovation (SmartWorld/SCALCOM/UIC/ATC/CBDCom/IOP/SCI). IEEE, pp 88–93
Dequan K, Desheng L, Zhang L, Lili H, Qingwu S, Xiaojun M (2020) Sensor anomaly detection in the industrial internet of things based on edge computing. Turkish J Electric Eng Comput Sci 28(1):331–346
Perera C, Qin Y, Estrella JC, Reiff-Marganiec S, Vasilakos AV (2017) Fog computing for sustainable smart cities: a survey. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 50(3):1–43
Östberg P-O, Byrne J, Casari P, Eardley P, Anta AF, Forsman J, Kennedy J, Le Duc T, Marino MN, Loomba R et al (2017) Reliable capacity provisioning for distributed cloud/edge/fog computing applications. In: 2017 European conference on networks and communications (EuCNC). IEEE, pp 1–6
Lu Y, Chen W, Poor HV (2019) Source coding at the edge: user preference oriented lossless data compression. In: ICC 2019–2019 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC). IEEE, pp 1–6
Nguyen TT, Ha VN, Le LB, Schober R (2019) Joint data compression and computation offloading in hierarchical fog-cloud systems. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 19:293–309
Bose T, Bandyopadhyay S, Kumar S, Bhattacharyya A, Pal A (2016) Signal characteristics on sensor data compression in IoT-an investigation. In: 2016 13th annual IEEE international conference on sensing, communication, and networking (SECON). IEEE, pp 1–6
Stojkoska BR, Nikolovski Z (2017) Data compression for energy efficient IoT solutions. In: 2017 25th telecommunication forum (TELFOR). IEEE, pp 1–4
Deepu CJ, Heng C-H, Lian Y (2016) A hybrid data compression scheme for power reduction in wireless sensors for IoT. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 11(2):245–254
Ying B (2016) An energy-efficient compression algorithm for spatial data in wireless sensor networks. In: 2016 18th international conference on advanced communication technology (ICACT). IEEE, pp 161–164
Ghahramani Z (2015) Probabilistic machine learning and artificial intelligence. Nature 521(7553):452–459
Ward DJ, MacKay DJ (2002) Fast hands-free writing by gaze direction. Nature 418(6900):838
Qiao W, Fang Z, Chang M-CF, Cong J (2019) An FPGA-based BWT accelerator for Bzip2 data compression. In: 2019 IEEE 27th annual international symposium on field-programmable custom computing machines (FCCM). IEEE, pp 96–99
Schoellhammer T, Greenstein B, Osterweil E, Wimbrow M, Estrin D (2004) Lightweight temporal compression of microclimate datasets. UCLA: Center for Embedded Network Sensing, 05
Suárez-Albela M, Fernández-Caramés TM, Fraga-Lamas P, Castedo L (2017) A practical evaluation of a high-security energy-efficient gateway for IoT fog computing applications. Sensors 17(9):1978
Yu C-H, Gao F, Lin S, Wang J (2019) Quantum data compression by principal component analysis. Quantum Inf Process 18(8):249
Rao KR, Yip PC (2018) The transform and data compression handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Zhao H, Li T, Chen G, Dong Z, Bo M, Pang C (2019) An online PLA algorithm with maximum error bound for generating optimal mixed-segments. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 1–17
Lin J-W, Liao S-W, Leu F-Y (2019) Sensor data compression using bounded error piecewise linear approximation with resolution reduction. Energies 12(13):2523
Grützmacher F, Beichler B, Hein A, Kirste T, Haubelt C (2018) Time and memory efficient online piecewise linear approximation of sensor signals. Sensors 18(6):1672
Al-Marridi AZ, Mohamed A, Erbad A, Al-Ali A, Guizani M (2019) Efficient EEG mobile edge computing and optimal resource allocation for smart health applications. In: 2019 15th international wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC). IEEE, pp 1261–1266
Du J, Liu S, Wei Y, Liu H, Wang X, Nan K (2017) Understanding sensor data using deep learning methods on resource-constrained edge devices. In: China conference on wireless sensor networks. Springer, pp 139–152
Dabholkar A, Muthiyan B, Srinivasan S, Ravi S, Jeon H, Gao J (2017) Smart illegal dumping detection. In: 2017 IEEE third international conference on big data computing service and applications (BigDataService). IEEE, pp 255–260
Akmandor AO, Hongxu Y, Jha NK (2018) Smart, secure, yet energy-efficient, internet-of-things sensors. IEEE Trans Multi-Scale Comput Syst 4(4):914–930
