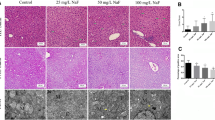
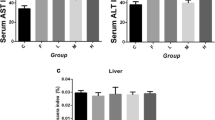
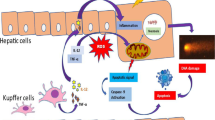
Abstract
At present, no reports are focused on fluoride-induced hepatic inflammatory responses in human beings and animals. This study aimed to investigate the mRNA and protein levels of inflammatory cytokines and signaling molecules for evaluating the effect of different doses (0, 12, 24, and 48 mg/kg) of sodium fluoride (NaF) on inflammatory reaction in the mouse liver by using methods of experimental pathology, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), and western blot analysis. We found that NaF in excess of 12 mg/kg caused the hepatic inflammatory responses, and the results showed that NaF activated the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) signaling pathway by markedly increasing (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) mRNA and protein levels of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1), mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 1/2 (MEK1/2), extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1/2 (Erk1/2), mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 4/7 (MEK4/7), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 3/6 (MEK3/6), and the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway by increasing (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) the production of NF-κB and inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta (IKK-β) and reducing (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) the production of the inhibitory kappa B (IκB). Thus, NaF that caused the hepatic inflammatory responses was characterized by increasing (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) the production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) via the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB pathways, and by significantly inhibiting (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) the production of anti-inflammatory mediators including interleukin-4 (IL-4) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β).









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NaF:
-
Sodium fluoride
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- ASK1:
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
- MEK1/2:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 1/2
- Erk1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1/2
- MEK4/7:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 4/7
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MEK3/6:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 3/6
- p38:
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- IKK-β:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta
- IκB:
-
Inhibitory kappa B
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein 1
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- IL-4:
-
Interleukin-4
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
References
Bouaziz H, Ketata S, Jammoussi K, Boudawara T, Ayedi F, Ellouze F, Zeghal N (2006) Effects of sodium fluoride on hepatic toxicity in adult mice and their suckling pups. Pestic Bioche Phy 86(3):124–130
Agalakova NI, Gusev GP (2012) Molecular mechanisms of cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by inorganic fluoride. ISRN Cell Biol 2012:1–16. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/403835
Fordyce FM, Vrana K, Zhovinsky E, Povoroznuk V, Toth G, Hope BC, Iljinsky U, Baker J (2007) A health risk assessment for fluoride in Central Europe. Environ Geochem Hlth 29(2):83–102
Barbier O, Arreolamendoza L, Del Razo LM (2010) Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 188(2):319–333
Mohammadi AA, Yousefi M, Yaseri M, Jalilzadeh M, Mahvi AH (2017) Skeletal fluorosis in relation to drinking water in rural areas of West Azerbaijan, Iran. Sci Rep 7(1):1–7
Wang Y-N, Xiao K-Q, Liu J-L, Dallner G, Guan Z-Z (2000) Effect of long term fluoride exposure on lipid composition in rat liver. Toxicology 146(2):161–169
Perumal E, Paul V, Govindarajan V, Panneerselvam L (2013) A brief review on experimental fluorosis. Toxicol Lett 223(2):236–251
Deng H, Kuang P, Cui H, Chen L, Luo Q, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Wang X, Zhao L (2016) Sodium fluoride (NaF) induces the splenic apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway in vivo and in vitro. Aging 8(12):3552–3567
