Abstract
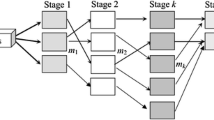
Hybrid flow shops can be encountered in various industrial settings. In this paper we develop methods for scheduling hybrid flow shops with hard time windows. Specifically, we study a two-stage hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with time windows to minimize the total weighted completion times. Each stage consists of one or more identical parallel machines, and each job visits two processing stages in series. Finding a feasible schedule with hard time windows is a challenging task in this setting, because it is NP-complete in the strong sense even for a single machine in a single stage. We propose two matheuristics to find an initial feasible solution by local branching. We also develop two schedule improvement procedures, one based on stage-by-stage decomposition, and one using adapted local branching. The performance of our methods is validated via extensive computational experiments.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AL:
-
Adapted local branching
- ALP:
-
Job ordering in average starting time of the linear relaxation
- ED:
-
Earliest-deadline-first rule
- FSSA:
-
Feasible schedule search by artificial variables
- ISR:
-
Infeasible schedule repair
- JFA:
-
Job window heuristic and adapted local branching
- JFS:
-
Job window heuristic and stage-by-stage decomposition
- JWH:
-
Job window heuristic
- RP:
-
Random priority rule
- SD:
-
Stage-by-stage decomposition
- \(\triangle _r^{AL}\) :
-
Radius decrement in AL
- \(\triangle _r^{ISR}\) :
-
Radius increment in ISR
- \(\triangle _t\) :
-
Time increment in AL
- \(G_{node}\) :
-
threshold on the gap in a node in AL
- \(K^{AL}\) :
-
Predetermined number of rounds for AL
- \(T_{ini}\) :
-
Initialization time
- \(T_{B}\) :
-
Time limit for bottleneck stage in SD
- \(T_{N}\) :
-
Time limit for non-bottleneck stage in SD
- \(T^{AL}\) :
-
Time limit for AL
- \(T_{node}\) :
-
Time limit for each node in AL
References
Allaoui, H., Artiba, A.: Scheduling two-stage hybrid flow shop with availability constraints. Comput. Oper. Res. 33(5), 1399–1419 (2006)
Azizoglu, M., Cakmak, E., Kondakci, S.: A flexible flowshop problem with total flow time minimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 132(3), 528–538 (2001)
Balas, E., Lancia, G., Serafini, P., Vazacopoulos, A.: Job shop scheduling with deadlines. J. Comb. Optim. 1(4), 329–353 (1998)
Balas, E., Simonetti, N., Vazacopoulos, A.: Job shop scheduling with setup times, deadlines and precedence constraints. J. Sched. 11(4), 253–262 (2008)
Bang, J.Y., Kim, Y.D.: Scheduling algorithms for a semiconductor probing facility. Comput. Oper. Res. 38(3), 666–673 (2011)
Baumann, P., Trautmann, N.: A continuous-time MILP model for short-term scheduling of make-and-pack production processes. Int. J. Prod. Res. 51(6), 1707–1727 (2013)
Belaid, R., T’kindt, V., Esswein, C.: Scheduling batches in flowshop with limited buffers in the shampoo industry. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 223(2), 560–572 (2012)
Berghman, L., Leus, R.: Practical solutions for a dock assignment problem with trailer transportation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 246(3), 787–799 (2015)
Berghman, L., Leus, R., Spieksma, F.C.R.: Optimal solutions for a dock assignment problem with trailer transportation. Ann. Oper. Res. 213(1), 1–23 (2014)
Brah, S.A., Hunsucker, J.L.: Branch and bound algorithm for the flow shop with multiple processors. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 51(1), 88–99 (1991)
Chamnanlor, C., Sethanan, K., Chien, C.F., Gen, M.: Re-entrant flow shop scheduling problem with time windows using hybrid genetic algorithm based on auto-tuning strategy. Int. J. Prod. Res. 52(9), 2612–2629 (2014)
Chamnanlor, C., Sethanan, K., Gen, M., Chien, C.-F.: Embedding ant system in genetic algorithm for re-entrant hybrid flow shop scheduling problems with time window constraints. J. Intell. Manuf. 28(8), 1915–1931 (2017)
Chen, Z.L., Vairaktarakis, G.L.: Integrated scheduling of production and distribution operations. Manage. Sci. 51(4), 614–628 (2005)
