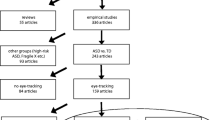
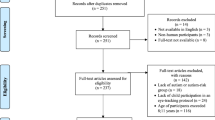
Abstract
Eye-tracking studies have shown potential in effectively discriminating between autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and non-ASD groups. The main objective of the present study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of eye-tracking studies in adults with ASD. A total of 22 studies were included for meta-analysis. Eyes and Non-Social regions proved better for discriminating between ASD and non-ASD adults, while fixation duration seems to be the outcome to choose. Active engaged tasks seem to reduce differences between ASD and non-ASD adults, regardless of the emotional content of the stimuli/task. Proportional fixation duration on eyes and non-social areas in non-active tasks (e.g. free viewing) seems to be the best eye-tracking design for increasing the sensitivity and specificity in ASD adults.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
An Excel spreadsheet with meta-analysis raw data is available for researchers to replicate the statistical analyses reported here.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. American Psychiatric Association. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596
Amestoy, A., Guillaud, E., Bouvard, M. P., & Cazalets, J. R. (2015). Developmental changes in face visual scanning in autism spectrum disorder as assessed by data-based analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 989.
Anderson, G. M. (2015). Autism biomarkers: Challenges, pitfalls and possibilities. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(4), 1103–1113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2225-4
Åsberg Johnels, J., Hovey, D., Zürcher, N., Hippolyte, L., Lemonnier, E., Gillberg, C., & Hadjikhani, N. (2017). Autism and emotional face-viewing. Autism Research, 10(5), 901–910. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1730
Auyeung, B., Lombardo, M. V., Heinrichs, M., Chakrabarti, B., Sule, A., Deakin, J. B., Bethlehem, R. A., Dickens, L., Mooney, N., Sipple, J. A., Thiemann, P., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2015). Oxytocin increases eye contact during a real-time, naturalistic social interaction in males with and without autism. Translational Psychiatry, 5(2), e507.
Black, M. H., Chen, N. T. M., Iyer, K. K., Lipp, O. V., Bölte, S., Falkmer, M., Tan, T., & Girdler, S. (2017). Mechanisms of facial emotion recognition in autism spectrum disorders: Insights from eye tracking and electroencephalography. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 80, 488–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.06.016
Black, M. H., Chen, N. T., Lipp, O. V., Bölte, S., & Girdler, S. (2020). Complex facial emotion recognition and atypical gaze patterns in autistic adults. Autism, 24(1), 258–262. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361319856969
Boraston, Z. L., Corden, B., Miles, L. K., Skuse, D. H., & Blakemore, S. J. (2008). Brief report: Perception of genuine and posed smiles by individuals with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(3), 574–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-007-0421-1
Braddick, O., Atkinson, J., & Innocenti, G. (2011). How special is social looking in ASD: A review. In Gene expression to neurobiology and behaviour: Human brain development and developmental disorders (p. 209). Elsevier.
Brothers, L., Ring, B., & Kling, A. (1990). Response of neurons in the macaque amygdala to complex social stimuli. Behavioural Brain Research, 41(3), 199–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(90)90108-Q
Cassidy, S., Ropar, D., Mitchell, P., & Chapman, P. (2014). Can adults with autism spectrum disorders infer what happened to someone from their emotional response? Autism Research, 7(1), 112–123. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1351
Chawarska, K., MacAri, S., & Shic, F. (2012). Context modulates attention to social scenes in toddlers with autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 53(8), 903–913. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2012.02538.x
Chita-Tegmark, M. (2016a). Attention allocation in ASD: A review and meta-analysis of eye-tracking studies. Review Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 3(3), 209–223.
Chita-Tegmark, M. (2016b). Social attention in ASD: A review and meta-analysis of eye-tracking studies. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 48, 79–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2015.10.011
Corden, B., Chilvers, R., & Skuse, D. (2008). Emotional modulation of perception in Asperger’s Syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(6), 1072–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-007-0485-y
Cuve, H. C., Gao, Y., & Fuse, A. (2018). Is it avoidance or hypoarousal? A systematic review of emotion recognition, eye-tracking, and psychophysiological studies in young adults with autism spectrum conditions. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 55(March), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2018.07.002
Del Bianco, T., Mazzoni, N., Bentenuto, A., & Venuti, P. (2018). An investigation of attention to faces and eyes: Looking time is task-dependent in autism spectrum disorder. Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02629
Del Valle Rubido, M., Hollander, E., McCracken, J. T., Shic, F., Noeldeke, J., Boak, L., Khwaja, O., Sadikhov, S., Fontoura, P., & Umbricht, D. (2020). Exploring social biomarkers in high-functioning adults with autism and Asperger’s versus healthy controls: A cross-sectional analysis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 50(12), 4412–4430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-020-04493-5
Egger, M., Smith, G. D., Schneider, M., & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ, 315(7109), 629–634.
