Abstract
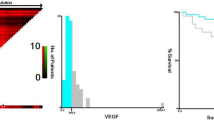
The aim of this study was to verify whether pretreatment plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) correlate with prognosis and survival of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Plasma VEGF levels were assessed at the time of diagnosis in 157 DLBCL patients treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Plasma VEGF levels greater than or equal to the highest quartile (high VEGF levels) were associated with lower probability of a complete remission achievement (odds ratio 0.3; 95 % confidence interval [CI]: 0.1–0.6; p = 0.002) in univariate as well as in multivariate analysis (p = 0.04). The estimated 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) rate of patients with high VEGF levels was 31.7 % (95 % CI 17–51) compared to the 62.5 % 3-year PFS rate (95 % CI 53–71; p = 0.0004) in the patients with lower values. The former group of patients demonstrated an estimated 3-year overall survival (OS) rate of 47.1 % (95 % CI 30–65) in contrast to the 3-year OS rate of 64.3 % (95 % CI 54–73; p = 0.02) in the latter. In multivariate analysis, the high VEGF level retained its independent impact on shorter PFS (p = 0.02). Our results suggest that VEGF plays an important role in the clinical course of DLBCL. VEGF may be a useful marker for selecting the patients for whom new treatment approaches, especially those based on VEGF inhibitors, could be recommended.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks RE, Forbes MA, Kinsey SE et al (1998) Release of the angiogenic cytokine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from platelets: significance for VEGF measurements and cancer biology. Br J Cancer 77:956–964
Bellamy WT, Richter L, Frutiger Y et al (1999) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in hematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Res 59:728–733
Bertolini F, Paolucci M, Peccatori F et al (1999) Angiogenic growth factors and endostatin in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Br J Haematol 106:504–509
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B et al (1999) Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol 17:1244–1253
Coiffier B, Gisselbrecht C, Herbrecht R et al (1989) LNH-84 regimen: a multicenter study of intensive chemotherapy in 737 patients with aggressive malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 7:1018–1026
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J et al (2002) CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346:235–242
Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M et al (1995) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 146:1029–1039
Etto L, Lacerda E, Baiocchi O et al (2008) Clinical correlations and prognostic relevance of HGF, VEGF AND FGF expression in Brazilian patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 49:257–264
Gabrilovich D, Chen HL, Girgis KR et al (1996) Production of vascular endothelial growth factor by human tumors inhibits the functional maturation of dendritic cells. Nat Med 2:1096–1103
Ganjoo KN, An CS, Robertson MJ et al (2006) Rituximab, bevacizumab and CHOP (RA-CHOP) in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: safety, biomarker and pharmacokinetic analysis. Leuk Lymphoma 47:998–1005
Gerber HP, Malik AK, Solar GP et al (2002) VEGF regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival by an internal autocrine loop mechanism. Nature 417:954–958
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Pezzella F et al (2008a) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas is associated with hypoxia regulated proteins. Leuk Lymphoma 49:2181–2186
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Pezzella F et al (2008b) Phosphorylated VEGFR2/KDR receptors are widely expressed in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and correlate with hypoxia inducible factor activation. Hematol Oncol 26:219–224
Gratzinger D, Zhao S, Marinelli RJ et al (2007) Microvessel density and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subtypes. Am J Pathol 170:1362–1369
Gratzinger D, Zhao S, Tibshirani RJ et al (2008) Prognostic significance of VEGF, VEGF receptors, and microvessel density in diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Lab Invest 88:38–47
Gratzinger D, Advani R, Zhao S et al (2010) Lymphoma cell VEGFR2 expression detected by immunohistochemistry predicts poor overall survivalin diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy (R-CHOP). Br J Haematol 148:235–244
Hanahan D, Folkman J (1996) Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86:353–364
Hazar B, Paydas S, Zorludemir S et al (2003) Prognostic significance of microvessel density and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 44:2089–2093
Koster A, Raemaekers JM (2005) Angiogenesis in malignant lymphoma. Curr Opin Oncol 17:611–616
Labidi SI, Ménétrier-Caux C, Chabaud S et al (2010) Serum cytokines in follicular lymphoma. Correlation of TGF-beta and VEGF with survival. Ann Hematol 89:25–33
Masood R, Cai J, Zheng T et al (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an autocrine growth factor for VEGF receptor-positive human tumors. Blood 98:1904–1913
Negaard HF, Iversen N, Bowitz-Lothe IM et al (2009) Increased bone marrow microvascular density in haematological malignancies is associated with differential regulation of angiogenic factors. Leukemia 23:162–169
Niitsu N, Okamato M, Nakamine H et al (2002) Simultaneous elevation of the serum concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6 as independent predictors of prognosis in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 68:91–100
Paydas S, Seydaoglu G, Ergin M et al (2009) The prognostic significance of VEGF-C and VEGF-A in non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma 50:366–373
Pedersen LM, Klausen TW, Davidsen UH et al (2005) Early changes in serum IL-6 and VEGF levels predict clinical outcome following first-line therapy in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Hematol 84:510–516
Pfreundschuh M, Trümper L, Osterborg A et al (2006) CHOP-like chemotherapy plus rituximab versus CHOP-like chemotherapy alone in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: a randomized controlled trial by the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. Lancet Oncol 7:379–391
Podar K, Anderson KC (2005) The pathophysiologic role of VEGF in hematologic malignancies: therapeutic implications. Blood 105:1383–1395
Roberts DM, Kearney JB, Johnson JH et al (2004) The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) modulates Flk-1 (VEGFR-2) signaling during blood vessel formation. Am J Pathol 164:1531–1535
Salven P, Teerenhovi L, Joensuu H (1997) A high pretreatment serum vascular endothelial growth factor concentration is associated with poor outcome in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 90:3167–3172
Salven P, Orpana A, Joensuu H (1999) Leukocytes and platelets of patients with cancer contain high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 5:487–491
Salven P, Orpana A, Teerenhovi L et al (2000) Simultaneous elevation in the serum concentrations of the angiogenic growth factors VEGF and bFGF is an independent predictor of poor prognosis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a single-institution study of 200 patients. Blood 96:3712–3718
Stopeck AT, Unger JM, Rimsza LM et al (2009) A phase II trial of single agent bevacizumab in patientswith relapsed, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Southwest oncology group study S0108. Leuk Lymphoma 50:728–735
Vacca A, Ribatti D, Ruco L et al (1999) Angiogenesis extent and macrophage density increase simultaneously with pathological progression in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Br J Cancer 79:965–970
Wang ES, Teruya-Feldstein J, Wu Y et al (2004) Targeting autocrine and paracrine VEGF receptor pathways inhibits human lymphoma xenografts in vivo. Blood 104:2893–2902
Wosztyl A, Wolowiec D, Ziolkowska E et al (2012) Plasma concentration of cytokines involved in lympho- and angiogenesis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Acta Haematol Pol 43:277–284
Wróbel T, Mazur G, Usnarska-Zubkiewicz L et al (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) serum concentration in non Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. Pol Arch Med Wewn 112:919–923
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lech-Maranda, E., Bienvenu, J., Broussais-Guillaumot, F. et al. Pretreatment Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Plasma Predict a Complete Remission Rate and Time to Relapse or Progression in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 61, 165–174 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-012-0215-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-012-0215-9