Christofides, N., Alvarez-Valdes, R., Tamarit, J.M.: Project scheduling with resource constraints: a branch and bound approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 29(3), 262–273 (1987)
Davari, M., Demeulemeester, E., Leus, R., Talla Nobibon, F.: Exact algorithms for single-machine scheduling with time windows and precedence constraints. J. Sched. 19(3), 309–334 (2016)
Debels, D., Vanhoucke, M.: A decomposition-based genetic algorithm for the resource-constrained project-scheduling problem. Oper. Res. 55(3), 457–469 (2007)
Della Croce, F., Grosso, A., Salassa, F.: A matheuristic approach for the two-machine total completion time flow shop problem. Ann. Oper. Res. 213(1), 67–78 (2014)
Fischetti, M., Lodi, A.: Local branching. Math. Program. 98(1–3), 23–47 (2003)
Fischetti, M., Lodi, A.: Repairing MIP infeasibility through local branching. Comput. Oper. Res. 35(5), 1436–1445 (2008)
Fischetti, M., Glover, F., Lodi, A.: The feasibility pump. Math. Program. 104(1), 91–104 (2005)
Garcia, J.M., Lozano, S.: Production and delivery scheduling problem with time windows. Comput. Indu. Eng. 48(4), 733–742 (2005)
Garey, M.R., Johnson, D.S., Sethi, R.: The complexity of flowshop and jobshop scheduling. Math. Oper. Res. 1(2), 117–129 (1976)
Gicquel, C., Hege, L., Minoux, M., Van Canneyt, W.: A discrete time exact solution approach for a complex hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem with limited-wait constraints. Comput. Oper. Res. 39(3), 629–636 (2012)
Grabowski, J., Pempera, J.: Sequencing of jobs in some production system. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 125(3), 535–550 (2000)
Graham, R.L., Lawler, E.L., Lenstra, J.K., Kan, A.R.: Optimization and approximation in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: a survey. Ann. Discrete Math. 5, 287–326 (1979)
Guirchoun, S., Martineau, P., Billaut, J.C.: Total completion time minimization in a computer system with a server and two parallel processors. Comput. Oper. Res. 32(3), 599–611 (2005)
Hadda, H., Dridi, N., Hajri-Gabouj, S.: Exact resolution of the two-stage hybrid flow shop with dedicated machines. Optim. Lett. 8(8), 2329–2339 (2014)
Hall, N.G., Potts, C.N., Sriskandarajah, C.: Parallel machine scheduling with a common server. Discrete Appl. Math. 102(3), 223–243 (2000)
Ham, A., Fowler, J.W., Cakici, E.: Constraint programming approach for scheduling jobs with release times, non-identical sizes, and incompatible families on parallel batching machines. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 30(4), 500–507 (2017)
Haouari, M., Hidri, L., Gharbi, A.: Optimal scheduling of a two-stage hybrid flow shop. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 64(1), 107–124 (2006)
Huang, R.-H., Yang, C.-L.: Ant colony system for job shop scheduling with time windows. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 39(1–2), 151–157 (2008)
Jain, V., Grossmann, I.E.: Algorithms for hybrid MILP/CP models for a class of optimization problems. INFORMS J. Comput. 13(4), 258–276 (2001)
Jula, P., Kones, I.: Continuous-time algorithms for scheduling a single machine with sequence-dependent setup times and time window constraints in coordinated chains. Int. J. Prod. Res. 51(12), 3654–3670 (2013)
Kaveshgar, N., Huynh, N.: Integrated quay crane and yard truck scheduling for unloading inbound containers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 159, 168–177 (2015)
Klemmt A, Mönch L (2012) Scheduling jobs with time constraints between consecutive process steps in semiconductor manufacturing. In: Simulation conference (WSC), proceedings of the 2012 Winter, pp 1–10. IEEE
Kolisch, R.: Serial and parallel resource-constrained project scheduling methods revisited: theory and computation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 90(2), 320–333 (1996)
Komaki, G., Teymourian, E., Kayvanfar, V.: Minimising makespan in the two-stage assembly hybrid flow shop scheduling problem using artificial immune systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 54(4), 963–983 (2016)
