Abstract
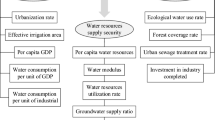
With the social progress and economic development, people have put forward requirements for the ecological operation of built reservoirs. However, there are conflicts between the ecological landscape and the existing benefits such as irrigation and flood control, so it is necessary to build a decision-making model for the comprehensive value of the ecological operation of reservoirs. Taking a reservoir project which needs to satisfy multi-objective requirements as an example, this paper proposes a set of decision-making methods for ecological operation of built reservoirs based on improved comprehensive fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method and constructs a multi-objective decision-making model and optimization strategy combination. Through case analysis in this paper, the improved comprehensive fuzzy evaluation method has a good effect on multi-objective decision-making of ecological dispatching of built reservoirs. The research shows that the combination strategy of improving the reservoir’s water storage capacity and the water-saving supporting transformation measures has a good effect, which can reduce the waste of the reservoir diversion project and large-scale high-efficiency water-saving transformation project construction. It embodies the idea of water-saving priorities and space balance and has broad application prospects in the optimization of reservoir ecological dispatch.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Acreman MC, Harding RJ, Lloyd C et al (2011) Trade-off in ecosystem services of the Somerset levels and moors wetlands. Hydrol Sci J 56(8):1543–1565
Braga, Benedito, Barbosa et al (2001) Multiobjective real-time reservoir operation with a network flow algorithm. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37(4):837–852
Chang FJ, Wang KW (2013) A systematical water allocation scheme for drought mitigation. J Hydrol 507:124–133
Chen S (2010) Quantity change theorem and quality change theorem. ACFIE2010 78(1):109–112
Chuntian C, Chau KW (2002) Three-person multi-objective conflict decision in reservoir flood control. Eur J Oper Res 142(3):625–631
Demertzi KA, Papamichail DM, Georgiou PE et al (2014) Assessment of rural and highly seasonal tourist activity plus drought effects on reservoir operation in a semi-arid region of Greece using the weap model. Water Int 39(1):23–34
Despic O, Simonovic SP (2000) Aggregation operators for soft decision making in water resources. Fuzzy Sets Syst 115(1):11–33
Dubois D (2011) The role of fuzzy sets in decision sciences: old techniques and new directions. Fuzzy Sets Syst 184(1):3–28
Edwards JA, Priestley GK (1996) Waterfronts, tourism and economic sustainability: The UK experience. Sustainable Tourism? European Experiences
Godo L, Gottwald S (2015) Fuzzy sets and formal logics. Fuzzy Sets Syst 281:S0165011415003103
Gospodini A (2001) Urban waterfront redevelopment in greek cities: a framework for redesigning space. Cities 18(5):285–295
Hadi T, Hossein JA, Ahmad MS, Hedayat F (2018) Multi-objective surface water resource management considering conflict resolution and utility function optimization. Water Resour Manag 32(14):4487–4509
Hoyle B (2002) Urban waterfront revitalization in developing countries: the example of zanzibar’s stone town. Geogr J 168(2):141–162
Khazaei B, Hosseini SM (2015) Improving the performance of water balance equation using fuzzy logic approach. J Hydrol 524:538–548
Lagarense BES, Walansendow A (2015) Exploring residents’ perceptions and participation on tourism and waterfront development: the case of Manado waterfront development in Indonesia. Asia Pac J Tourism Res 20(2):223–237
Li DF (2005) An approach to fuzzy multiattribute decision making under uncertainty. Inf Sci 169(1–2):97–112
Machacha LL, Bhattacharya P (2000) A fuzzy-logic-based approach to project selection. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 47(1):65–73
Mazvimavi D, Nhapi I, Mulwafu W (2010) 10th waternet/warfsa/gwp-sa symposium: IWRM-environmental sustainability, climate change and livelihoods. Phys. Chem. Earth A/B/C 35(13):561–564
Mereu S, Sušnik J, Trabucco A et al (2015) Operational resilience of reservoirs to climate change, agricultural demand, and tourism: a case study from Sardinia. Sci Total Environ 543(Pt B:1028–1038
Miller ML (1993) The rise of coastal and marine tourism. Ocean Coast Manag 20:181–199
Nelson C, Morgan R, Williams AT et al (2000) Beach awards and management. Ocean Coast Manag 43(1):87–98
Raju KS, Pillai CRS (2007) Multicriterion decision making in river basin planning and development. Eur J Oper Res 112(2):249–257
Turpie J, Joubert A (2001) Estimating potential impacts of a change in river quality on the tourism value of kruger national park: an application of travel cost, contingent, and conjoint valuation methods. WaterSA 27(3):387–398
Wang L, Meng W, Guo H, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Fan Y (2006) An interval fuzzy multiobjective watershed management model for the Lake Qionghai watershed, China. Water Resour Manag 20(5):701–721
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by the Building Energy Conservation and Science and Technology Plan of Hunan Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Department, China (no. KY201413).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Zhang, F., Wan, W. et al. Multi-objective Decision-Making for the Ecological Operation of Built Reservoirs Based on the Improved Comprehensive Fuzzy Evaluation Method. Water Resour Manage 33, 3949–3964 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02349-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02349-x