Falkmer, M., Bjällmark, A., Larsson, M., & Falkmer, T. (2011). Recognition of facially expressed emotions and visual search strategies in adults with Asperger syndrome. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 5(1), 210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2010.03.013
Fletcher-Watson, S., Leekam, S. R., Benson, V., Frank, M. C., & Findlay, J. M. (2009). Eye-movements reveal attention to social information in autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychologia, 47(1), 248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.07.016
Frazier, T. W., & Goodwin, M. S. (2020). Developing more clinically useful biomarkers in autism spectrum disorder. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 62(2), 153. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.14414
Frazier, T. W., Strauss, M., Klingemier, E. W., Zetzer, E. E., Hardan, A. Y., Eng, C., & Youngstrom, E. A. (2017). A meta-analysis of gaze differences to social and nonsocial information between individuals with and without autism. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 56(7), 546–555.
Frigaux, A., Evrard, R., & Lighezzolo-Alnot, J. (2019). ADI-R and ADOS and the differential diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders: Interests, limits and openings. Encephale, 45(5), 441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.encep.2019.07.002
Frijda, N. H. (2007). The laws of emotion. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Fujioka, T., Inohara, K., Okamoto, Y., Masuya, Y., Ishitobi, M., Saito, D. N., Jung, M., Arai, S., Matsumura, Y., Fujisawa, T. X., Narita, K., Suzuki, K., Tsuchiya, K. J., Mori, N., Katayama, T., Sato, M., Munesue, T., Okazawa, H., Tomoda, A., Wada, Y., & Kosaka, H. (2016). Gazefinder as a clinical supplementary tool for discriminating between autism spectrum disorder and typical development in male adolescents and adults. Molecular Autism. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-016-0083-y
Guillon, Q., Hadjikhani, N., Baduel, S., & Rogé, B. (2014). Visual social attention in autism spectrum disorder: Insights from eye tracking studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 42, 279–297.
Hagenmuller, F., Rössler, W., Wittwer, A., & Wittwer, H. (2014). Empathic resonance in Asperger syndrome. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 8(7), 851–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2014.04.008
Hanley, M., McPhillips, M., Mulhern, G., & Riby, D. M. (2013). Spontaneous attention to faces in Asperger syndrome using ecologically valid static stimuli. Autism, 17(6), 754–761. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361312456746
Harrer, M., Cuijpers, P., Furukawa, T., & Ebert, D. D. (2019). dmetar: Companion R package for the guide ‘Doing meta-analysis in r’ (Version 0.0. 9000).
Hernandez, R. N., Feinberg, R. L., Vaurio, R., Passanante, N. M., Thompson, R. E., & Kaufmann, W. E. (2009). Autism spectrum disorder in fragile X syndrome: A longitudinal evaluation. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 149A(6), 1125–1137. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.32848
Higgins, J. P. T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M. J., & Welch, V. A. (2019). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Thompson, S. G. (2004). Controlling the risk of spurious findings from meta-regression. Statistics in Medicine, 23(11), 1663–1682.
Hosozawa, M., Tanaka, K., Shimizu, T., Nakano, T., & Kitazawa, S. (2012). How children with specific language impairment view social situations: An eye tracking study. Pediatrics. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-2278
Howlin, P., & Moss, P. (2012). Adults with autism spectrum disorders. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 57(5), 275–283. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371205700502
Jones, W., Carr, K., & Klin, A. (2008). Absence of preferential looking to the eyes of approaching adults predicts level of social disability in 2-year-old toddlers with autism spectrum disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 65(8), 946–954. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.65.8.946
Kirchner, J. C., Hatri, A., Heekeren, H. R., & Dziobek, I. (2011). Autistic symptomatology face processing abilities and eye fixation patterns. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41(2), 158–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-010-1032-9
Kliemann, D., Dziobek, I., Hatri, A., Baudewig, J., & Heekeren, H. R. (2012). The role of the amygdala in atypical gaze on emotional faces in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(28), 9469–9476. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5294-11.2012
Kliemann, D., Dziobek, I., Hatri, A., Steimke, R., & Heekeren, H. R. (2010). Atypical reflexive gaze patterns on emotional faces in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(37), 12281–12287. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0688-10.2010
Klin, A., Jones, W., Schultz, R., Volkmar, F., & Cohen, D. (2002). Visual fixation patterns during viewing of naturalistic social situations as predictors of social competence in individuals with autism. Archives of General Psychiatry, 59(9), 809–816.