Shi Z, Zhan Y, Zhao J, Wang J, Ma H (2016) Effects of fluoride on the expression of p38MAPK signaling pathway-related genes and proteins in spleen lymphocytes of mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 173(2):1–6
Yousefi M, Yaseri M, Nabizadeh R, Hooshmand E, Jalilzadeh M, Mahvi AH, Mohammadi AA (2018) Association of hypertension, body mass index, and waist circumference with fluoride intake; water drinking in residents of fluoride endemic areas, Iran Biol Trace Elem Res 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1269-2
Moghaddam VK, Yousefi M, Khosravi A, Yaseri M, Mahvi AH, Hadei M, Mohammadi AA, Robati Z, Mokammel A (2018) High concentration of fluoride can be increased risk of abortion. Biol Trace Elem Res 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1250-0
Yousefi M, Mohammadi AA, Yaseri M, Mahvi AH (2017) Epidemiology of drinking water fluoride and its contribution to fertility, infertility, and abortion: an ecological study in West Azerbaijan Province, Poldasht County. Iran Fluoride 50(2017):343–353
Thrane EV, Refsnes M, Thoresen GH, Låg M, Schwarze PE (2001) Fluoride-induced apoptosis in epithelial lung cells involves activation of MAP kinases p38 and possibly JNK. Toxicol Sci 61(1):83–91
Lund K, Refsnes M, Ramis I, Dunster C, Boe J, Schwarze PE, Skovlund E, Kelly FJ, Kongerud J (2002) Human exposure to hydrogen fluoride induces acute neutrophilic, eicosanoid, and antioxidant changes in nasal lavage fluid. Inhal Toxicol 14(2):119–132
Aydin G, Ciçek E, Akdoğan M, Gökalp O (2003) Histopathological and biochemical changes in lung tissues of rats following administration of fluoride over several generations. J Appl Toxicol 23(6):437–446
Mendoza-Schulz A, Solano-Agama C, Arreola-Mendoza L, Reyes-Márquez B, Barbier O, Razo LMD, Mendoza-Garrido ME (2009) The effects of fluoride on cell migration, cell proliferation, and cell metabolism in GH4C1 pituitary tumour cells. Toxicol Lett 190(2):179–186
Zhang M, Wang A, Xia T, He P (2008) Effects of fluoride on DNA damage, S-phase cell-cycle arrest and the expression of NF-kappaB in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Toxicol Lett 179(1):1–5
Medzhitov R (2010) Inflammation 2010: new adventures of an old flame. Cell 140(6):771–776
Lee S, Shin S, Kim H, Han S, Kim K, Kwon J, Kwak JH, Lee CK, Ha NJ, Yim D (2011) Anti-inflammatory function of arctiin by inhibiting COX-2 expression via NF-κB pathways. J Inflamm 8(1):1–9
Sun P, Zhou K, Wang S, Li P, Chen S, Lin G, Zhao Y, Wang T (2013) Involvement of MAPK/NF-κB signaling in the activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in experimental colitis by chronic vagus nerve stimulation. PLoS One 8(8):e69424
Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L (2018) Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 9(6):7204–7218
Jayandharan GR, Aslanidi G, Martino AT, Jahn SC, Perrin GQ, Herzog RW, Srivastava A (2011) Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors and its implications in immune response and gene therapy. P Natl Acad Sci USA 108(9):3743–3748
Wang Z, Jiang W, Zhang Z, Qian M, Du B (2012) Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines production via MAPK and NF-kappaB pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 144(1):145–150
Luo Q, Cui H, Deng H, Kuang P, Liu H, Lu Y, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y (2017) Sodium fluoride induces renal inflammatory responses by activating NF-κB signaling pathway and reducing anti-inflammatory cytokine expression in mice. Oncotarget 8(46):80192–80207
Zhang S, Jiang C, Liu H, Guan Z, Zeng Q, Zhang C, Lei R, Xia T, Gao H, Yang L (2013) Fluoride-elicited developmental testicular toxicity in rats: roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammatory response. Toxicol Appl Pharm 271(2):206–215
Ma Y, Niu R, Sun Z, Wang J, Luo G, Zhang J, Wang J (2012) Inflammatory responses induced by fluoride and arsenic at toxic concentration in rabbit aorta. Arch Toxicol 86(6):849–856
Gutowska I, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Goschorska M, Kolasa A, Łukomska A, Jakubczyk K, Dec K, Chlubek D (2015) Fluoride as a factor initiating and potentiating inflammation in THP1 differentiated monocytes/macrophages. Toxicol in Vitro 29(7):1661–1668
Ridley W, Matsuoka M (2009) Fluoride-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E 2 production in A549 human pulmonary epithelial cells. Toxicol Lett 188(3):180–185