Ye L, Liu Q, Zhong W, Zhang Q (2017) A novel image compression framework at edges. In: 2017 IEEE visual communications and image processing (VCIP). IEEE, pp 1–5
Wang Y, Zhang H (2018) Visualize and compress single logo recognition neural network. In: International conference on bio-inspired computing: theories and applications. Springer, pp 331–342
Saha S, Rajasekaran S (2016) Nrgc: a novel referential genome compression algorithm. Bioinformatics 32(22):3405–3412
Watanabe T, Ae T, Nakamura A (1983) On the NP-hardness of edge-deletion and-contraction problems. Discret Appl Math 6(1):63–78
Shannon CE (2001) A mathematical theory of communication. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob Comput Commun Rev 5(1):3–55
Chen F, Ren H (2010) Comparison of vector data compression algorithms in mobile GIS. In: 2010 3rd international conference on computer science and information technology, vol 1. IEEE, pp 613–617
Wu Z-B, Yu J-Q (2019) Vector quantization: a review. Front Inf Technol Electron Eng 20(4):507–524
Safieh M, Freudenberger J (2018) Pipelined decoder for the limited context order Burrows–Wheeler transformation. IET Circuits Dev Syst 13(1):31–38
Zaharov V, Farahi RH, Snyder PJ, Davison BH, Passian A (2014) Karhunen–Loeve treatment to remove noise and facilitate data analysis in sensing, spectroscopy and other applications. Analyst 139(22):5927–5935
Cheng AF, Hawkins III SE, Nguyen L, Monaco CA, Seagrave GG (2007) Data compression using chebyshev transform. In: United States Patent, 07. Patent number US 7,249,153 B2
Tomasi M (2016) Polycomp: efficient and configurable compression of astronomical timelines. Astron Comput 16:88–98
Deorowicz S, Grabowski S (2018) Deltacomp: fast and efficient compression of astronomical timelines. New Astron 65:59–66
Kehtarnavaz N (2008) Chapter 7–frequency domain processing. In: Kehtarnavaz N (ed) Digital signal processing system design, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Burlington, pp 175–196
Maccone C (2016) Evolution of seti technology to pick up messages from et. In: Proceedings of the forty-eighth history symposium of the international academy of astronautics, vol 46
Alsing J, Wandelt B (2018) Generalized massive optimal data compression. Mon Notices R Astron Soc Lett 476(1):L60–L64
Galli L, Salzo S (2004) Lossless hyperspectral compression using KLT. In: IGARSS 2004. 2004 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium, vol 1. IEEE
Gerbrands JJ (1981) On the relationships between SVD, KLT and PCA. Pattern Recognit 14(1):375–381
Chatterjee A, Shah RJ, Hasan KS (2018) Efficient data compression for IoT devices using huffman coding based techniques. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on big data (big data). IEEE, pp 5137–5141
Apostolico A (2007) Fast gapped variants for Lempel–Ziv–Welch compression. Inf Comput 205(7):1012–1026
Yazdanpanah A, Hashemi MR (2010) A new compression ratio prediction algorithm for hardware implementations of LZW data compression. In: 2010 15th CSI international symposium on computer architecture and digital systems. IEEE, pp 155–156
Chowdary KMR, Tiwari V, Jebarani ME (2019) Edge computing by using LZW algorithm. Int J Adv Res Ideas Innov Technol 5(1):228–230
Swaraja K, Meenakshi K, Kora P (2020) An optimized blind dual medical image watermarking framework for tamper localization and content authentication in secured telemedicine. Biomed Signal Process Control 55:101665
Anand A, Singh AK (2020) An improved DWT-SVD domain watermarking for medical information security. Comput Commun 152:72–80
Singh P, Gupta AK, Singh R (2020) Improved priority-based data aggregation congestion control protocol. Mod Phys Lett B 34(02):2050029
Chou C-Y, Wu A-YA (2019) Low-complexity compressive analysis in sub-eigenspace for ECG telemonitoring system. In: ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP). IEEE, pp 7575–7579
Baraniuk RG, Foucart S, Needell D, Plan Y, Wootters M (2017) Exponential decay of reconstruction error from binary measurements of sparse signals. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 63(6):3368–3385