Kuhn, G., Benson, V., Fletcher-Watson, S., Kovshoff, H., McCormick, C. A., Kirkby, J., & Leekam, S. R. (2010). Eye movements affirm: Automatic overt gaze and arrow cueing for typical adults and adults with autism spectrum disorder. Experimental Brain Research, 201(2), 155–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2019-7
Lai, M.-C., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2015). Identifying the lost generation of adults with autism spectrum conditions. The Lancet Psychiatry, 2(11), 1013–1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00277-1
Lai, M.-C., Lombardo, M. V., Pasco, G., Ruigrok, A. N. V., Wheelwright, S. J., Sadek, S. A., Chakrabarti, B., MRC AIMS Consortium, & Baron-Cohen, S. (2011). A behavioral comparison of male and female adults with high functioning autism spectrum conditions. PLoS ONE, 6(6), e20835. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020835
Langton, S. R., Watt, R. J., & Bruce, I. I. (2000). Do the eyes have it? Cues to the direction of social attention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(2), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1364-6613(99)01436-9
Lord, C., Brugha, T. S., Charman, T., Cusack, J., Dumas, G., Frazier, T., Jones, E. J. H., Jones, R. M., Pickles, A., State, M. W., Taylor, J. L., & Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. (2020). Autism spectrum disorder. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 6(1), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0138-4
Lugo-Marín, J., Magán-Maganto, M., Rivero-Santana, A., Cuellar-Pompa, L., Alviani, M., Jenaro-Rio, C., Díez, E., & Canal-Bedia, R. (2019). Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in adults with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 59, 22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2018.12.004
Ma, X., Gu, H., & Zhao, J. (2021). Atypical gaze patterns to facial feature areas in autism spectrum disorders reveal age and culture effects: A meta-analysis of eye-tracking studies. Autism Research: Official Journal of the International Society for Autism Research, 14(12), 2625–2639. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2607
Mandell, D. S., Novak, M. M., & Zubritsky, C. D. (2005). Factors associated with age of diagnosis among children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics, 116(6), 1480–1486. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2005-0185
Mathersul, D., McDonald, S., & Rushby, J. (2013). Understanding advanced theory of mind and empathy in high-functioning adults with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803395.2013.809700
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097.
Neumann, D., Spezio, M. L., Piven, J., & Adolphs, R. (2006). Looking you in the mouth: Abnormal gaze in autism resulting from impaired top-down modulation of visual attention. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 1(3), 194–202. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsl030
Norbury, C. F., Brock, J., Cragg, L., Einav, S., Griffiths, H., & Nation, K. (2009). Eye-movement patterns are associated with communicative competence in autistic spectrum disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 50(7), 834–842. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02073.x
Papagiannopoulou, E. A., Chitty, K. M., Hermens, D. F., Hickie, I. B., & Lagopoulos, J. (2014). A systematic review and meta-analysis of eye-tracking studies in children with autism spectrum disorders. Social Neuroscience, 9(6), 610–632. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2014.934966
Rutherford, M. D., & Towns, A. M. (2008). Scan path differences and similarities during emotion perception in those with and without autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(7), 1371–1381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-007-0525-7
Sasson, N. J., Pinkham, A. E., Weittenhiller, L. P., Faso, D. J., & Simpson, C. (2016). Context effects on facial affect recognition in schizophrenia and autism: Behavioral and eye-tracking evidence. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42(3), 675–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbv176
Sasson, N., Tsuchiya, N., Hurley, R., Couture, S. M., Penn, D. L., Adolphs, R., & Piven, J. (2007). Orienting to social stimuli differentiates social cognitive impairment in autism and schizophrenia. Neuropsychologia, 45(11), 2580–2588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.03.009
Sawyer, A. C. P, Williamson, P., & Young, R. L. (2012). Can gaze avoidance explain why individuals with asperger’s syndrome can’t recognise emotions from facial expressions? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(4), 606–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-011-1283-0
Schwarzer, G. (2007). meta: An R package for meta-analysis. R News, 7(3), 40–45.
