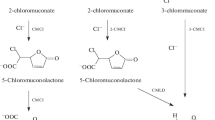
Abstract
AnArthrobacter sp. growing on 4-Chlorobenzoic acid as its sole source of carbon excretes 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and protocatechuic acid into the culture medium. Protocatechuic acid is further attacked by “meta”-cleavage. During growth of theArthrobacter sp. on benzoic acid cis-cis muconic acid can be isolated from the medium, suggesting the involvement of the “ortho”-cleavage pathway. The enzymes both for the “meta”- and the “ortho”-cleavage pathway are inducible.
Zusammenfassung
EineArthrobacter-Species, die 4-Chlorobenzoesäure als einzige Kohlenstoffquelle verwerten kann, gibt beim Wachstum auf dieser Verbindung 4-Hydroxybenzoesäure und Protocatechusäure ins Medium ab. Der weiter Abbau des aromatischen Ringes erfolgt durch “meta”-Spaltung. Beim Wachstum derArthrobacter-Species auf Benzoesäure trit im Medium cis,cis-Muconsäure auf. In diesem Fallewird also der “ortho”-Weg eingeschlagen. Die Enzyme für beide Abbauwege sind induzierbar.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Daly, J. W., Jerina, D. M., Witkop, B.: Arene oxides and the NIH shift: The metabolism, toxicity and carcinogenicity of aromatic compounds. Experientia (Basel)28, 1129–1149 (1972)
Dorn, E., Hellwig, M., Reineke, W., Knackmuss, H. J.: Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading Pseudomonad. Arch. Microbiol.99, 61–70 (1974)
Goldman, P., Milne, G. W. A., Pignataro, M. T.: Fluorine containing metabolites formed from 2-fluorobenzoic acid byPseudomonas species. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.118, 178–184 (1967)
Harper, D. B., Blakley, E. R.: The metabolism of p-fluorobenzoic acid by aPseudomonas sp. Canad. J. Microbiol.17, 1015–1023 (1971)
Johnston, H. W., Briggs, G. G., Alexander, M.: Metabolism of 3-chlorobenzoic acid by aPseudomonad. Soil Biol. Biochem4, 187–190 (1972)
Köcher, H., Lingens, F., Koch, W.: Untersuchungen zum Abbau des Herbizids Chlorphenprop-methyl im Boden und durch Mikroorganismen. Weed Res.16, 93–100 (1976)
Ottow, J. C. G., Zolg, W.: Improved procedure and colorimetric test for the detection of ortho-and meta-cleavage of protocatechuate byPseudomonas isolates. Canad. J. Microbiol.20, 1059–1061 (1974)
Williams, P. A., Murray, K.: Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates byPseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: Evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J. Bact.120, 416–423 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dem Andenken an Professor Bernhauer gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruisinger, S., Klages, U. & Lingens, F. Abbau der 4-Chlorbenzoesäure durch eineArthrobacter-Species. Arch. Microbiol. 110, 253–256 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690235
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690235