Sherbert K et al (2022) Quantum compressive sensing: mathematical machinery, quantum algorithms, and quantum circuitry. Appl Sci 12(15):7525
Rădescu R, Paşca S (2017) Procedures of extending the alphabet in combined coding for prediction by partial string matching in text compression. In: 2017 9th international conference on electronics, computers and artificial intelligence (ECAI). IEEE, pp 1–6
Rădescu R, Paşca S (2017) Experimental results in prediction by partial matching and star transformation applied in lossless compression of text files. In: 2017 10th International symposium on advanced topics in electrical engineering (ATEE). IEEE, pp 17–22
Zhang Y, Adjeroh DA (2008) Prediction by partial approximate matching for lossless image compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(6):924–935
Neto FDN, de Souza-Baptista C, Campelo CE (2018) Combining Markov model and prediction by partial matching compression technique for route and destination prediction. Knowl Based Syst 154:81–92
Yang P, Hsieh C-J, Wang J-L (2018) History PCA: a new algorithm for streaming PCA. arXiv:1802.05447
Burrello A, Marchioni A, Brunelli D, Benini L (2019) Embedding principal component analysis for data reduction in structural health monitoring on low-cost IoT gateways. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM international conference on computing frontiers, pp 235–239
Luo G, Yi K, Cheng S-W, Li Z, Fan W, He C, Mu Y (2015) Piecewise linear approximation of streaming time series data with max-error guarantees. In: 2015 IEEE 31st international conference on data engineering. IEEE, pp 173–184
Bagherian M, Kim RB, Jiang C, Sartor MA, Derksen H, Najarian K (2021) Coupled matrix–matrix and coupled tensor-matrix completion methods for predicting drug-target interactions. Brief Bioinform 22(2):2161–2171
Acar E, Kolda TG, Dunlavy DM (2011) All-at-once optimization for coupled matrix and tensor factorizations. arXiv:1105.3422
Kuleshov V, Chaganty A, Liang P (2015) Tensor factorization via matrix factorization. In: Artificial intelligence and statistics. PMLR, pp 507–516
Bagherian M, Tarzanagh DA, Dinov I, Welch JD (2022) A bilevel optimization method for tensor recovery under metric learning constraints. arXiv:2209.00545
Ballester-Ripoll R, Lindstrom P, Pajarola R (2019) TTHRESH: Tensor compression for multidimensional visual data. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph arXiv:1806.05952
Liu H, Yang LT, Lin M, Yin D, Guo Y (2018) A tensor-based holistic edge computing optimization framework for internet of things. IEEE Network 32(1):88–95
Kolda TG, Bader BW (2009) Tensor decompositions and applications. SIAM Rev 51(3):455–500
Bai G, Yang Y, Chiribella G (2020) Quantum compression of tensor network states. New J Phys 22(4):043015
Cao X, Madria S, Hara T (2017) Efficient z-order encoding based multi-modal data compression in WSNs. In: 2017 IEEE 37th international conference on distributed computing systems (ICDCS). IEEE, pp 2185–2192
Cao X, Madria S, Hara T (2020) Multi-model z-compression for high speed data streaming and low-power wireless sensor networks. Distrib Parallel Database 38(1):153–191
Di S, Cappello F (2016) Fast error-bounded lossy HPC data compression with SZ. In: 2016 IEEE international parallel and distributed processing symposium (IPDPS). IEEE, pp 730–739
Khalaf W, Zaghar D, Hashim N (2019) Enhancement of curve-fitting image compression using hyperbolic function. Symmetry 11(2):291
Paek J, Ko J (2015) \(k\)-means clustering-based data compression scheme for wireless imaging sensor networks. IEEE Syst J 11(4):2652–2662
Beals R et al (2013) Efficient distributed quantum computing. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 469(2153):20120686
Bravyi S, Gosset D, König R (2018) Quantum advantage with shallow circuits. Science 362(6412):308–311
Pivoluska M, Plesch M (2022) Implementation of quantum compression on IBM quantum computers. Sci Rep 12(1):1–9
Khanian ZB, Winter A (2022) General mixed-state quantum data compression with and without entanglement assistance. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 68(5):3130–3138
Schumacher B (1995) Quantum coding. Phys Rev A 51(4):2738
Jozsa R, Schumacher B (1994) A new proof of the quantum noiseless coding theorem. J Mod Opt 41(12):2343–2349