Sterling, L., Dawson, G., Webb, S., Murias, M., Munson, J., Panagiotides, H., & Aylward, E. (2008). The role of face familiarity in eye tracking of faces by individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(9), 1666–1675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-008-0550-1
Tanaka, J. W., & Sung, A. (2016). The “eye avoidance” hypothesis of autism face processing. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46(5), 1538–1552.
Tatler, B. W., Kirtley, C., MacDonald, R. G., Mitchell, K. M. A., & Savage, S. W. (2014). The active eye: Perspectives on eye movement research. In M. Horsley, M. Eliot, B. A. Knight, & R. Reilly (Eds.), Current trends in eye tracking research (pp. 3–16). Springer.
Trevisan, D. A., Roberts, N., Lin, C., & Birmingham, E. (2017). How do adults and teens with self-declared autism spectrum disorder experience eye contact? A qualitative analysis of first-hand accounts. PLoS ONE, 12(11), e0188446.
Vandenbroucke, J. P., Von Elm, E., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Mulrow, C. D., Pocock, S. J., Poole, C., Schlesselman, J. J., Egger, M., STROBE Initiative. (2007). Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Medicine, 4(10), e297.
Vettori, S., Van der Donck, S., Nys, J., Moors, P., Van Wesemael, T., Steyaert, J., Rossion, B., Dzhelyova, M., & Boets, B. (2020). Combined frequency-tagging EEG and eye-tracking measures provide no support for the “excess mouth/diminished eye attention” hypothesis in autism. Molecular Autism, 11(1), 1–22.
Wang, S., & Adolphs, R. (2017). Reduced specificity in emotion judgment in people with autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychologia, 99, 286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.03.024
Watanabe, S., Miki, K., & Kakigi, R. (2002). Gaze direction affects face perception in humans. Neuroscience Letters, 325(3), 163–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00257-4
Wigham, S., Rodgers, J., Berney, T., Le Couteur, A., Ingham, B., & Parr, J. R. (2019). Psychometric properties of questionnaires and diagnostic measures for autism spectrum disorders in adults: A systematic review. Autism, 23(2), 287–305. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361317748245
Wilkinson, K. M., & Mitchell, T. (2014). Eye tracking research to answer questions about augmentative and alternative communication assessment and intervention. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 30(2), 106–119. https://doi.org/10.3109/07434618.2014.904435
Yi, L., Feng, C., Quinn, P. C., Ding, H., Li, J., Liu, Y., & Lee, K. (2014). Do individuals with and without autism spectrum disorder scan faces differently? A new multi-method look at an existing controversy. Autism Research, 7(1), 72–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1340
Yi, L., Quinn, P. C., Feng, C., Li, J., Ding, H., & Lee, K. (2015). Do individuals with autism spectrum disorder process own- and other-race faces differently? Vision Research, 107, 124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2014.11.021
Zamzow, R. M., Christ, S. E., Saklayen, S. S., Moffitt, A. J., Bodner, K. E., Higgins, K. F., & Beversdorf, D. Q. (2014). Effect of propranolol on facial scanning in autism spectrum disorder: A preliminary investigation. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 36(4), 431–445. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803395.2014.904844
Zürcher, N. R., Rogier, O., Boshyan, J., Hippolyte, L., Russo, B., Gillberg, N., Helles, A., Ruest, T., Lemonnier, E., Gillberg, C., & Hadjikhani, N. (2013). Perception of social cues of danger in autism spectrum disorders. PLoS ONE, 8(12), e81206. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081206
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the contacted authors for providing additional unpublished data/information to be included in the meta-analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ISR and JLM conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination and drafted the manuscript; LGG participated in the design and interpretation of the data, and helped draft the manuscript; EDV participated in the interpretation of the data, performed the statistical analysis and helped draft the manuscript; MMM and RCB participated in the design and interpretation of the data, and helped draft the manuscript. JARQ helped draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Setien-Ramos, I., Lugo-Marín, J., Gisbert-Gustemps, L. et al. Eye-Tracking Studies in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Autism Dev Disord 53, 2430–2443 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-022-05524-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-022-05524-z