Tian Y, Huo M, Li G, Li Y, Wang J (2016) Regulation of LPS-induced mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines via alteration of NF-κB activity in mouse peritoneal macrophages exposed to fluoride. Chemosphere 161:89–95
Refsnes M, Skuland T, Låg M, Schwarze PE, Øvrevik J (2014) Differential NF-κB and MAPK activation underlies fluoride- and TPA-mediated CXCL8 (IL-8) induction in lung epithelial cells. J Inflamm Res 7:169–185
Wang HW, Zhou BH, Cao JW, Zhao J, Zhao WP, Tan PP (2017) Pro-inflammatory cytokines are involved in fluoride-induced cytotoxic potential in HeLa cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 175(1):98–102
Bera I, Sabatini R, Auteri P, Flace P, Sisto G, Montagnani M, Potenza MA, Marasciulo FL, Carratu MR, Coluccia A (2007) Neurofunctional effects of developmental sodium fluoride exposure in rats. Eur Rev for Med Pharmaco 11(4):211–224
Pandiyan T (2013) An in vivo and in vitro studies on the antioxidant property of epigallocatechin gallate on sodium fluoride induced toxicity in rats. Int J Phytopharmacol 4(4):245–254
Almela P, García-Nogales P, Romero A, Milanés MV, Laorden ML, Puig MM (2009) Effects of chronic inflammation and morphine tolerance on the expression of phospho-ERK 1/2 and phospho-P38 in the injured tissue. N-S Arch Pharmacol 379(3):315–323
Che W, Lerner-Marmarosh N, Huang Q, Osawa M, Ohta S, Yoshizumi M, Glassman M, Lee JD, Yan C, Berk BC (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-1 enhances inflammatory responses in endothelial cells: role of Gab1 and MEKK3 in TNF-alpha-induced c-Jun and NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression. Circ Res 90(11):1222–1230
Su X, Pan J, Bai F, Yuan H, Dong N, Li D, Wang X (2016) Chen Z (2016) IL-27 attenuates airway inflammation in a mouse asthma model via the STAT1 and GADD45γ/p38 MAPK pathways. J Transl Med 14:283. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-1039-x
Ramadori G, Moriconi F, Malik I, Dudas J (2008) Physiology and pathophysiology of liver inflammation, damage and repair. J Physiol Pharmacol 59(supplement 1):107–117
Lv YY, Jin Y, Han GZ, Liu YX, Wu T, Liu P, Zhou Q, Liu KX, Sun HJ (2012) Ursolic acid suppresses IL-6 induced C-reactive protein expression in HepG2 and protects HUVECs from injury induced by CRP. Eur J Pharm Sci 45(1–2):190–194
Lu Y, Luo Q, Cui H, Deng H, Kuang P, Liu H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y (2017) Sodium fluoride causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in the mouse liver. Aging 9(6):1623–1639
Di A, Gao XP, Qian F, Kawamura T, Han J, Hecquet C, Ye RD, Vogel SM, Malik AB (2011) The redox-sensitive cation channel TRPM2 modulates phagocyte ROS production and inflammation. Nat Immunol 13(1):29–34
Ma JQ, Ding J, Zhang L, Liu CM (2014) Ursolic acid protects mouse liver against CCl4-induced oxidative stress and inflammation by the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37(3):975–983
Gang XU, Wang J, Shuhui MA, Zhan Y, Haili MA (2014) Effects of fluoride on the expression of ERK signaling pathway associated gene and proteins in the splenic lymphocytes of mouse. Acta Veterinaria Et Zootechnica Sinica 45(11):1888–1894
Qi M, Elion EA (2005) MAP kinase pathways. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 16):3569–3572
Wang ZQ, Wu DC, Huang FP, Yang GY (2004) Inhibition of MEK/ERK 1/2 pathway reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 expression in focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 996(1):55–66
Yang CS, Shin DM, Lee HM, Son JW, Lee SJ, Akira S, Gougerotpocidalo MA, Elbenna J, Ichijo H, Jo EK (2008) ASK1-p38 MAPK-p47phox activation is essential for inflammatory responses during tuberculosis via TLR2-ROS signalling. Cell Microbiol 10(3):741–754
Wagner EF, Nebreda ÁR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):537–549
Praveen F, Rashid J, Jamal I (2008) Role of the JNK signal transduction pathway in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 14(2):200–202
Weston CR, Davis RJ (2002) The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12(1):14–21
Han MS, Barrett T, Brehm M, Davis R (2016) Inflammation mediated by JNK in myeloid cells promotes the development of hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Rep 15(1):19–26
Schieven GL (2005) The biology of p38 kinase: a central role in inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem 5(10):921–928
Raingeaud J, Whitmarsh AJ, Barrett T, Derijard B, Davis RJ (1996) MKK3- and MKK6-regulated gene expression is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol 16(3):1247–1255