Mitsumori Y, Vaccaro JA, Barnett SM, Andersson E, Hasegawa A, Takeoka M, Sasaki M (2003) Experimental demonstration of quantum source coding. Phys Rev Lett 91(21):217902
Patra A et al (2021) Compression of high-resolution satellite images using optical image processing. In: Nguyen T (ed) Satellite systems: design, modeling, simulation and analysis. IntechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.94147
Beser ND (1994) Space data-compression standards. J Hopkins APL Tech Dig 15(3):206–223
Gia TN, Qingqing L, Queralta JP, Tenhunen H, Zou Z, Westerlund T (2019) Lossless compression techniques in edge computing for mission-critical applications in the IoT. In: Twelfth international conference on mobile computing and ubiquitous network (ICMU) vol 2019, pp 1–2. https://doi.org/10.23919/ICMU48249.2019.9006647
Ma L, Ding L (2022) Hybrid quantum edge computing network. Proc SPIE 12238:122380F–1
Gisin N, Ribordy G, Tittel W et al (2002) Quantum cryptography. Rev Mod Phys 74(1):145
Rozema LA, Mahler DH, Hayat A, Turner PS, Steinberg AM (2014) Quantum data compression of a qubit ensemble. Phys Rev Lett 113(16):160504
Huang C-J, Ma H, Yin Q, Tang J-F, Dong D, Chen C, Xiang G-Y, Li C-F, Guo G-C (2020) Realization of a quantum autoencoder for lossless compression of quantum data. Phys Rev A 102(3):032412
Fan C-R, Lu B, Feng X-T, Gao W-C, Wang C (2021) Efficient multi-qubit quantum data compression. Quantum Eng 3(2):e67
Yang Y, Chiribella G, Ebler D (2016) Efficient quantum compression for ensembles of identically prepared mixed states. Phys Rev Lett 116(8):080501
Renes JM, Renner R (2012) One-shot classical data compression with quantum side information and the distillation of common randomness or secret keys. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 58(3):1985–1991
Datta N, Renes JM, Renner R, Wilde MM (2013) One-shot lossy quantum data compression. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 59(12):8057–8076
Beals R, Brierley S, Gray O, Harrow AW, Kutin S, Linden N, Shepherd D, Stather M (2013) Efficient distributed quantum computing. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 469(2153):20120686
Barz S, Kashefi E, Broadbent A, Fitzsimons JF, Zeilinger A, Walther P (2012) Demonstration of blind quantum computing. Science 335(6066):303–308
Barnum H, Fuchs CA, Jozsa R, Schumacher B (1996) General fidelity limit for quantum channels. Phys Rev A 54(6):4707
Romero J, Olson JP, Aspuru-Guzik A (2017) Quantum autoencoders for efficient compression of quantum data. Quantum Sci Technol 2(4):045001
Hayden P, Jozsa R, Winter A (2002) Trading quantum for classical resources in quantum data compression. J Math Phys 43(9):4404–4444
Wilde MM (2013) Quantum information theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Von Neumann J (2013) Mathematical foundations of quantum mechanics, vol 38. Springer, Berlin
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27(3):379–423
Chehade SS, Vershynina A (2019) Quantum entropies. Scholarpedia 14(2):53131
Hayashi M, Matsumoto K (2002) Quantum universal variable-length source coding. Phys Rev A 66(2):022311
Yakubovich S (2020) Discrete Mehler–Fock transforms. Integral Transform Spec Funct 31(8):645–654
Ahmed N, Natarajan T, Rao KR (1974) Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Trans Comput 100(1):90–93
Pun C-M (2006) A novel DFT-based digital watermarking system for images. In: 2006 8th international conference on signal processing, vol 2. IEEE
Anitha T, Vijayalakshmi K (2018) FFT based compression approach for medical images. Int J Appl Eng Res 13(6):3550–3567
Mukhopadhyay J (2019) Image and video processing in the compressed domain. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London
Kok CW, Tam WS (2019) Fractal image interpolation: a tutorial and new result. Fractal Fract 3(1):7
Kish LB (2016) Comments on “Sub-k bt micro-electromechanical irreversible logic gate’’. Fluct Noise Lett 15(04):1620001
Hale JC, Sellars HL (1981) Historical data recording for process computers. Chem Eng Prog (United States) 77(11)
Fink E, Gandhi HS (2011) Compression of time series by extracting major extrema. J Exp Theor Artif Intell 23(2):255–270
