Abstract
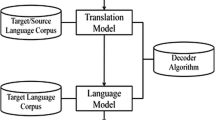
Languages with insufficient digitally available resources, such as, Indian–Indian and English–Indian language Machine Translation (MT) system developments, faces the difficulty to translate various lexical phenomena. In this paper, we present our work on a comparative study of 440 phrase-based statistical trained models for 110 language pairs across 11 Indian languages. We have developed 110 baseline statistical machine translation systems. Then, we have augmented the training corpus with Indowordnet synset word entries of lexical database and further trained 110 models on top of the baseline system. We have done a detailed performance comparison using various evaluation metrics such as BLEU score, METEOR, and TER. We observed significant improvement in evaluations of translation quality across all the 440 models after using the Indowordnet. These experiments give a detailed insight in two ways: (1) usage of lexical database with synset mapping for resource poor languages and (2) efficient usage of Indowordnet synset mapping. Moreover, synset mapped lexical entries helped the SMT system to handle the ambiguity to a great extent during the translation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Lavie A (2008) Meteor, M-Bleu, M-ter evaluation matrics for high correlation with human ranking of machine translation output. In: Proceedings of the third workshop on statistical machine translation. ACL, Columbus, pp 115–118
Ahsan A, Kolachina P, Kolachina S, Sharma DM, Sangal R (2010) Coupling statistical machine translation with rule-based transfer and generation. In:AMTA—The ninth conference of the association for machine translation in the Americas, Denver, Colorado
Antony PJ (2013) Machine translation approaches and survey for Indian Languages. Assoc Comput Ling Chin Lang Proc 18(1):47–78
Bhattacharyya P (2010) IndoWordnet. LREC—International language resources and evaluation conference. http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2010/pdf/939_Paper.pdf
Bhattacharyya P, Khapra M, Kunchukuttan A (2016) Statistical machine translation between related languages. In: Annual conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics: Tutorials
Brown PE, Pietra SA Della, Pietra VJD, Mercer RLJ (1993) The mathematics of statistical machine translation: parameter estimation. Comput Linguist 19(2):263–311
Chakrawarti RK, Bansal P (2017) Approaches for improving Hindi to English machine translation system. Indian J Sci Technol 10(16):1
Choudhary N, Jha GN (2011) Creating multilingual parallel corpora in Indian languages. In: Proceedings of language technology conference
Denkowski Michael, Lavie Alon (2014) Meteor universal: language specific translation evaluation for any target language. Proc Ninth Workshop Stat Mach Transl. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/W14-3348
Emeneau Murray B (1956) India as a linguistic area. Language 32(1):3–16
Khan Md, Anwarus S, Yamada S, Tetsuro N (2011) Translating unknown words using WordNet and IPA-based-transliteration. In: 14th international conference on computer and information technology (ICCIT). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccitechn.2011.6164838
Koehn P, Hoang H, Birch A, Burch CC, Federico M, Bertoldi N, Cowan B, Shen W, Moran C, Zens R, Dyer C, Bojar O, Constantin A, Herbst E (2007) Moses: open source toolkit for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the association for computational linguistics 2007 demo and poster sessions. Prague, pp 177–180
Kumar R, Mohanty, Bhattacharyya P, Kalele S, Pandey P, Sharma A, Kapra M (2008) Synset based multilingual dictionary: insights, applications and challenges. Global Wordnet Conference
Nair L, Peter DS (2012) Machine translation systems for Indian languages. Int J Comput Appl 39(1):7975–8887
Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W (2002) BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th association for computational linguistics (ACL), Philadelphia, July 2002, pp 311–318
Sreelekha S, Bhattacharyya P (2014) Lexical resources for Hindi–Marathi MT. In: WILDRE–3rd workshop on Indian language data resource evaluations. (LREC 2014)–International language resources and evaluation conference, Reykjavik, Iceland, WILDRE 2014 Proceedings, p 102
Sreelekha S, Bhattacharyya P (2016) Lexical resources to enrich English Malayalam Machine translation. In: LREC—international conference on lexical resources and evaluation, Slovenia
Sreelekha S, Bhattacharyya P (2017) Role of morphology injection in SMT: a case study from Indian language perspective. In: ACM transactions on Asian and low-resource language information processing (TALLIP) vol 17, No. 1, Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1145/3129208
Sreelekha S, Bhattacharyya P (2018) Morphology generation for English–Malayalam SMT. In: LREC—international conference on lexical resources and evaluation, Miyazaki (Japan)
Sreelekha S, Dabre R, Bhattacharyya P (2013) Comparison of SMT and RBMT, the requirement of hybridization for Marathi–Hindi MT, ICON-2013. In: 10th International conference on natural language processing, Noida, India
Sreelekha D, Bhattacharyya P, Malathi D (2015) Solving data spasity by morphology injection in factored SMT, ACL-Anthology, ICON 2015. In: 12th international conference on natural language processing
Sreelekha S, Bhattacharyya P, Malathi D (2018) Statistical vs. rule based; a case study on Indian language perspective. J Adv Intell Syst Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5520-1_60
Vintar Š, Fišer D (2016) Using WordNet-based word sense disambiguation to improve MT performance. In: Costa-jussà M, Rapp R, Lambert P, Eberle K, Banchs R, Babych B (eds) Hybrid approaches to machine translation. Theory and applications of natural language processing. Springer, Cham
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the pre-print version copy of the article in Arxiv.org. The authors would like to thank Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India for providing fund under Woman Scientist Scheme (WOS-A) with the project code-SR/WOS-A/ET/1075/2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
S., S., Bhattacharyya, P. Indowordnet’s help in Indian language machine translation. AI & Soc 35, 689–698 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-019-00907-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-019-00907-w