Abstract
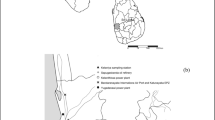
The purpose of the present work was to investigate the chemistry of rain in the Gulf of Iskenderun, North East Mediterranean, Turkey. The Gulf region has a large number of industries. Main industries existing in the region are iron and steel works, fertilizer plants, a cement plant, and several medium and mini size steel mills in addition to the international pipe line terminals. This study aims to apportion the local sources contributing to the overall pollution of the region. To this end a precipitation sampling program was started in January 2000, and over 48 precipitation samples were collected from each of 5 stations located at Iskenderun city center, Iskenderun industrial zone, Payas city center, the campus of Iskenderun Technical College and the campus of Mustafa Kemal University. Samples were analysed for pH, NO3 +, Cl-. Ca, Al, Ba, Na, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Pb, Li, Mg, Mn, Ni, Zn, Fe, K. Concentrations of metal ions were determined by ICP-AES. NO3 - ions and pH were determined by using NO3 - selective electrode and pH meter, respectively.pH values of the collected samples at the industrial zone and at Payas city center, ranged between 5.02 and 7.38, respectively. NO3 - and metal ions concentrations were highly variable. Concentrations of Ca and Fe ions were higher in the industrial zone and Payas city center. In the other three stations, concentrations of metal ions and NO3 - ion were lower than that of industrial zone and the values of pH ranged between 6 and 7.4. The average pH values at Iskenderun Gulf showed that the precipitation was not acidic, because of the high concentration of Ca. The highest concentrations of Na and Cl ions were recorded in the University campus because the campus is located by the Mediterranean Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Momani, I. F., A ygun, S. and Tuncel, G.: 1998, ‘Wet deposition of major ions and trace elements in the Eastern Mediterranean basin’, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 8287–8299
Al-Momani, I. F., Gullu, G., Olmez I., Eler, U., Ortel, E., Sirin G. and Tuncel, G.: 1997, ‘Chemical Composition of eastern Mediterranean aerosol and precipitation: Indications of long-range transport’, Pure Appl. Chem. 69, 41–46.
Al-Momani, I. F., Tuncel, S., Eler, U., Ortel, E., Sirin, G. and Tuncel, G.: 1995a, ‘Major ion composition of wet and dry deposition in the eastern Mediterranean basin’, Sci. Total Environ. 164, 175–185.
Al-Momani, I. F., Ataman, O. Y., Anwari, M. A., Tuncel, S., Kose, C. and Tuncel, G.: 1995b, ‘Chemical composition of precipitation near and industrial area at Izmir Turkey’, Atmosph. Environ. 29(10), 1131–1143.
Avila, A. and Alarcon, M.: 1999, ‘Relationship between precipitation chemistry and meteorological situations at a rural site in North Spain’, Atmosph. Environ. 33, 1663–1677.
Balls, P. W.: 1989, ‘Trace metal and major ion composition of precipitation at a North Sea coastal site’, Atmosph. Environ. 23(12), 2751–2759.
Chekushin, V. A., Bogaturev, I. V., Coritat, P., Miskavada, H. and Reimann, C.: 1998, ‘Annual atmospheric deposition of 16 elements in eight catchments of the central Barents region’, Sci. Total Environ. 220, 95–114.
Dulac, F., Buart-Menard, P., Arnold, M., Ezat, U. and Martin, D.: 1987, ‘Atmospheric input of trace metal to the western Mediterranean Sea, 1 Factors controlling the variability of atmospheric concentrations’, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 8437–8453.
Gulsoy, G., Tayanc, M. and Erturk, F.: 1999, ‘Chemical analyses of the major ions in the precipitation of Istanbul, Turkey’, Environ. Pollut. 105, 273–280.
Kaya, G. and Tuncel, G.: 1997, ‘Trace element and major ion composition of wet and dry deposition in Ankara, Turkey’, Atmosph. Environ. 31(23), 3985–3998.
Kubilay, N. N., Saydam, A. C., Yemencioğu, S., Kelling, G., Karpur, S., Karaman, C. and Akca, E.: 1997, ‘Seasonal chemical and mineralogical variabilty of atmospheric particles in the coastal region of the Northeast Mediterranean’, Catena 28, 313–328.
Lee, B. K., Hong, H. S. and Lee, D. S.: 2000, ‘Chemical composition of precipitation and wet deposition of major ions on the Korean peninsula’, Atmosph. Environ. 34, 563–575
Losno, R., Bergametti, G. and Baut-Menard, P.: 1988, ‘Zinc partitioning in Mediterranean rainwater’, Geophys, Res. Lett. 15, 1389–1392.
Luck, J. M. and Othman, D. B.: 2002, ‘Trace element and Pb isotope variability during rainy events in the NW Mediterranean: Constraints on anthropogenic’, Chem. Geology 182, 443–460.
Örnektekin, S., Mistikoğlu, S. and Ozyilmaz, G.: 1999, ‘Iskenderun Körfezinde kurulu endüstrilerin hava kirlenmesine etkilerinin partiküler madde içerigi açisindan incelenmesi’, Hava Kirlenmesi ve Kontrolü Ulusal Sempozyumu, pp. 222–231.
Ozsoy, T., Saydam, C., Kubilay, N. and Salihoğlu, I.: 2000, ‘Aerosol nitrate and non-seasalt sulfate over the eastern Mediterrannean’, Global Atmosph. Ocean Syst. 40, 41–76.
Ozsoy, T. and Saydam, A. C.: 2000, ‘Acidic and alkaline precipitation in the Cilician Basin, northeastern Mediterranean Sea’, Sci. Total Environ. 250, 93–109.
Ozsoy, T. and Saydam, A. C.: 2001, ‘Iron speciation in precipition in the north-eastern Mediterranean and its relationship with Sahara dust’, J. Atmosph. Chem. 40, 41–76.
Seto, S., Ohara, M. and Ikeda, Y.: 1999, ‘Analysis of precipitation chemistry at a rural site in Hiroshima prefecture Japan’, Atmosph. Environ. 34, 621–628.
Takeda, K., Marumonto, K., Minamikawa, T., Sakugawa, H. and Fujiwara, K.: 2000, ‘Three-year determination of trace metals and the lead isotope ratio in rain and snow depositions collected in Higashi-Hiroshima, Japan’, Atmosph. Environ. 34, 4525–4535.
Zeng, Y. and Hopke, P. K.: 1989, ‘A study of the sources of acid precipitation in Ontario, Canada’, Atmosph. Environ. 23, 1499–1509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Örnektekin, S., Cakmakli, S. Chemical Composition and Acidity of Rain at the Gulf of Iskenderun, North-East Mediterranean. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus 3, 151–166 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026009313334
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026009313334