Sharma L, Dandapat S, Mahanta A (2012) Multichannel ECG data compression based on multiscale principal component analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 16(4):730–736
Al-Wahaib MS, Wong K (2010) A lossless image compression algorithm using duplication free run-length coding. In: 2010 second international conference on network applications, protocols and services. IEEE, pp 245–250
Aviyente S (2007) Compressed sensing framework for EEG compression. In: 2007 IEEE/SP 14th workshop on statistical signal processing. IEEE, pp 181–184
Gunasheela S, Prasantha H (2019) Compressed sensing for image compression: survey of algorithms. In: Emerging research in computing, information, communication and applications. Springer, pp 507–517
Begleiter R, El-Yaniv R, Yona G (2004) On prediction using variable order Markov models. J Artif Intell Res 22:385–421
Tiwari VS, Arya A, Chaturvedi S (2018) Scalable prediction by partial match (PPM) and its application to route prediction. Appl Inform 5:1–16
Lu T, Liu Q, He X, Luo H, Suchyta E, Choi J, Podhorszki N, Klasky S, Wolf M, Liu T et al (2018) Understanding and modeling lossy compression schemes on HPC scientific data. In: 2018 IEEE International parallel and distributed processing symposium (IPDPS). IEEE, pp 348–357
Zeybek EH, Fournier R, Naït A (2012) Multimodal compression applied to biomedical data. J Biomed Sci Eng 5:755–761
Monica D, Widipaminto A (2020) Fuzzy transform for high-resolution satellite images compression. Telkomnika 18(2):1130–1136
Nagaraj N (2019) Using cantor sets for error detection. PeerJ Comput Sci 5:e171
Howard PG, Vitter JS (1992) Analysis of arithmetic coding for data compression. Inf Proces Manag 28(6):749–763
Kahu S, Rahate R (2013) Image compression using singular value decomposition. Int J Adv Res Technol 2(8):244–248
Prasantha H, Shashidhara H, Murthy KB (2007) Image compression using SVD. In: International conference on computational intelligence and multimedia applications (ICCIMA 2007), vol 3. IEEE, pp 143–145
Chen S, Lu R, Zhang J (2017) A flexible privacy-preserving framework for singular value decomposition under internet of things environment. In: IFIP International conference on trust management. Springer, pp 21–37
Wang L, Wu J, Jiao L, Shi G (2009) Lossy-to-lossless hyperspectral image compression based on multiplierless reversible integer TDLT/KLT. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 6(3):587–591
Hao P, Shi Q (2003) Reversible integer KLT for progressive-to-lossless compression of multiple component images. In: Proceedings 2003 international conference on image processing (Cat. No. 03CH37429), vol 1. IEEE, pp I–633
Aubert P, Vuillaume T, Maurin G, Jacquemier J, Lamanna G, Emad N (2018) Polynomial data compression for large-scale physics experiments. Comput Softw Big Sci 2(1):1–9
Al-Khafaji G, Rajab MA (2016) Lossless and lossy polynomial image compression. OSR J Comput Eng 18:56–62
Mulcahy C (1997) Image compression using the Haar wavelet transform. Spelman Sci Math J 1(1):22–31
Arvind Pande BP, Patil SB (2019) Analysis of Haar and slant transformation for image compression. JASC J Appl Sci Comput 6(3):1130–1136
Nain G, Pattanaik KK, Sharma GK (2022) Towards edge computing in intelligent manufacturing: past, present and future. J Manuf Syst 62:588–611
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Dr. Richard Archibald of the Computer Science and Mathematics Division at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) for reviewing the manuscript. This work was in part supported by the United States Department of Defense (DoD) and used resources of the Computational Research and Development Programs at ORNL. ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle, LLC, for the US DOE under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725. S.C. acknowledges DOE ASCR funding under the Quantum Computing Application Teams program, FWP No. ERKJ347.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bagherian, M., Chehade, S., Whitney, B. et al. Classical and quantum compression for edge computing: the ubiquitous data dimensionality reduction. Computing 105, 1419–1465 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-023-01154-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-023-01154-0