Lee, G.C., Kim, Y.D.: A branch-and-bound algorithm for a two-stage hybrid flowshop scheduling problem minimizing total tardiness. Int. J. Prod. Res. 42(22), 4731–4743 (2004)
Lei, D., Guo, X.: Hybrid flow shop scheduling with not-all-machines options via local search with controlled deterioration. Comput. Oper. Res. 65, 76–82 (2016)
Lenstra, J.K., Rinnooy Kan, A., Brucker, P.: Complexity of machine scheduling problems. Ann. Discrete Math. 1, 343–362 (1977)
Liu, M., Yang, X., Zhang, J., Chu, C.: Scheduling a tempered glass manufacturing system: a three-stage hybrid flow shop model. Int. J. Prod. Res. 55(20), 6084–6107 (2017)
Néron, E., Baptiste, P., Gupta, J.N.: Solving hybrid flow shop problem using energetic reasoning and global operations. Omega 29(6), 501–511 (2001)
Pan, Q.K.: An effective co-evolutionary artificial bee colony algorithm for steelmaking-continuous casting scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 250(3), 702–714 (2016)
Pan, Q.K., Ruiz, R., Alfaro-Fernandez, P.: Iterated search methods for earliness and tardiness minimization in hybrid flowshops with due windows. Comput. Oper. Res. 80, 50–60 (2017)
Pan, Y., Shi, L.: Dual constrained single machine sequencing to minimize total weighted completion time. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2(4), 344–357 (2005)
Panwalkar, S., Dudek, R., Smith, M.: Sequencing research and the industrial scheduling problem. In: Symposium on the theory of scheduling and its applications, Vol 86, pp 29–38. Springer, Berlin (1973)
Pinedo, M.L.: Scheduling: theory, algorithms, and systems. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Quadt, D., Kuhn, H.: A taxonomy of flexible flow line scheduling procedures. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 178(3), 686–698 (2007)
Ribas, I., Leisten, R., Framinan, J.M.: Review and classification of hybrid flow shop scheduling problems from a production system and a solutions procedure perspective. Comput. Oper. Res. 37(8), 1439–1454 (2010)
Ruiz, R., Vazquez-Rodriguez, J.A.: The hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 205(1), 1–18 (2010)
Sawik, T.: Mixed integer programming for scheduling surface mount technology lines. Int. J. Prod. Res. 39(14), 3219–3235 (2001)
Schulze, M., Rieck, J., Seifi, C., Zimmermann, J.: Machine scheduling in underground mining: an application in the potash industry. OR Spectr. 38(2), 365–403 (2016)
Shahvari, O., Logendran, R.: A comparison of two stage-based hybrid algorithms for a batch scheduling problem in hybrid flow shop with learning effect. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 195, 227–248 (2018)
Tan, Y., Mönch, L., Fowler, J.W.: A hybrid scheduling approach for a two-stage flexible flow shop with batch processing machines. J. Sched. 21(2), 209–226 (2018)
Tang, L., Wang, X.: An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for the hybrid flowshop scheduling to minimize total weighted completion time in process industry. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 18(6), 1303–1314 (2010)
Tang, L., Wang, G., Liu, J.: A branch-and-price algorithm to solve the molten iron allocation problem in iron and steel industry. Comput. Oper. Res. 34(10), 3001–3015 (2007)
T’kindt, V., Monmarché, N., Tercinet, F., Laügt, D.: An ant colony optimization algorithm to solve a 2-machine bicriteria flowshop scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 142(2), 250–257 (2002)
Wang, S., Liu, M., Chu, C.: A branch-and-bound algorithm for two-stage no-wait hybrid flow-shop scheduling. Int. J. Prod. Res. 53(4), 1143–1167 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
A description in pseudo-code of the job window heuristic and the stage-by-stage decomposition are provided below as Algorithm 1 and Algorithm 2, respectively.


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Leus, R. Scheduling hybrid flow shops with time windows. J Heuristics 27, 133–158 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10732-019-09425-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10732-019-09425-w