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ramos AM, Moreno JA, Santamaria B, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A (2010) NF-κB in renal inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(8):1254–1262
Kadhim H, Tabarki B, Verellen G, De PC, Rona AM, Sébire G (2001) Inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of periventricular leukomalacia. Neurology 56(10):1278–1280
Ghosh S, Karin M (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell 109(2):S81–S96
Nakayama H, Ikebe T, Beppu M, Shirasuna K (2001) High expression levels of nuclear factor kappaB, IkappaB kinase alpha and Akt kinase in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer 92(12):3037–3044
He G, Karin M (2011) NF-κB and STAT3—key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res 21(1):159–168
Ghosh S, Hayden MS (2008) New regulators of NF-κB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 8(11):837–848
Xiao YQ, Malcolm K, Worthen GS, Gardai S, Schiemann WP, Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Henson PM (2002) Cross-talk between ERK and p38 MAPK mediates selective suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines by transforming growth factor-β. J Biol Chem 277(17):14884–14893
Zhou H, Huang QL, Li ZY, Wu YM, Xie XB, Ma KK, Cao WJ, Zhou Z, Lu CX, Zhong GM (2013) pORF5 plasmid protein of chlamydia trachomatis induces MAPK-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokines via TLR2 activation in THP-1 cells. Sci China Life Sci 56(5):460–466
Gadaleta RM, Oldenburg B, Willemsen ECL, Spit M, Murzilli S, Salvatore L, Klomp LWJ, Siersema PD, Erpecum KJV, Mil SWCV (2011) Activation of bile salt nuclear receptor FXR is repressed by pro-inflammatory cytokines activating NF-κB signaling in the intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812(8):851–878
Tak PP, Firestein GS (2001) NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest 107(1):7–11
Shin DS, Kim KW, Chung HY, Yoon S, Moon JO (2013) Effect of sinapic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic injury in rats. Arch Pharm Res 36(5):626–633
Turner MD, Nedjai B, Hurst T, Pennington DJ (2014) Cytokines and chemokines: at the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1843(11):2563–2582
Morino F, Robecchi M (2008) Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: an education in pathophysiology and therapeutics. Immunol Rev 223(1):7–19
Cieślak M, Wojtczak A, Cieślak M (2015) Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines of pancreatic islets and prospects of elaboration of new methods for the diabetes treatment. Acta Biochim Pol 62(1):15–21
Gerard C, Rollins BJ (2001) Chemokines and disease. Nat Immunol 2(2):108–115
Alhouayek M, Muccioli GG (2014) COX-2-derived endocannabinoid metabolites as novel inflammatory mediators. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35(6):284–292
Morita Y, Yamamura M, Kawashima M, Aita T, Harada S, Okamoto H, Inoue H, Makino H (2001) Differential in vitro effects of IL-4, IL-10, and IL-13 on proinflammatory cytokine production and fibroblast proliferation in rheumatoid synovium. Rheumatol Int 20(2):49–54
Bermúdezhumarán LG, Motta JP, Aubry C, Kharrat P, Rousmartin L, Sallenave JM, Deraison C, Vergnolle N, Langella P (2015) Serine protease inhibitors protect better than IL-10 and TGF-β anti-inflammatory cytokines against mouse colitis when delivered by recombinant lactococci. Microb Cell Factories 14(1):26–42
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the program for Changjiang scholars and innovative research team in university (IRT 0848) and the Shuangzhi Project of Sichuan Agricultural University (03572437; 03573050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L. Chen, P. Kuang, and H. Cui designed the experiments. L. Chen, P. Kuang, H. Liu, and Q. Wei carried out the experiments. L. Chen, P. Kuang, H. Liu, Q. Wei, J. Fang, Z. Zuo, J. Deng., Y. Li, X. Wang, and L. Zhao analyzed and interpreted data. L. Chen, P. Kuang, H. Liu, and H. Cui wrote and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Kuang, P., Liu, H. et al. Sodium Fluoride (NaF) Induces Inflammatory Responses Via Activating MAPKs/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Reducing Anti-inflammatory Cytokine Expression in the Mouse Liver. Biol Trace Elem Res 189, 157–171 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1458-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1458-z